Report

한눈에 보기
- The supply of blue and green hydrogen is still small, but energy, natural resources, and industrial companies are beginning to explore how customers will use hydrogen.
- Economic feasibility will vary greatly depending on the availability of low-carbon alternatives, which will affect whether regions export or import blue and green hydrogen.
- Consortia of companies are forming around the opportunity to climb the experience curve and gain early-mover advantages.
This article is part of Bain's 2021 Energy and Natural Resources Report.
As climate change has risen to the top of the agenda for governments, investors, and companies, it’s becoming clear that traditional abatement strategies won’t get us to the goal of net-zero emissions, even with better energy efficiency and the introduction of vast amounts of renewable energy, biofuels, batteries, and carbon capture. Other innovations will be needed, and among the most promising is low-carbon hydrogen, which will help close the gap in industries that could prove hard to abate otherwise, including heavy-duty transportation, steel manufacturing, and production of fertilizer and methanol.
The current market for hydrogen is about 115 million metric tons, but Bain’s research estimates this could increase to 300 million metric tons by 2050, with the low-carbon component growing from virtually nonexistent to most of the supply. (For more on the developing market for hydrogen, see “Five Imperatives to Thrive in a Hydrogen Future.") Growth rates in green hydrogen (produced from zero-carbon sources) and blue hydrogen (produced from low-carbon sources) will outpace traditional energy markets, creating attractive opportunities along the value chain.
Hydrogen’s feasibility will vary across regions and industries, and many companies are already experimenting in consortia to expand hydrogen’s reach. Most are grappling with the same questions. What’s the best way to participate in the burgeoning hydrogen market? What are the most attractive opportunities, where should we play in the value chain, and how do we ensure we have the right capabilities to move forward?
Identifying opportunities
Much of the attention has focused on how to supply low-carbon hydrogen at prices competitive with gray hydrogen (made from fossil fuels) or other low-carbon energy sources, but customer demand will ultimately drive the market. Leaders start by developing a clear understanding of their customer’s needs, then figure out where hydrogen could make sense in filling them. This requires determining whether the cost of hydrogen can be competitive, given regional dynamics, regulatory incentives, and other low-carbon alternatives. Even when it cannot, some customers may be willing to pay more to meet their own sustainability goals.
Early projects show several different approaches, including some that are already feasible without subsidies, and others intended to develop new markets (see Figure 1).
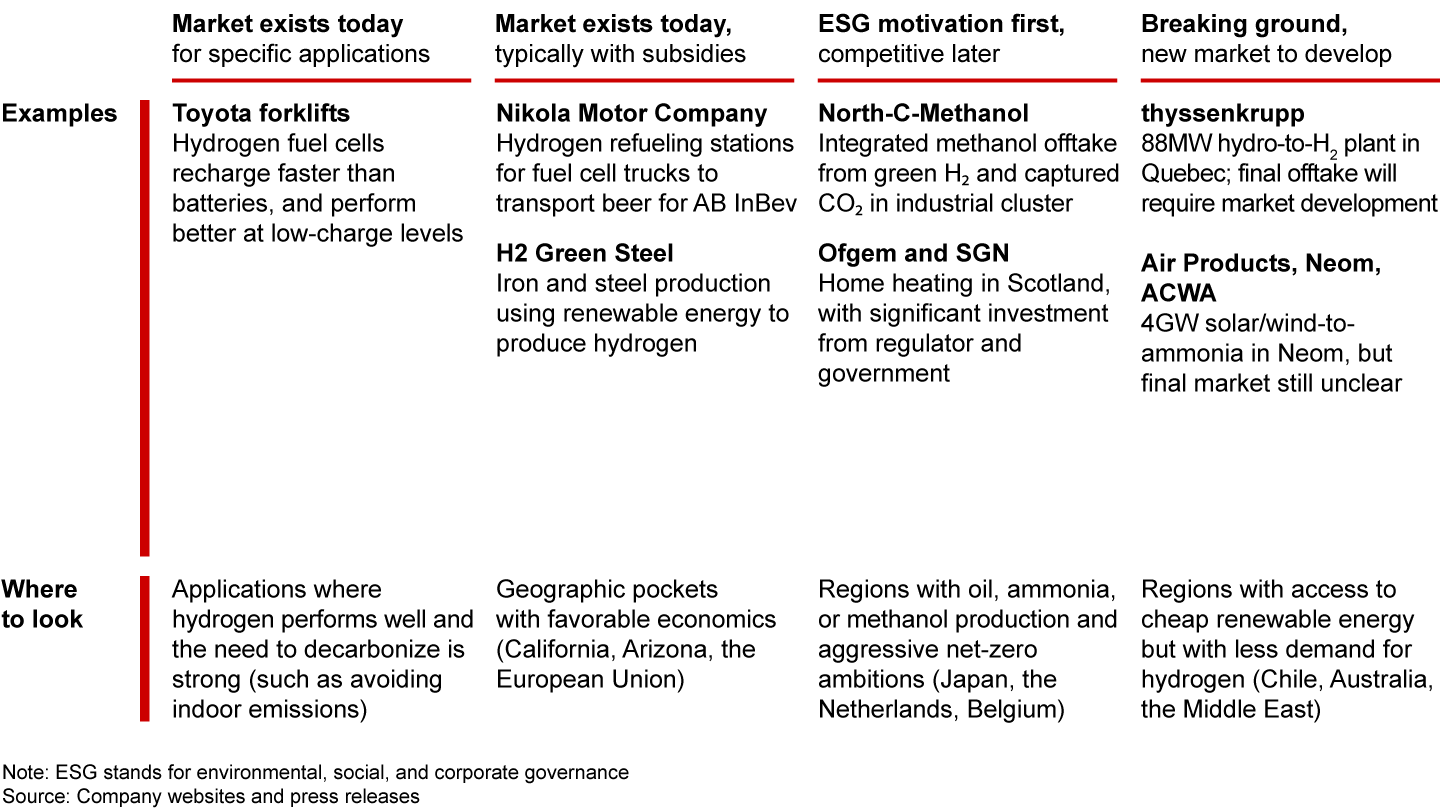

