Report

Executive Summary
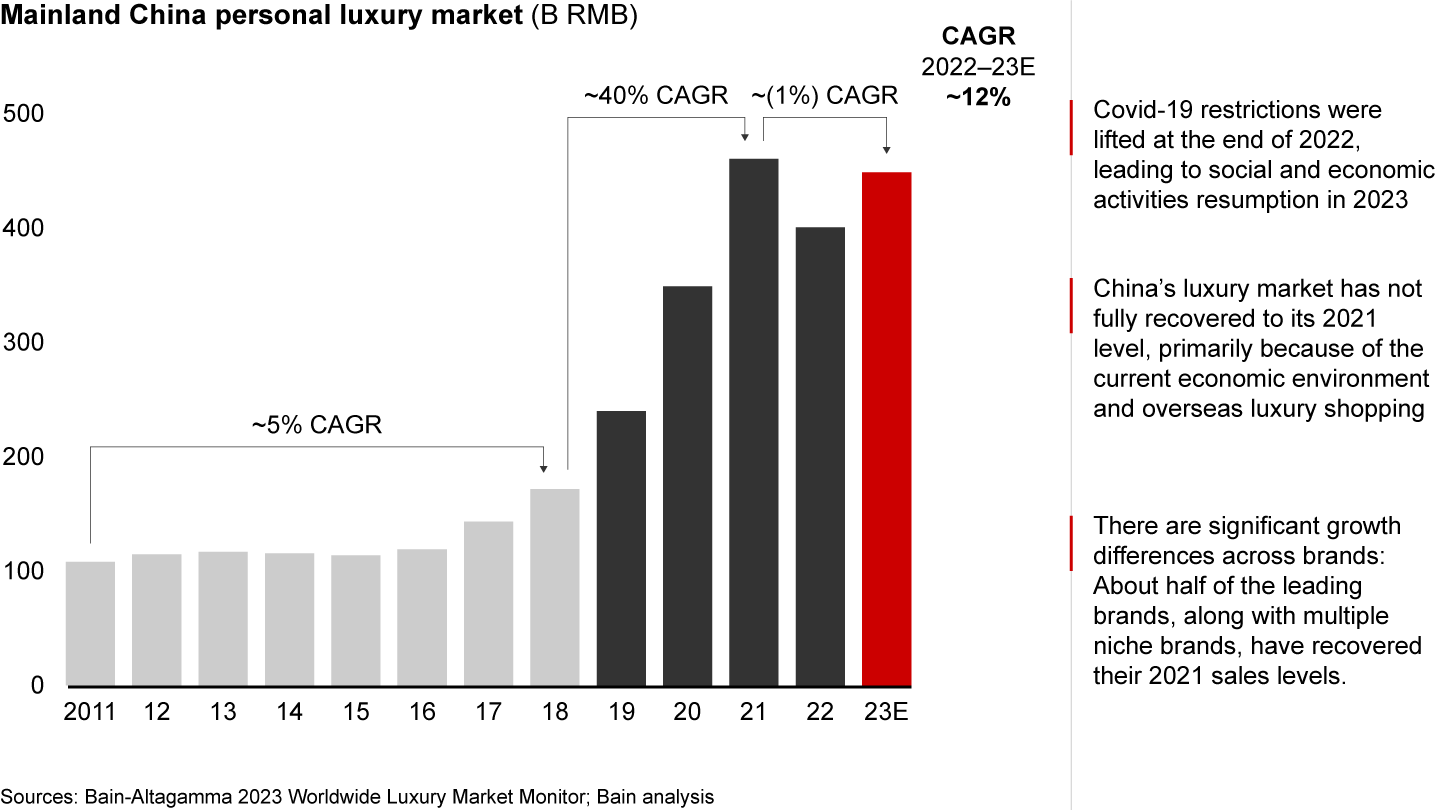
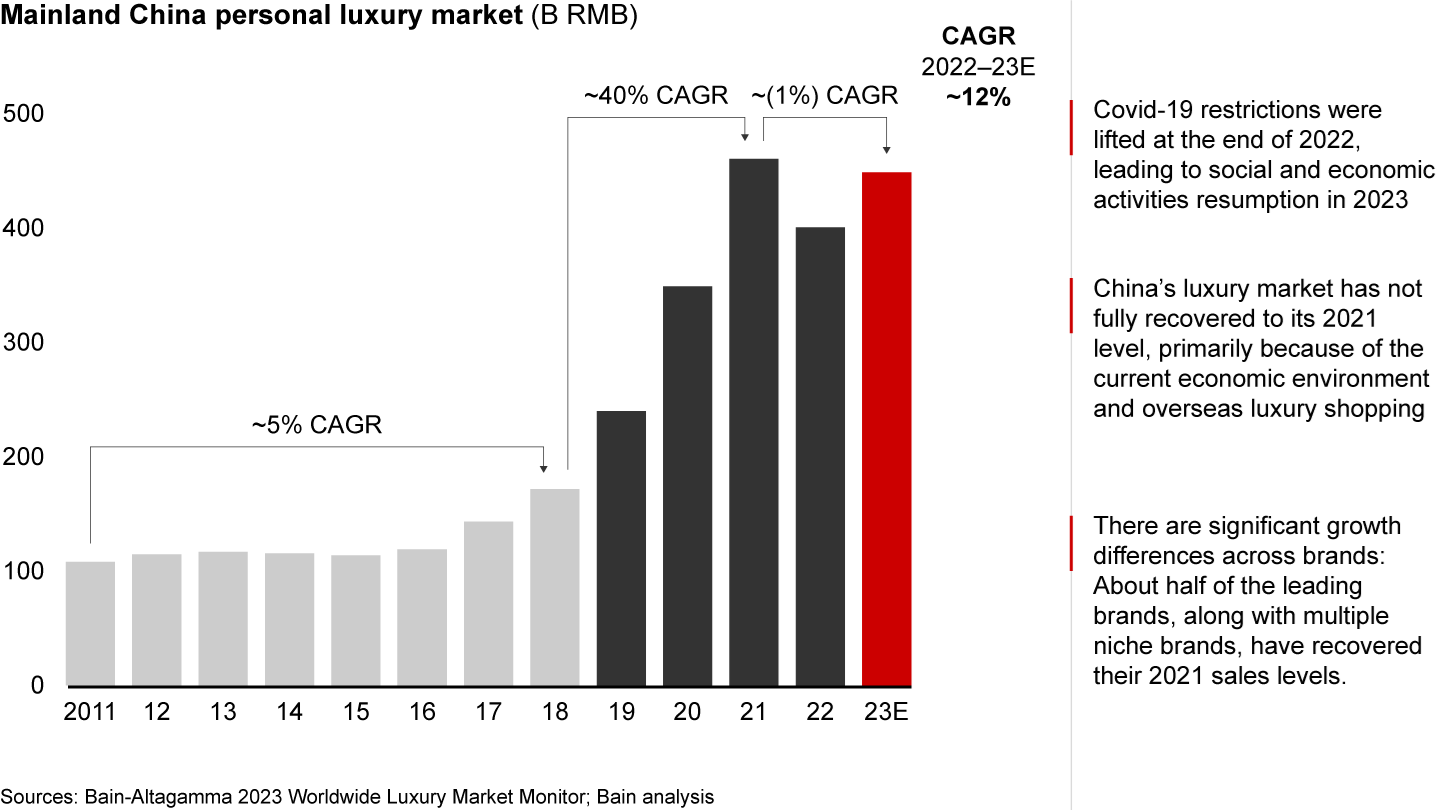
- In 2023, China’s luxury market saw a 12% yearly increase, recovering from the previous year’s decline due to Covid-19 but landing slightly below 2021’s record level.
- While China’s long-term fundamentals for luxury consumption remain robust, there are near-term uncertainties. It is projected that China’s luxury market will experience mid-single-digit growth in 2024.
Over the span of five years, from 2017 to 2021, China’s luxury market tripled in size. However, the boom came to an end in 2022 due to the impact of Covid-19, resulting in a double-digit decline in annual growth rate. The lifting of Covid restrictions in December 2022 paved the way for the resumption of social and economic activities in 2023. Consequently, the market witnessed a significant rebound, with an estimated year-on-year growth of 12% (see Figure 1).
