Management Tools
What Is Supply Chain Management?
Supply Chain Management is a system that synchronizes the efforts of all parties—suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, dealers, customers, and so on—involved in meeting a customer’s needs. It forges closer relationships among all links in the value chain to deliver the right products to the right places at the right times. The goal is to establish such strong bonds of connection and trust among all parties that they can effectively function as a single unit, aligned to streamline business processes and achieve total customer satisfaction.
Usage and satisfaction among survey respondents
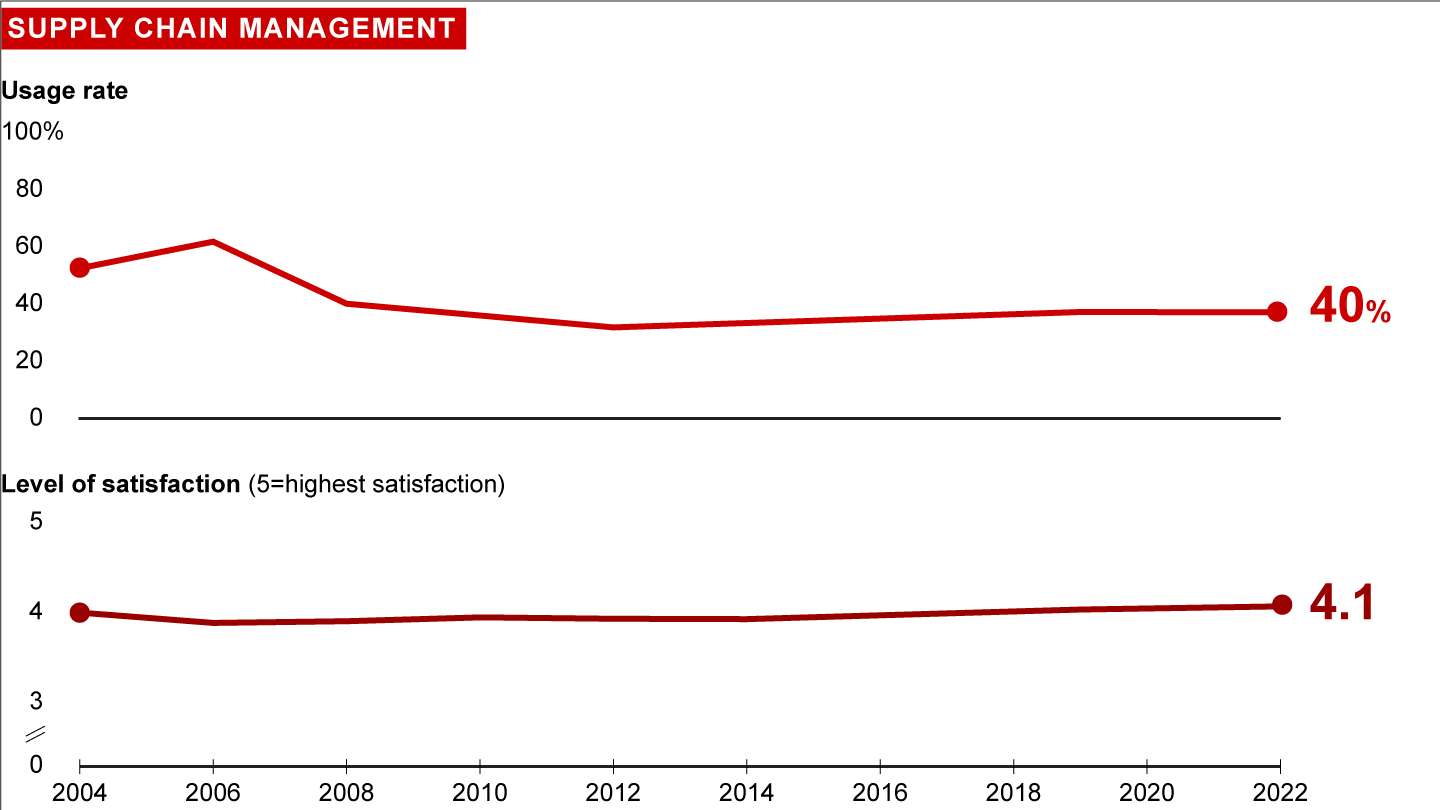
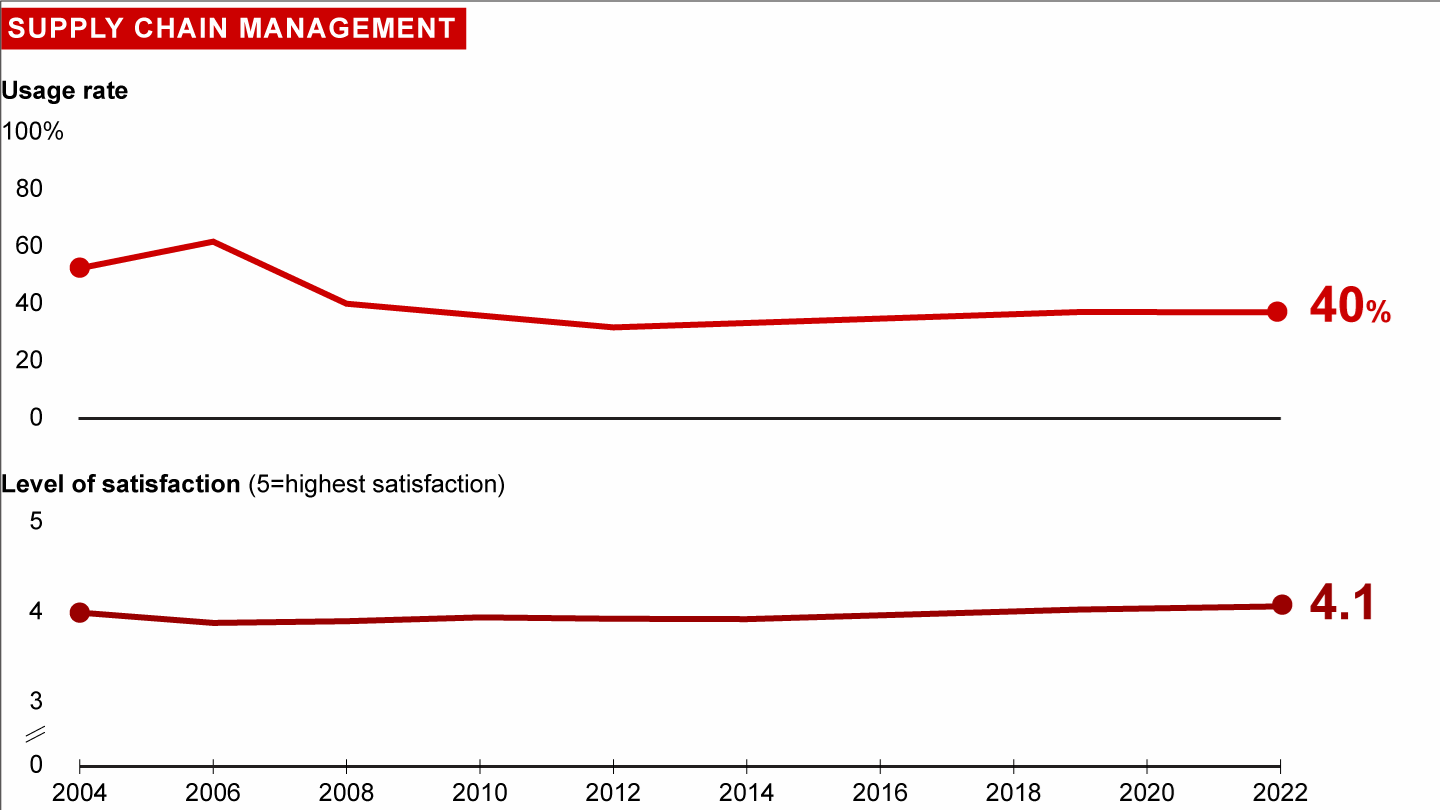
In response to a host of external forces (e.g., trade wars, demand and supply shortfalls), Supply Chain Management increasingly goes beyond reducing cost and inventory and improving service and quality, and includes developing resilience, creating responsible (e.g., sustainable, traceable) operations, and winning on responsiveness. Supply Chain Management capitalizes on the rise of digital technologies and automation to provide seamless, real-time visibility, accelerated processes, and improved flexibility and decision making.
How Is Supply Chain Management Implemented?
Companies typically implement Supply Chain Management in four stages:
- Stage One seeks to increase the level of trust among vital links in the supply chain. Managers learn to treat former adversaries as valuable partners. This stage often leads to longer commitments with preferred partners.
- Stage Two increases the exchange of information. It creates more accurate, up-to-date knowledge of demand forecasts, inventory levels, capacity utilization, production schedules, delivery dates, and other data that could help supply chain partners improve performance.
