Brief

Utility executives are accustomed to planning 5, 10 or even 20 years out. But now many find themselves learning to move at a faster pace to keep up with digital technology. Bankers, retailers and media executives are already a decade into their industries’ digital transformations. Now, as digital innovations take root in the power sector—things like online customer engagement, smart sensors and better use of analytics—utilities are beginning to adopt and adapt, motivated by a range of forces, including digitally savvy competitors, new regulations, innovative business models and evolving consumer preferences.
In our work with utility executives, we see them probing for value and identifying areas where new competitors are starting to take bites out of their business. These executives want to know how digital can strengthen relationships with customers and guard against being disintermediated by new competitors. And they want to understand where technology can help them improve operations and develop topline opportunities, including new products and services.
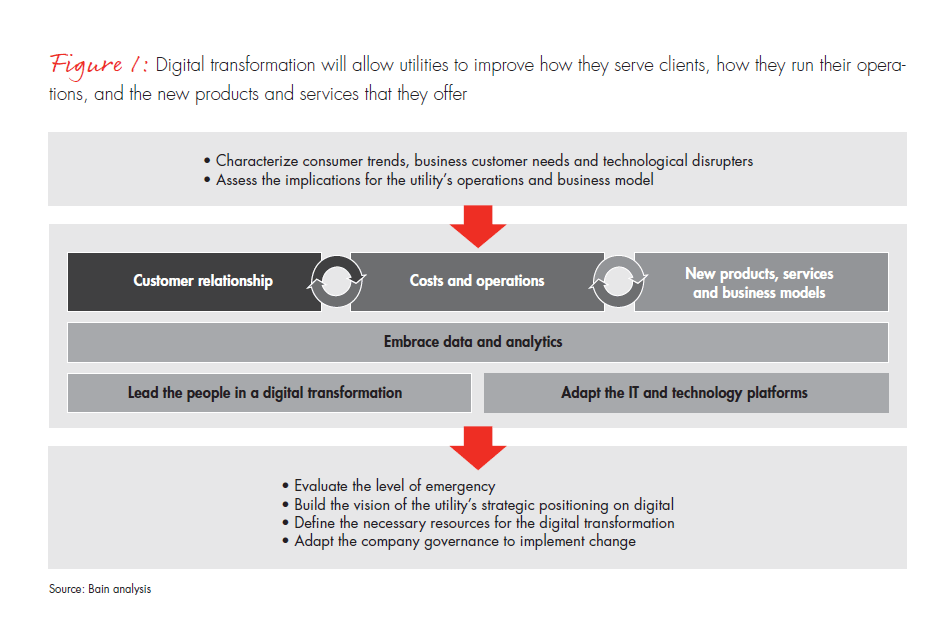
Bain’s research on this topic identifies three areas where digital technologies are beginning to show potential (see Figure 1).
- Customer engagement. Mobile, social and web interfaces give customers a better view of their energy use and enable richer two-way communication between the utility and customers. They also improve utilities’ ability to test and deliver new capabilities such as customized rate plans based on individual customer usage and needs.
- Products and services. Digital technology opens the way for new energy products and services, but the organization will need to change, too, in order to make the most of these new opportunities. For example, inexpensive sensing and communications technologies will support a range of energy management services from residential smart homes to large commercial and industrial energy efficiency programs. But utilities will need to develop new capabilities to research, develop, market and support these new services. Executives will also need to improve their ability to innovate and experiment to help determine which offers make the most sense given their regulatory landscape, competitive markets and customer base.
- Operations. For decades, utilities have used remote sensing and communications technologies such as supervisory control and data acquisition to optimize their generation, transmission and distribution systems. Digitalization increases the number of sensors and amount of data that they must manage by one or two orders of magnitude. The opportunity to understand how energy is consumed closer to the consumer grows bigger—but so does the challenge of extracting meaningful information from volumes of data.
Customer engagement
European energy retailers were among the first to identify opportunities to create successful business models based on digital technology. New entrants to the industry, such as NEM in the Netherlands or Lampiris in Belgium and France, developed pure online commercial models that provided a lower-cost way to serve customers who don’t value a direct relationship.