The mainland China luxury market is predicted to grow ~12% in 2023, not fully back to its 2021 level because of the current economic environment and overseas luxury shopping
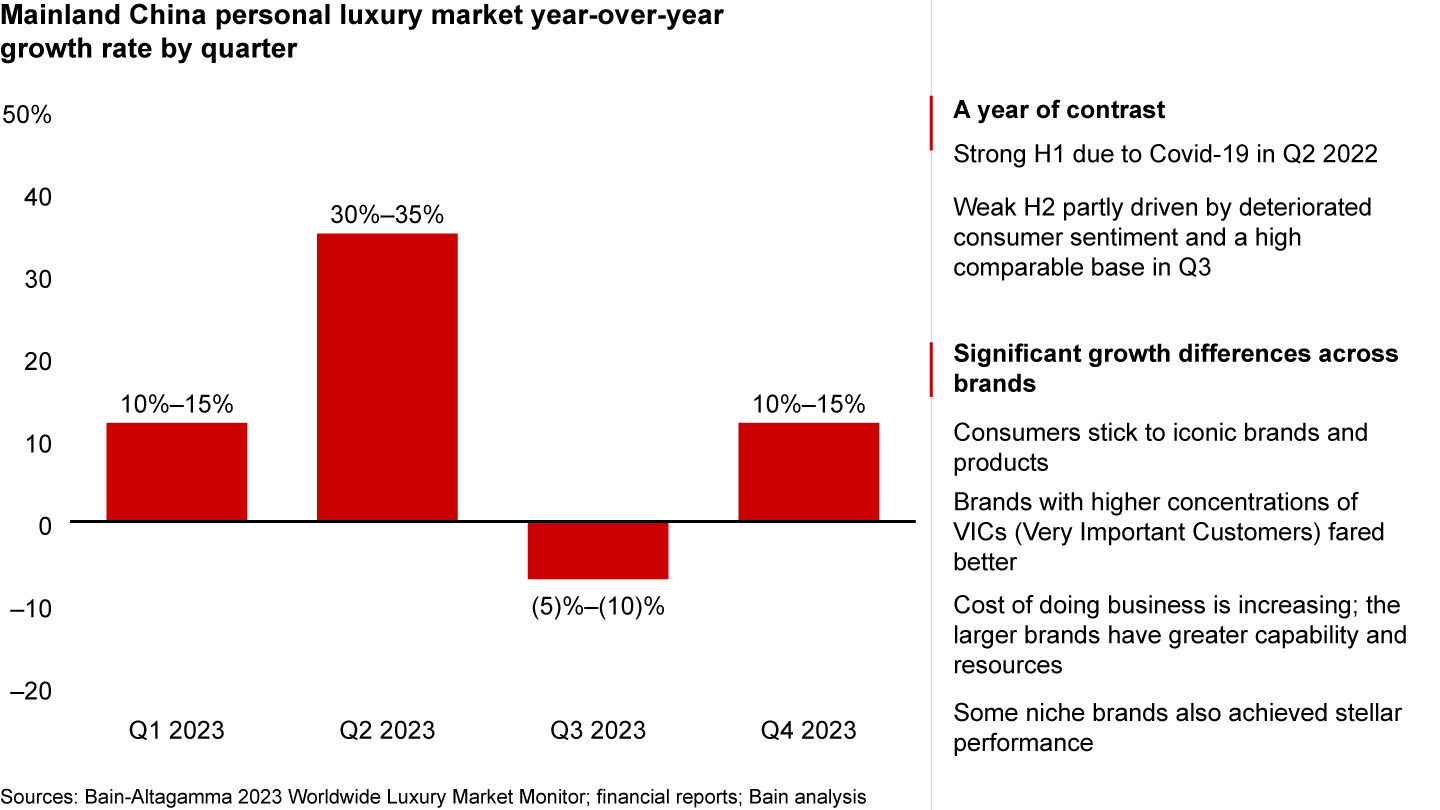
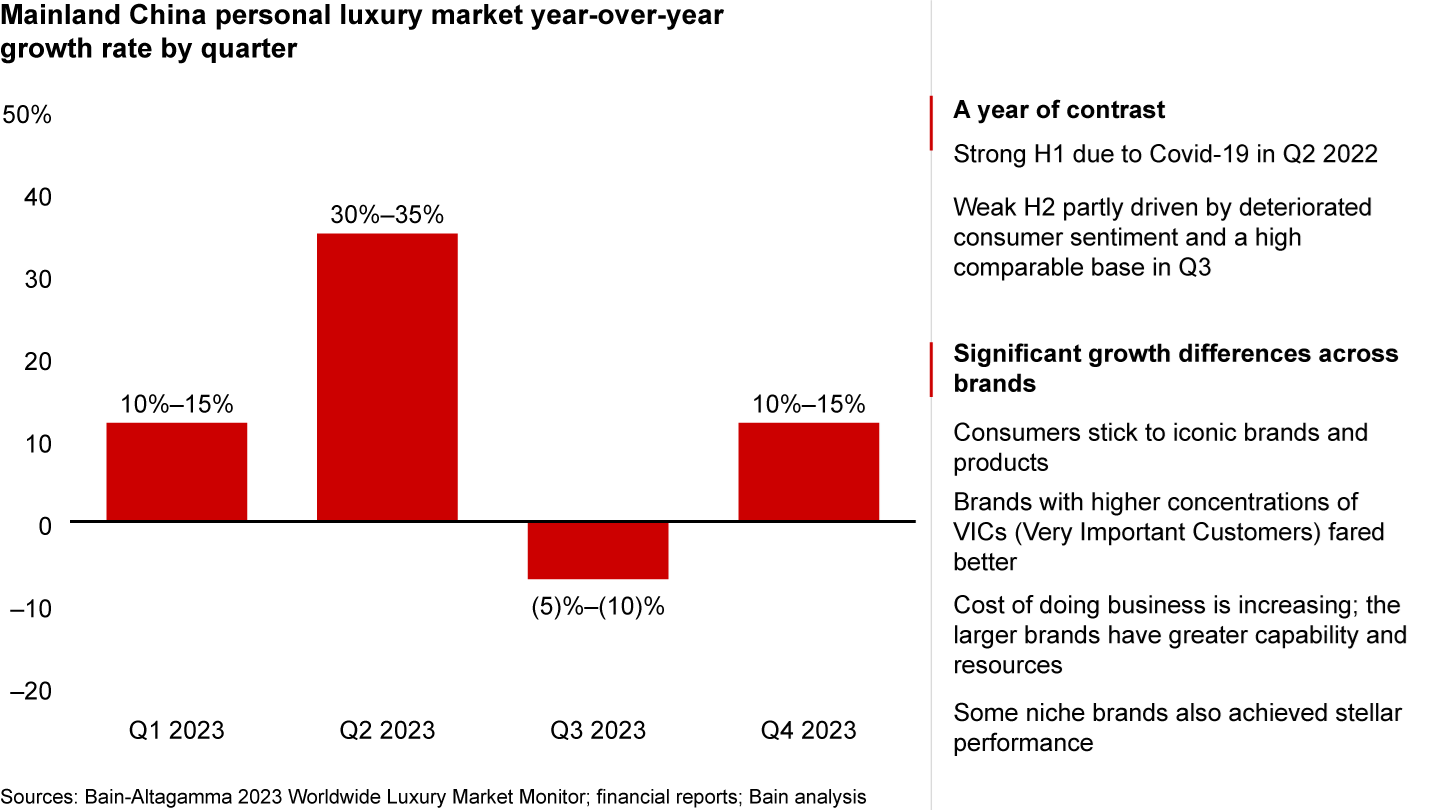
The year 2023 presented a stark contrast in performance, with a strong rebound in the first half (H1) followed by a more subdued second half (H2) (see Figure 2). The robust performance in H1 can be attributed to the low base created by the lockdowns in the second quarter of 2022, which set the stage for a significant rebound. However, H2 witnessed weaker growth, primarily driven by a decline in consumer sentiment and a high comparable base in the third quarter. It is expected that December will experience a strong rebound, as there was limited shopping activity in the previous December due to the lifting of restrictions.