- Stage Three expands efforts to manage the supply chain as one overall process rather than dozens of independent functions. It leverages the core competencies of each player, automates information exchange, changes management processes and incentive systems, eliminates unproductive activities, improves forecasting, reduces inventory levels, cuts cycle times, and involves customers more deeply in the Supply Chain Management process.
- Stage Four identifies and implements radical ideas to transform the supply chain with improved processes, digitization, or simplification. It develops a view of future supply chain performance, considering innovative solutions to address current constraints as well as future needs. Scenarios are typically developed for transforming the performance of the supply chain that span different risk and benefit profiles. For leading scenarios, initiatives are identified, sequenced, and piloted.
Related Topics
What Are Common Uses of Supply Chain Management?
Recognizing that value is leaking out of the supply chain, but that only limited improvement can be achieved by any single company, managers turn to Supply Chain Management to help them deliver products and services faster, better, and less expensively.
Effective supply chain management can:
- Accelerate revenue growth: Increases ability to rapidly serve changes in market demand and expand output capacity through operation optimization
- Boost customer satisfaction and advocacy: Increases customer collaboration through feedback loops and perfect order rate by eliminating operational silos
- Unlock savings and cash flow: Reduces manufacturing and logistics costs through outsourcing and redesigning routes. Also helps optimize safety stock levels.
- Minimize risk and increase reliability: Helps enhance forecast accuracy with improved tools and reduces disruptions by building buffers within network.
- Improve environmental and social impacts

Management Tools & Trends 2023
On the 30th anniversary of our survey, managers seem surprisingly upbeat.