Following their lead, utilities around the world will increasingly use digital platforms to communicate with customers and develop a more complete picture of customers’ needs and opportunities. In the southeastern US, Entergy launched a service in 2009 allowing customers to text them to report an outage. This has helped improve Entergy’s customer satisfaction scores, particularly around communications.
Cultivating partnerships with technology vendors will become more important for utilities to deliver on the digital experience. Vendors such as Opower, C3 Energy, EnerNOC, Tendril and others can augment utilities’ own capabilities in customer insights, communications and engagement. Based on their experiences from working with multiple utilities, these companies bring scale and knowledge beyond what’s possible for any individual utility to replicate, especially in the fragmented retail markets of the US and Western Europe. Incumbent utilities can bring vast amounts of customer data to these efforts, a resource that new entrants typically lack. The right partnerships can help utilities unlock greater value from this data and fend off competitive threats.
New products and services
The smart home, which integrates features such as security, entertainment and energy management, is a prime example of the sort of new service enabled by new technologies in sensing and communications. Utilities operating in competitive retail environments such as Europe or parts of the US can view the smart home as a premium offer and a way to improve customer loyalty. UK utilities have bundled premium residential services for years as a way to improve customer loyalty and reduce churn. While it’s still early for smart home services, they are likely to bring some of the same benefits to utilities across North America and Europe.
The opportunities in smart homes and buildings are not limited to utilities in competitive retail environments. Electric and gas distribution utilities may use data from smart homes and businesses to improve their forecasting and demand management. For example, customer behavior data from smart thermostats such as Google’s Nest, Honeywell’s Lyric or ecobee can provide insight into individual consumption patterns. This information helps utilities develop additional, more granular insight into daily and intraday demand patterns at the local circuit and individual customer level. This helps utilities plan and price energy for the next day, dispatch demand response, meet energy efficiency targets and plan for long-term local capacity.
To succeed in smart home, utilities will need to navigate a complicated ecosystem of platform providers (including Nest, Apple’s HomeKit and Samsung SmartThings), subscription service providers and hundreds of device manufacturers. The same applies in the commercial and industrial sectors with original equipment manufacturers such as Schneider Electric, ABB, Siemens and GE-Alstom offering energy efficiency solutions. Here, too, utilities will need to partner with the right subset of players to tailor offerings to their business and regulatory environments, and test and scale across their customer bases.
Core operations
In addition to customer-facing opportunities, digital technologies create opportunities further upstream in operations. For example, energy suppliers in Europe typically sell a large part of their expected production up to three years in advance. But with more energy entering the grid from intermittent renewable resources such as wind and solar, it’s become more difficult to predict demand. Applying advanced analytics to real-time data on weather conditions and electricity demand has allowed one Western European utility generator to gain enough market intelligence in the short term—sometimes only minutes or hours—to allow it to optimize its pricing model. The intraday optimization and trading activity allowed them to generate tens of millions of euros of additional earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization every year.
Digital technologies also help inform planning decisions about distribution networks. In California, regulators and utilities are working together to determine how to use private and public data on the performance of the distribution network (for example, individual circuit peak load) to choose the best sites for solar, storage and other resources. The data and lessons from it will shape how the state’s three large investor-owned electric utilities plan their networks over the next decade and beyond.
Digital and mobile tools are also a boon to field operations. Technologies such as fleet telematics, ruggedized tablets and others all help to improve efficiency and effectiveness. For example, utilities can improve outage management by pinpointing which customers are experiencing them (integrating advanced metering infrastructure, social media, text messages, and other data), directing resources toward restoration (through traditional distributed and outage management systems, mapping and GPS), and communicating with customers. Field forces can improve productivity by adopting new technologies such as tablets, fleet telematics and bar code scanners. In our work with field forces, the important lever is to get maximum adoption of a common platform and work processes, even if the fleet uses technologies that are a few years old. One European energy service provider was able to reduce its energy consumption by 5% over an already well-optimized asset base by using remote management technologies of decentralized installations. It also increased the productivity of its field force by 12% to 15% through better planning and management of site operations.