2023 was a year of contrast, with H1 rebounding strongly, especially in Q2, while H2 was much more muted
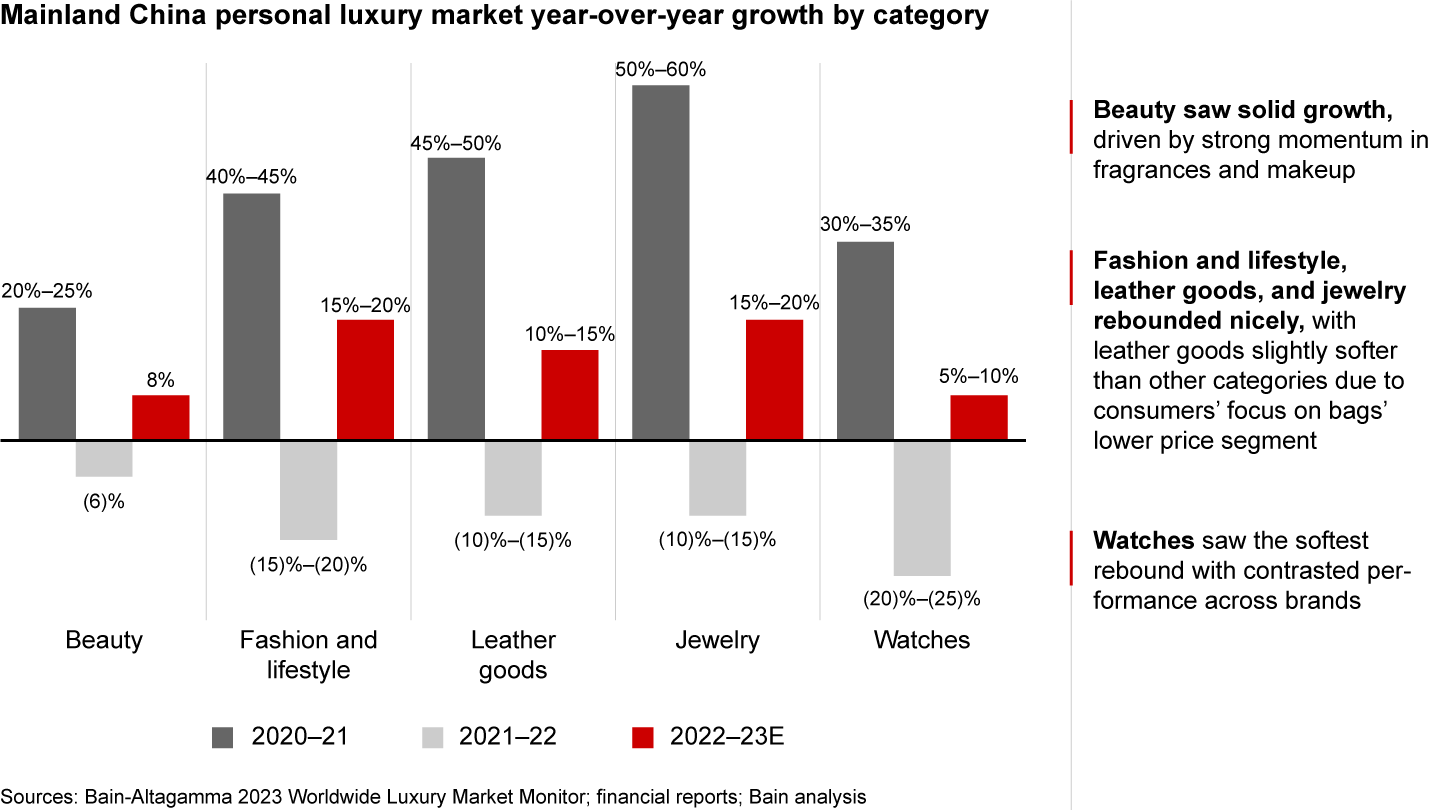
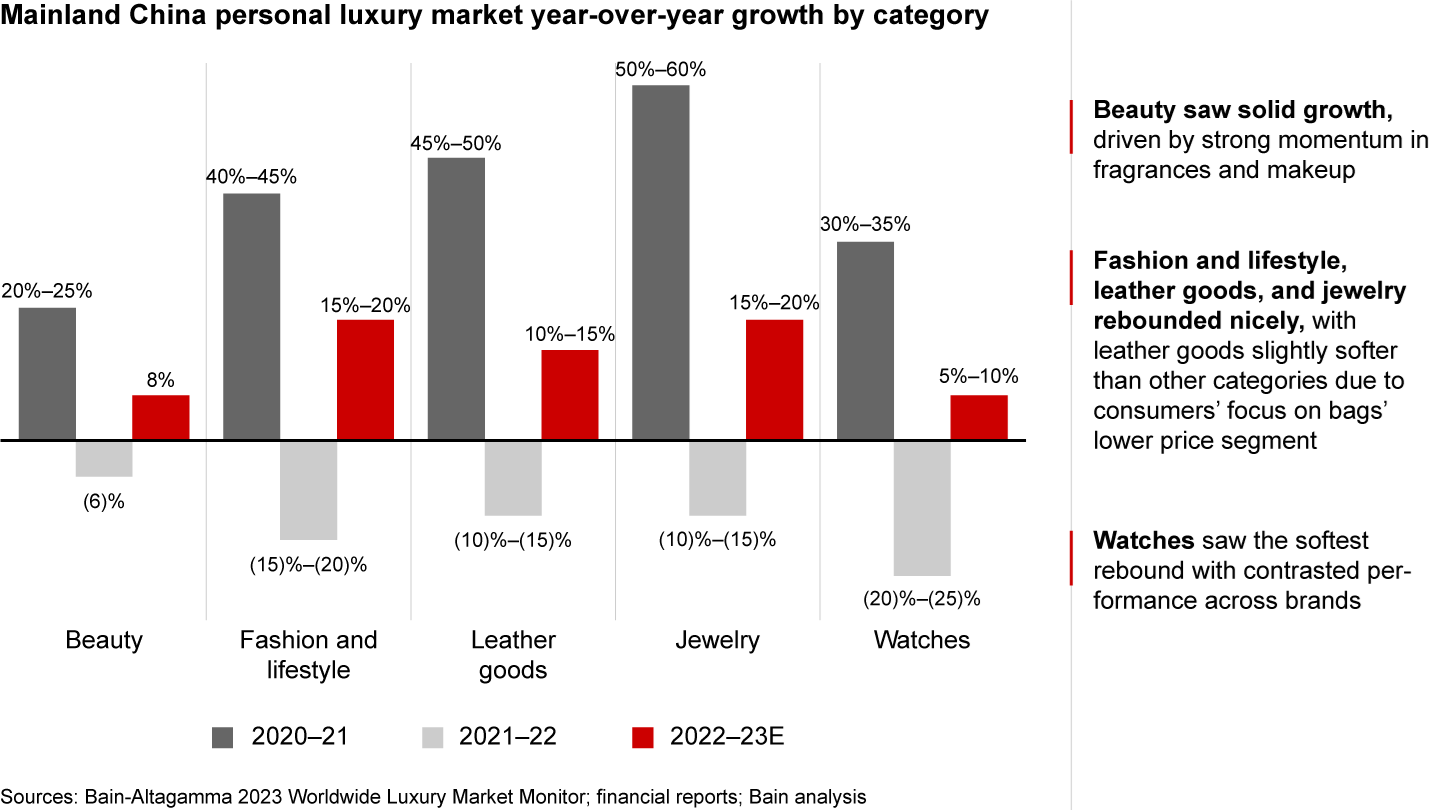
All categories within the luxury market in China experienced a rebound in 2023. The beauty category saw solid growth of approximately 8%, driven by strong momentum in fragrances and makeup (see Figure 3). Fashion and lifestyle, leather goods, and jewelry also rebounded nicely, with growth rates ranging from 10% to 20%. However, the leather goods category was slightly softer compared to other categories, as consumers focused more on the lower-price bag segment. The watches category saw the softest rebound, with growth rates ranging from 5% to 10%, driven by the polarization of brands.
All luxury categories rebounded—beauty, fashion, jewelry, and leather goods saw strong growth, while watches continue to lag other categories
In 2022, the concentration of Very Important Customers (VICs) increased as a result of reduced shopping mall traffic. However, in 2023, shopping malls saw a significant rebound in both VIC and non-VIC traffic. While conversion and average spending for non-VIC consumers declined, VICs continued to exhibit strong performance in these metrics.
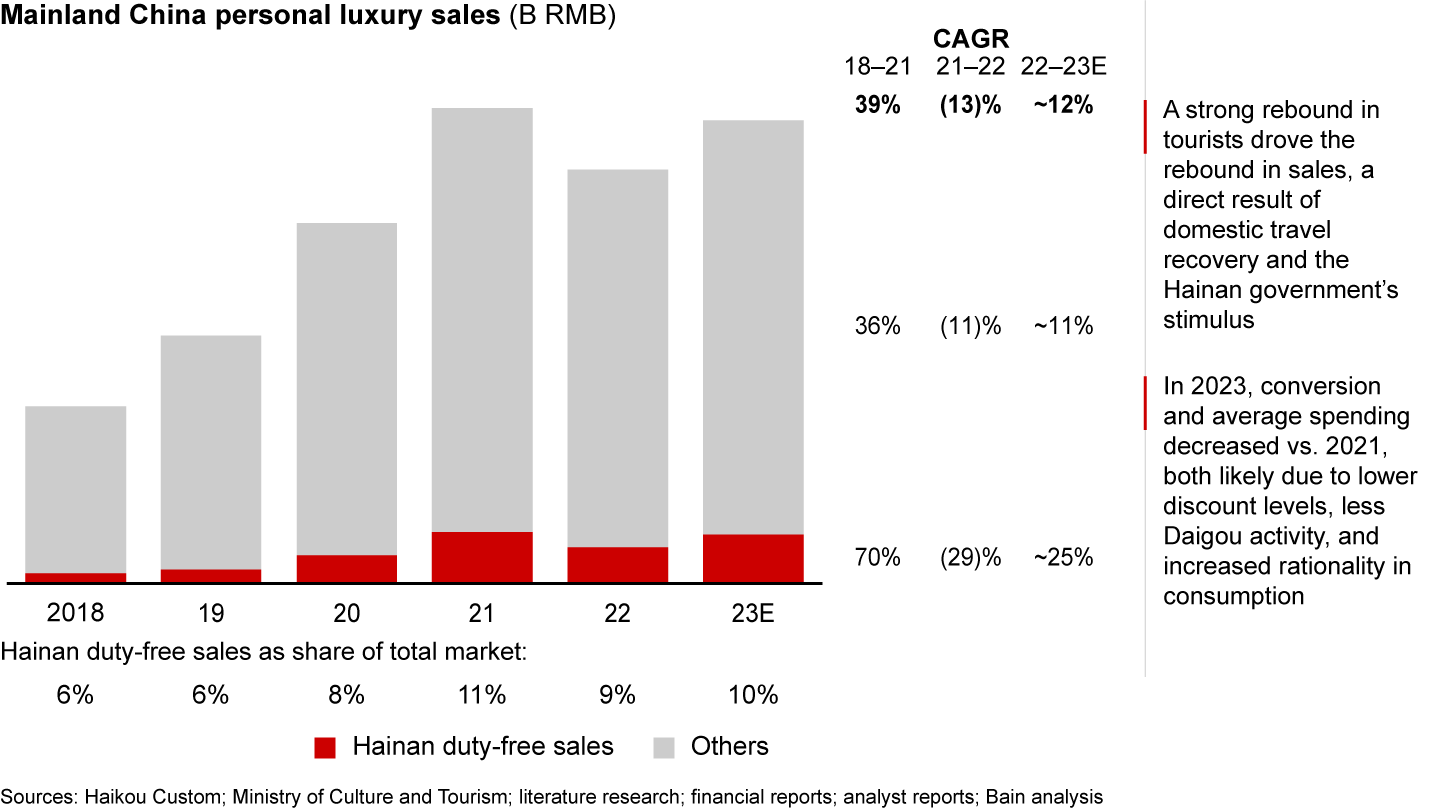
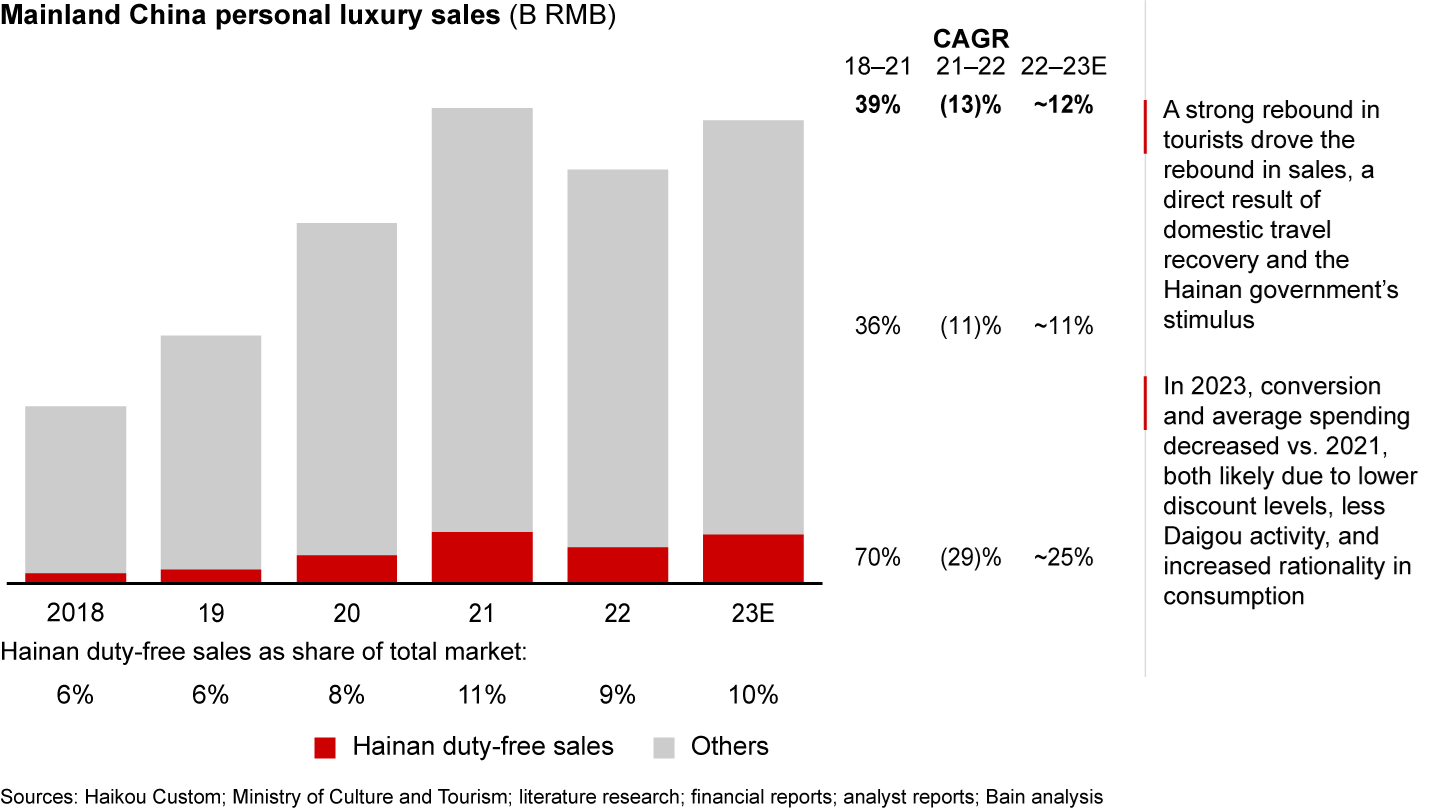
Hainan duty-free sales declined by approximately 30% in 2022. In 2023, Hainan’s duty-free sales grew by about 25%, though not back to their 2021 level (see Figure 4). This rebound can be attributed to the return of many tourists, which was a direct result of the recovery in domestic travel and the stimulus measures implemented by the Hainan government. It is worth noting that although the traffic increased, the number of duty-free shoppers did not grow as significantly, indicating a reduced conversion rate. Additionally, the average spending per shopper decreased by more than 25%, likely due to lower discount levels, less Daigou activity, and an increased rationality among consumers.
Duty-free sales in Hainan rebounded in 2023, benefiting from domestic travel recovery, and the Hainan government’s stimulus
To summarize, China’s luxury market has experienced a double-digit rebound, although it’s not yet back to the historical high of 2021. This can be attributed to factors such as low consumer confidence, a slower-than-expected economic recovery, and Chinese consumers’ return to luxury shopping overseas.