Priorities for different types of utilities
Utilities will decide where to invest in digital technologies, depending on their market structure and their place in the value chain (see Figure 2). Many will derive value over the long term by using technology to bridge siloes within their own organizations to improve operations. Successfully deploying these new technologies will require an effective cross-functional approach that may include:
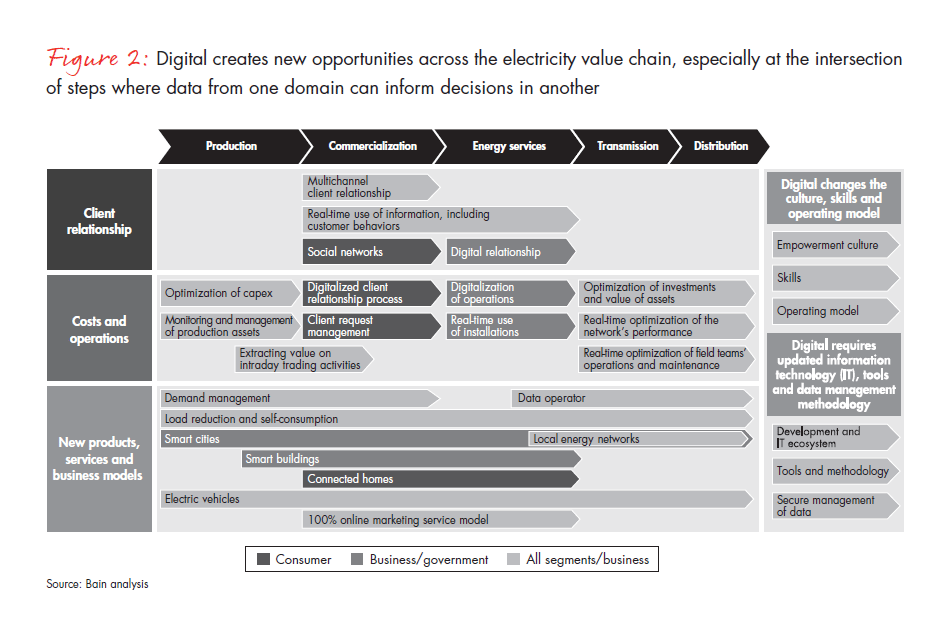
- Centralized and decentralized generation teams sharing technologies and practices to develop a more flexible asset portfolio
- Commodity and services retail teams sharing customer intelligence and leads to maximize cross-selling opportunities
- Generation and retail working together to identify new sources of value in an increasingly fragmented and interconnected market structure
- Information technology (IT) and human resources departments identifying the necessary skills and talent to succeed in an era of digitized energy management
- The management team developing an ideal partnership strategy and make-or-buy approach across functions and value chain steps
Many will also provide more real-time data from customers’ industrial and commercial sites back to their customers as well as to their own engineers, creating new opportunities but also raising challenges about transparency.
Of course, they will have to build new capabilities to get the most from their investment. For example, retail utilities will see fewer customer interactions in their call centers and more online. Energy service companies working with the commercial and industrial sectors will require fewer field technicians and more engineers who can manage energy installations remotely. And this will require all utilities to rethink the way they deploy IT skills as they adopt more agile methods and upgrade security to manage the risks inherent in a digital era.
Digital transformation offers massive opportunity for utilities, but success will require a significant investment in new talent and capabilities, and careful prioritization. Senior executives must be deliberate about picking the right opportunities for their market and regulatory environment. As with all large transformations, they should think of this as a yearslong journey, even though in this case one of the most important aspects of the change will be acquiring the ability to innovate in short cycles and deploy new products and services more rapidly.
Successful transformations begin with a diagnostic that explores how digital is changing the energy sector and the utilities industry. This process should also assess the evolving needs of customers and the digital capabilities and services of competitors. Within the utility, this initial diagnostic should present a comprehensive view of the organization’s own digital initiatives (current and planned) and capability gaps, along with some evaluation of the execution risks and organizational readiness for the transformation. With this fact base, executives can begin to prioritize their digital initiatives for customer engagement, new products and services, and optimization of operations, acting on those that are most likely to increase margin and raise the share price.
Jason Glickman is a partner with Bain & Company in San Francisco. Arnaud Leroi is a Bain partner in Paris. Both work with Bain’s Global Utilities practice.