When examining the growth differences across brands, it becomes evident that about half of the leading brands, as well as several niche brands, have managed to recover their 2021 sales levels. Several factors have contributed to the success of these brands:
- Brands with iconic offers over-performed those with seasonal offers, as consumers value longer-term investment in times of uncertainty.
- Brands with a higher concentration of VICs have shown greater resilience in the uncertain economic situation.
- Bigger brands tend to outperform smaller brands due to more resources and stronger capabilities. This scale advantage enables them to execute high-quality marketing events and provide exceptional in-store services.
- Niche brands that have consistently invested in building brand desirability over multiple years have experienced success.
This year, our research explores two significant trends and their impact on the luxury market’s growth outlook: luxury shopping overseas and the Daigou market.
Trend 1: Luxury shopping overseas
Prior to the Covid-19 pandemic, approximately one-third of mainland Chinese luxury spending took place within mainland China, while the majority occurred outside mainland. However, due to closed borders, the ratio shifted dramatically to over 90% in both 2021 and 2022. As Chinese overseas tourism progressively resumed throughout the year, we estimated that in 2023 about 70% of mainland Chinese luxury spending happened within the mainland (see Figure 5). The recovery of Chinese tourists’ luxury spending in Europe and Asia has been significant. Mainland Chinese spending abroad in 2023 recovered to 40% of 2019 level in Europe and 65% in Asia. This recovery can be attributed to a combination of increased traffic and higher average spending compared to pre-Covid levels.
The mainland China share of spending on luxury goods peaked in 2021 because of closed borders but declined as China overseas tourism resumed
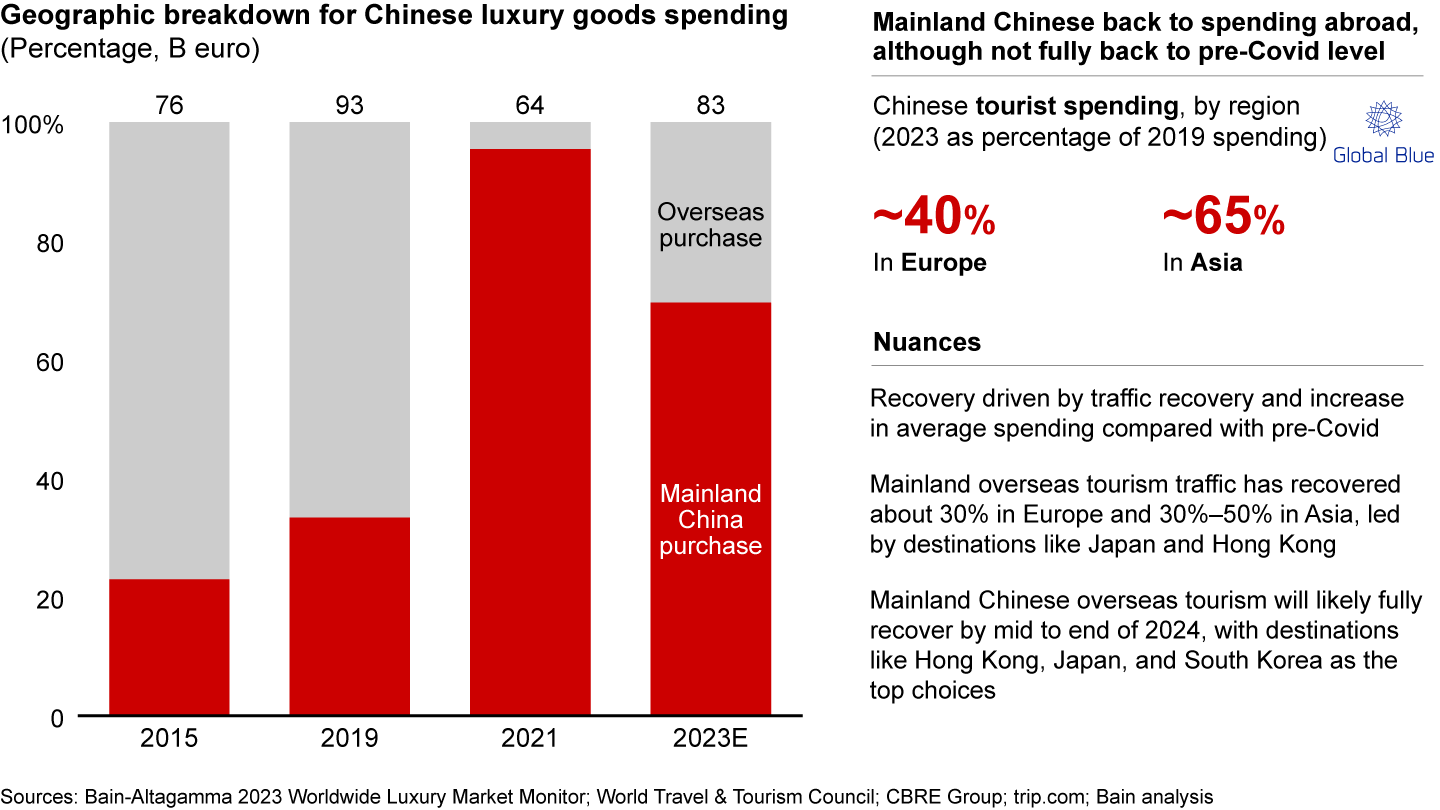
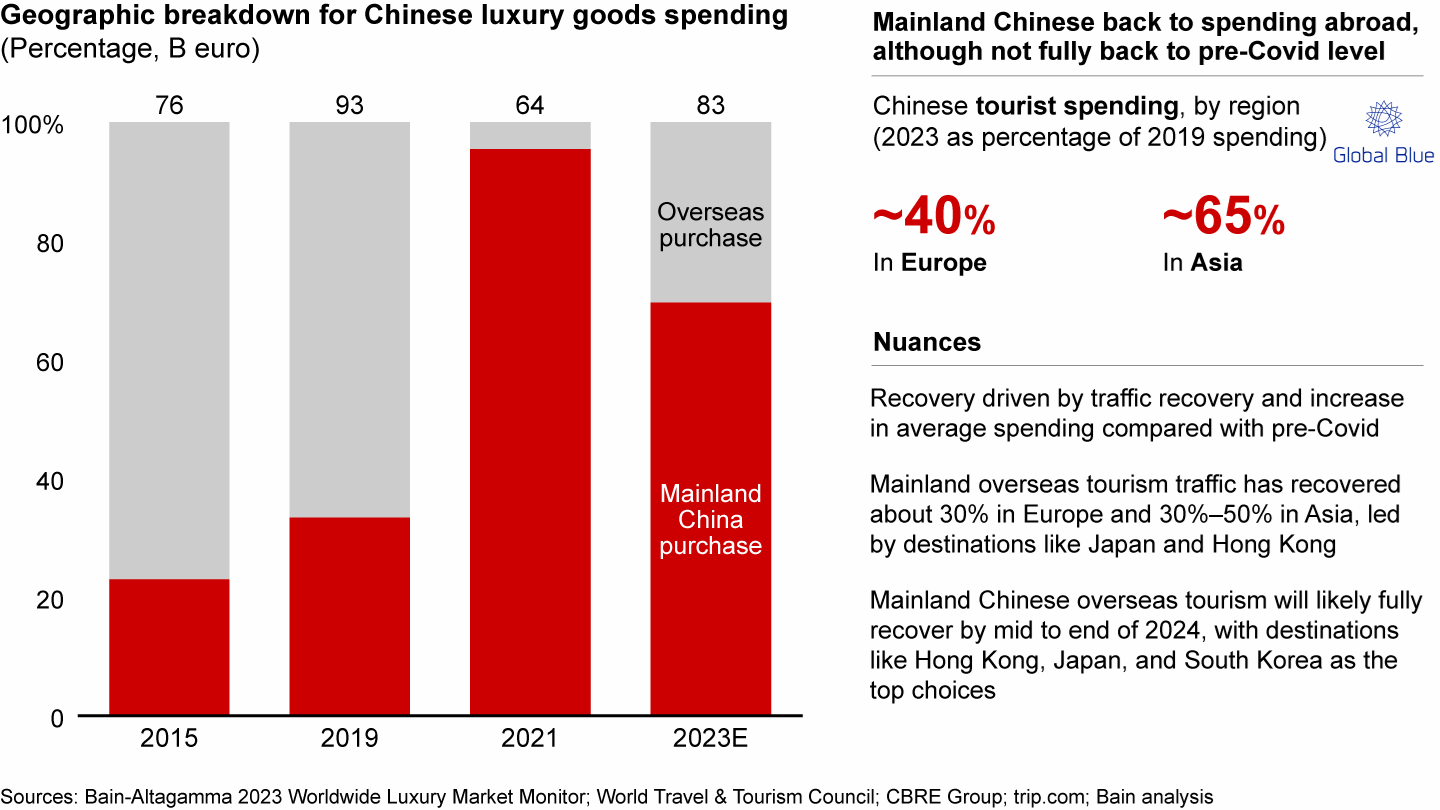
Various factors have contributed to this partial recovery, including increased traveling and lodging costs abroad. European tourism has seen a slower recovery, as many middle- and high-income consumers have opted for closer Asian destinations that provide better travel options in a context of high travel fares, particularly taking advantage of exchange rate advantages in countries like Japan.
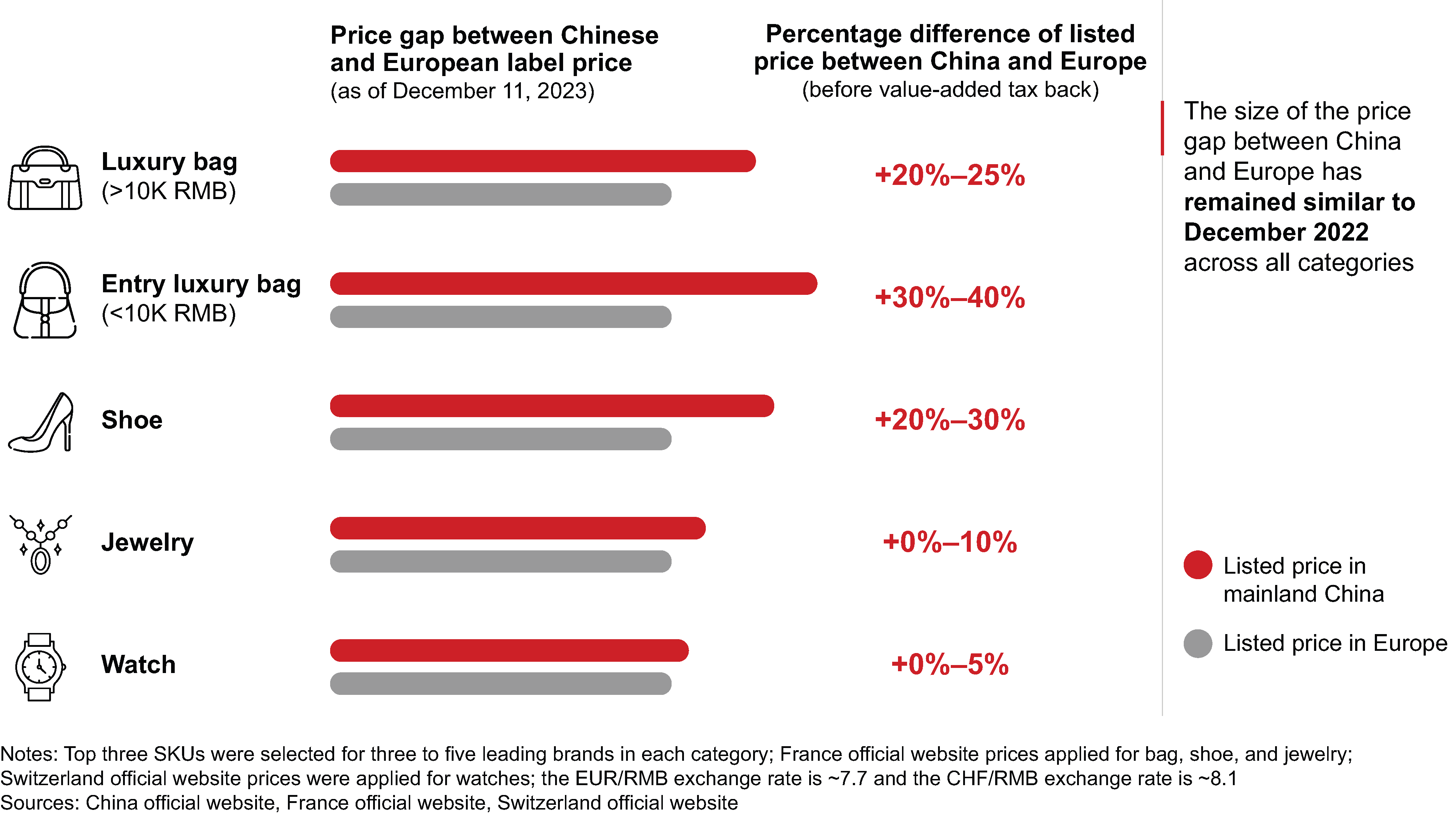
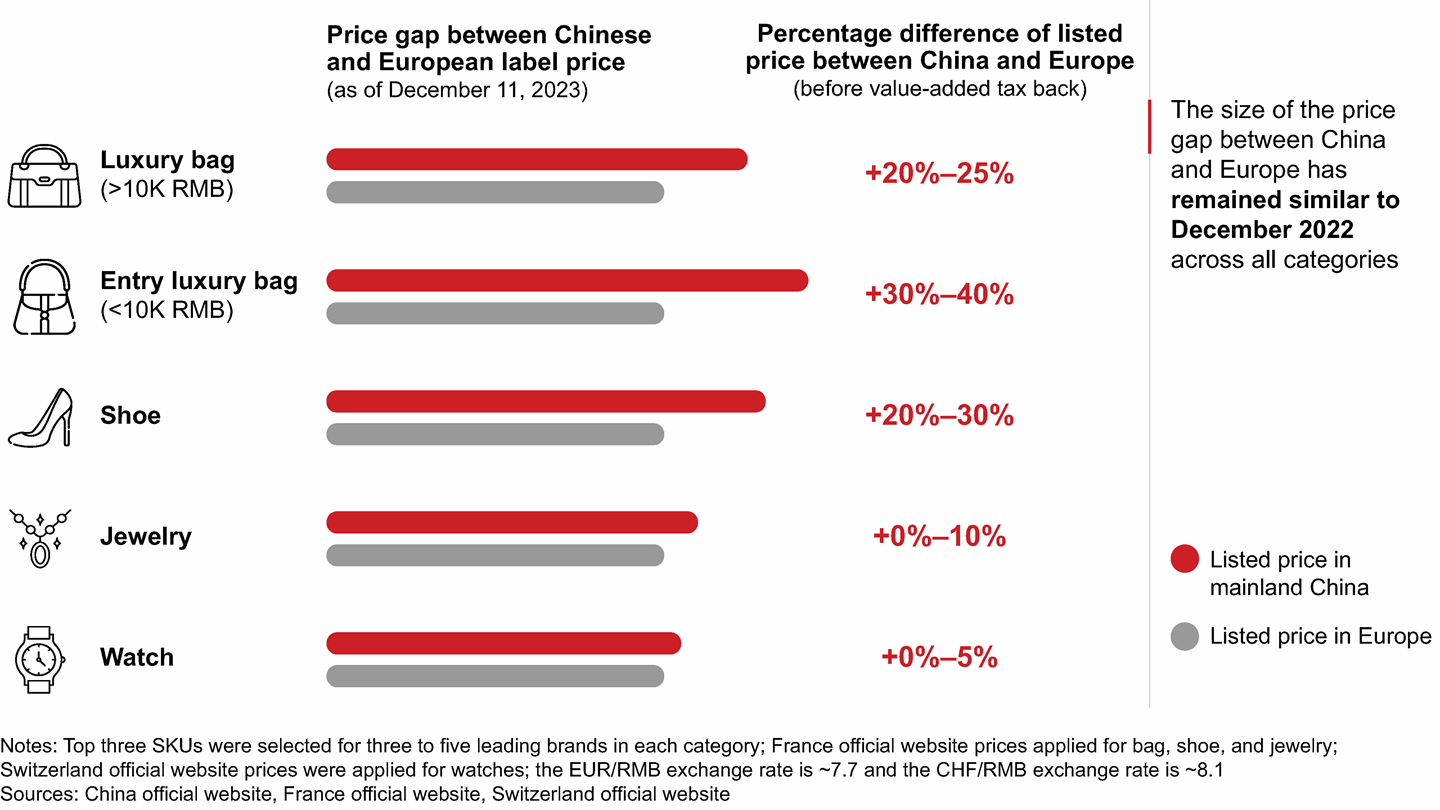
The pricing gaps between luxury goods in mainland China and other markets have played a critical role in the resurgence of overseas shopping. A sample check of leading products in mainland China, European, and Asian markets revealed significant price gaps across categories such as fashion and leather products, making luxury shopping abroad more attractive. Importantly, these price gaps have remained unchanged compared to 2022 (see Figure 6).
The price gaps between China and Europe play a critical role in the return of overseas shopping, and they remained unchanged since 2022
Trend 2: The Daigou market
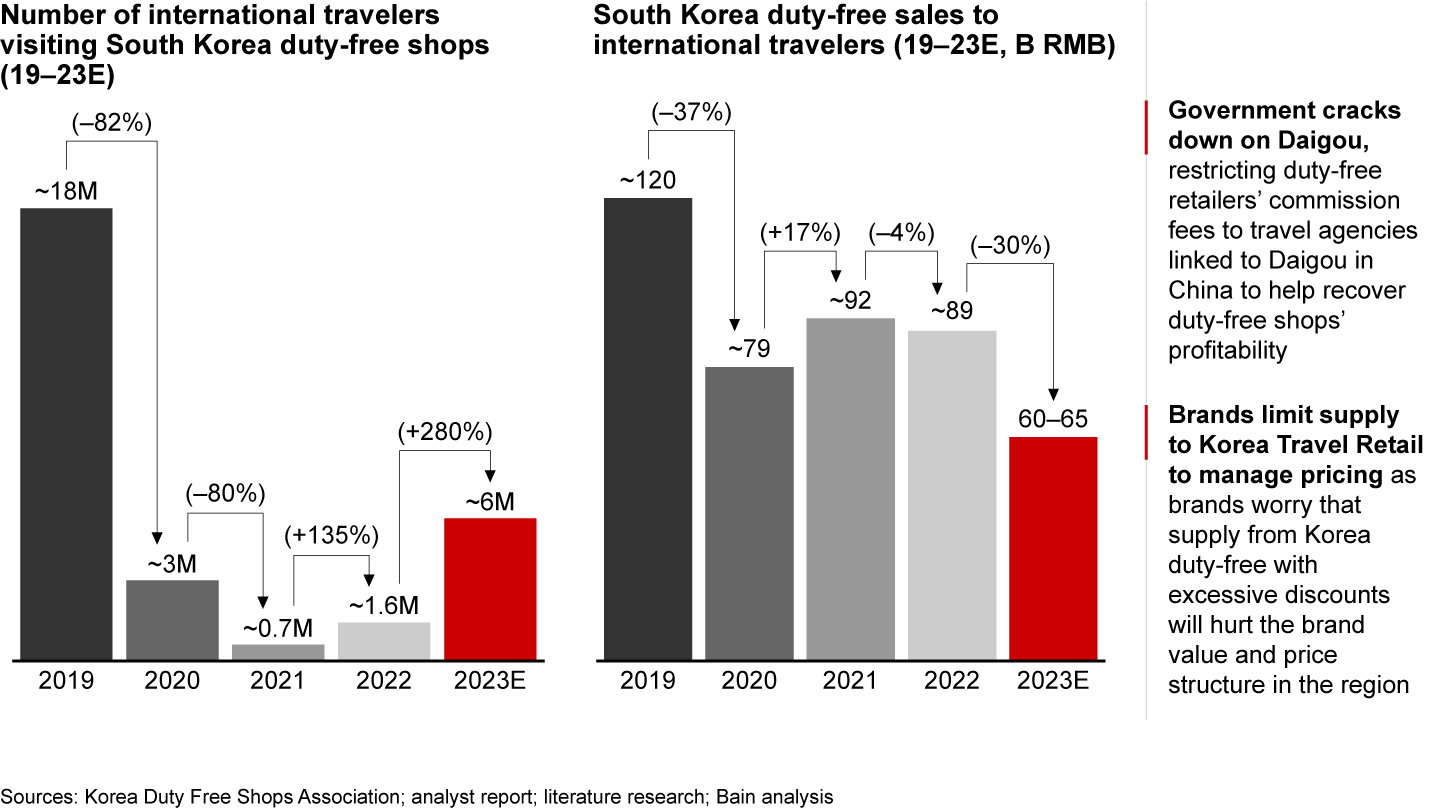
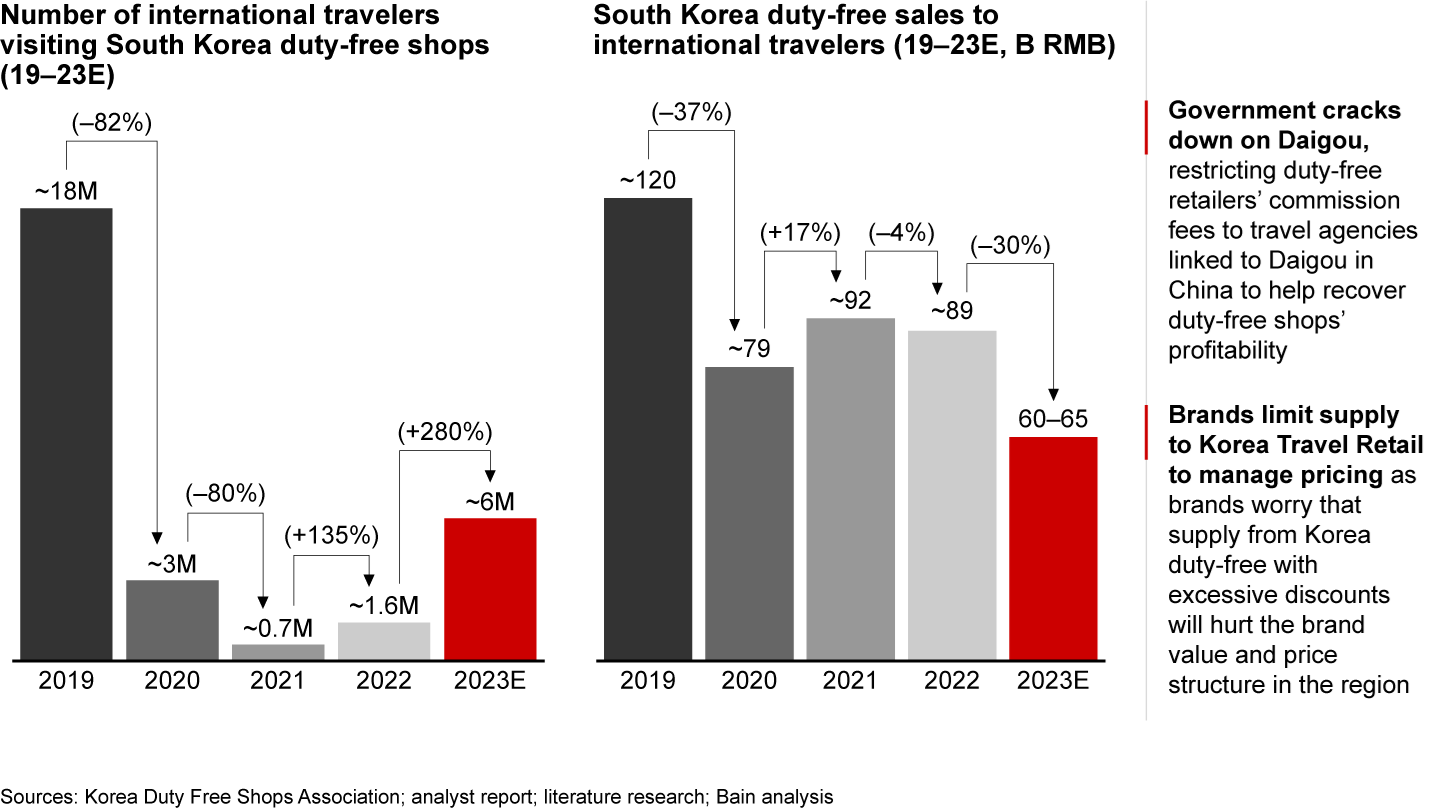
South Korea’s duty-free market has historically been a significant source for Daigou, particularly in the luxury beauty sector. In 2022, visits to South Korea were over 90% lower than in 2019 due to travel restrictions. However, sales remained at about 75% of the 2019 level, primarily due to the bulk resale of goods through Daigou channels. In 2023, despite a drastic recovery in international travelers, Korean duty-free sales to international travelers is expected to experience a 30% decline
to approximately RMB 60–65 billion. This decline can be attributed to the actions taken by the government and brands to address the Daigou market (see Figure 7). The Korean government restricted duty-free retailers’ commission fees to travel agencies linked to Daigou, aiming to restore profitability to duty-free shops. Additionally, the supply of popular beauty products has been limited, as brands are concerned that excessive discounts will negatively impact brand equity and pricing structures in the Chinese market.
Despite recovery in international travelers, Korean duty-free sales shrunk as South Korean government and brands took actions against Daigou
Despite higher restrictions on Daigou activities in the beauty sector, new and more professional Daigou models are emerging, particularly in the fashion and leather goods sectors. According to
Re-Hub, Daigou operators have become more professional by accessing overseas goods from wholesalers at lower prices. They have also embraced a more platformized approach, providing consumers with an aggregated and authenticated platform for shopping.
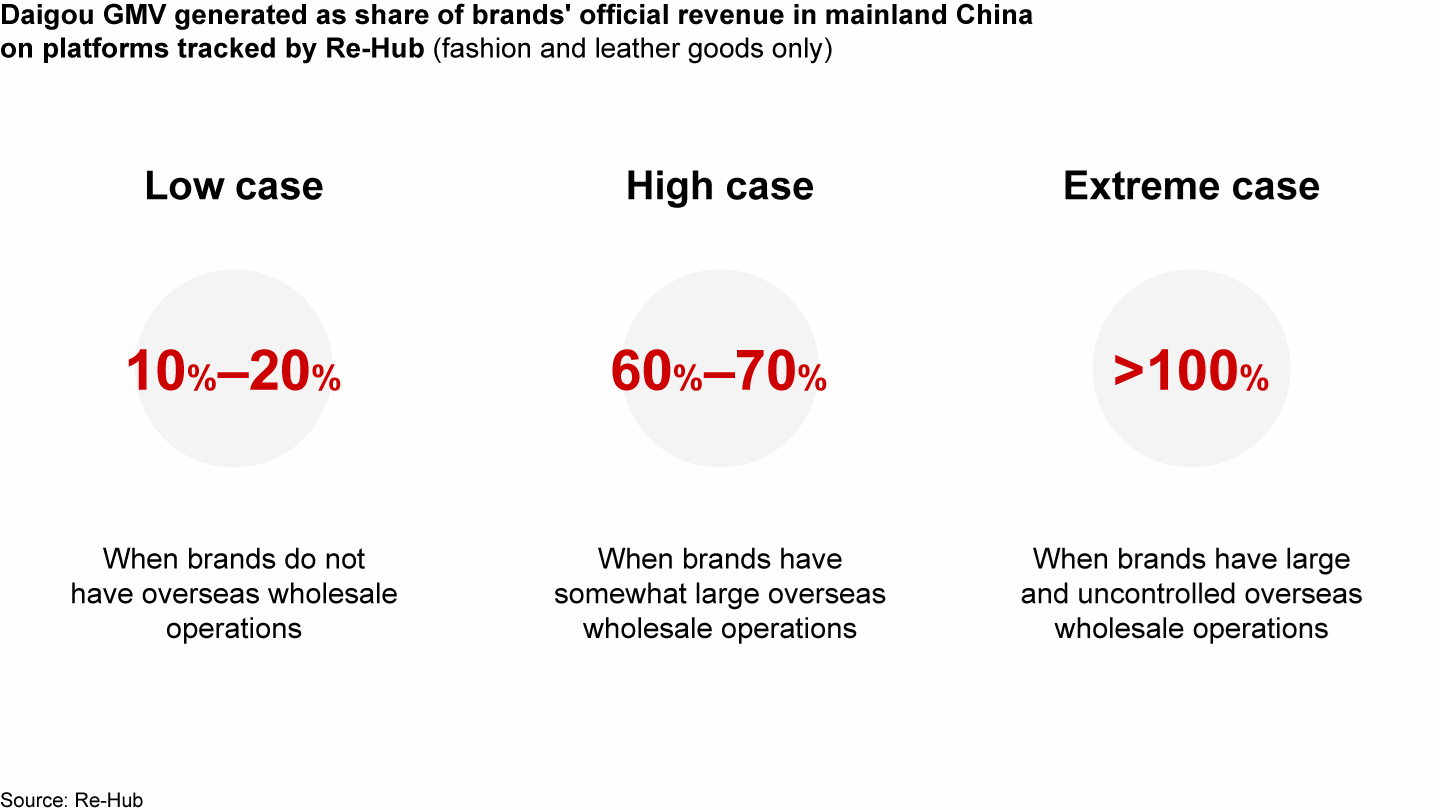
According to Re-Hub, Daigou channels that Re-Hub tracks offer prices that can be up to 40% lower than the brands’ official prices in mainland China. The larger price gaps are often a result of luxury brands’ control and size of their wholesale channels worldwide. For brands that have no or tightly controlled wholesale channels, fashion and leather goods sales on these platforms can account for 10%–20% of their official sales in mainland China. However, for brands with a large and somewhat uncontrolled wholesale channel, sales on these platforms can represent 60%–70% or even more of their total mainland China sales (see Figure 8). According to Re-Hub, some of the platforms it tracks have experienced double-digit luxury GMV growth per year, including in 2023.
New and more professional Daigou models are emerging, especially in fashion and leather goods, reaching a substantial GMV scale

Looking ahead
After a turbulent three years due to the Covid-19 pandemic, it is believed that 2023 marked the beginning of China’s luxury market transitioning toward a normalized post-Covid growth trajectory. The fundamentals of luxury consumption in China remain strong in the long run, although there are uncertainties in the near term regarding the speed of consumer confidence recovery and the growth of luxury shopping overseas. It is expected that most of the trends witnessed in 2023 will continue or amplify, leading to a mid-single-digit growth rate in China’s luxury market in 2024.
The recovery of overseas luxury shopping will continue as cross-border tourism develops. The extent of cross-border tourism recovery in 2024 will primarily depend on the speed of economic recovery and changes in travel and lodging costs. Various travel agencies and organizations project that China’s overseas tourism will fully recover by mid to end 2024, with destinations like Hong Kong and Japan being the top choices. Therefore, in the context of expanding luxury spending outside the mainland in 2024, it is expected that there will be another year of recovery of Chinese overseas luxury consumption. It remains crucial for brands to implement harmonized global pricing strategies to reduce the incentives for consumers to buy outside the mainland.
The total investable assets of China’s high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) are projected to grow at a double-digit rate, serving as a primary driver of mainland China’s luxury growth. However, these individuals are more likely to allocate a portion of their budget to overseas shopping. In 2023, middle- to high-income consumers displayed more rational and discerning behavior. It may take some time for their sentiment to improve, which could impact volume and blended pricing. The entry-level consumers, who have demonstrated resiliency in 2023 with entry-level items, will remain an important segment for luxury brands. However, their ticket price is lower, and they buy more online.
We expect most brands to slow down their store footprint expansion, except for a few leading brands that experienced exceptional growth in 2023. Brands will focus on optimizing their existing store network and improving same-store productivity.
The Hainan duty-free market is poised to become a duty-free island by 2025. As Hainan’s shopping environment matures, it will attract a more diverse consumer base and receive increased investment from luxury brands.
The Daigou market is unlikely to cool off, and its future trends will depend on brands’ control over their wholesale market overseas.
In the long run, China’s growth is stabilizing at a lower yet still significant rate. Real GDP is projected to grow at 4%–5% in the coming years, creating a substantial incremental market and solidifying China’s position as a powerhouse for luxury growth. In 2023, Chinese luxury consumption is estimated to account for approximately 22%–24% of the world’s total, with mainland China comprising about 16% (both excluding Daigou). By 2030, Chinese luxury consumption is expected to reach 35%–40% of the world’s total, with mainland China reaching 24%–26%, solidifying its position as one of the leading luxury markets globally.
Lastly, China’s luxury operations will continue to set the standard worldwide, encompassing the quality of retail establishments, amazing consumer experiences, sophisticated clienteling activities, extraordinary events planning and execution, the versatility of the digital landscape, and the necessary capabilities and talent to meet the ever-increasing expectations of Chinese consumers.