For most applications, low-carbon hydrogen isn’t yet competitive with other low-carbon technologies, but there are a few exceptions, depending on location and other factors. Forklifts are one example. Because the refueling time is much faster than for a battery, and because a fuel cell’s output doesn’t wane at low-charge levels, forklifts powered with hydrogen fuel cells already present a competitive option with superior performance and flexibility. An electrolyzer running from grid-sourced renewable electricity can produce enough green hydrogen for a fleet of forklifts. Vehicles used in mining are another example where hydrogen could make sense as a tool for decarbonizing, given the similar uptime requirements. (For more analysis on timing for different use cases, see “When Will Hydrogen Be Cost Competitive?”)

When Less Carbon Means More Growth
Winning companies play both offense and defense for a full-potential carbon transformation.
Other applications make economic sense only in certain places with unique economics. To identify these opportunities, companies need to determine regional differences in the economics of hydrogen—in other words, they must “de-average” global costs. For example, at a global average, green hydrogen is about two to three times as expensive as gray hydrogen. But much of that cost difference lies between the renewable electricity used to generate green and the price of natural gas to produce gray, whose prices vary widely by region. Places endowed with rich renewable energy conditions (such as plenty of wind and sunshine) can offer far better economics for green hydrogen. In Chile, for example, few hydrogen projects are underway, but ample wind and solar could help it produce low-carbon hydrogen for less than $2 per kilogram by 2025. Understanding where below-average low-carbon hydrogen costs align with above-average alternative costs will lead to the earliest pairings of supply and demand.
In regions with excess renewable energy, hydrogen offers a low-cost way to use electricity that might otherwise be curtailed.
In regions with excess renewable energy, hydrogen offers a low-cost way to use electricity that might otherwise be curtailed. For example, in the sunny southwestern US, zero-emission truck maker Nikola Motor Company secured a below-market rate for solar-generated electricity ($27 per megawatt hour) to produce more competitive hydrogen, some of which will refuel trucks for Anheuser-Busch’s shipping lane from Arizona to California. This agreement highlights how hydrogen can help companies meet their decarbonization commitments.
Smelting is another example of an application with long-term potential for hydrogen, but where unique economics and government subsidies enable early applications. ArcelorMittal, for example, has announced plans to retrofit two of its plants in Germany to make carbon-neutral (or green) steel. In Sweden, the steel manufacturer H2 Green Steel provides yet another example. In this case, an abundance of renewable energy and iron ore makes green hydrogen an attractive route to produce low-carbon steel.
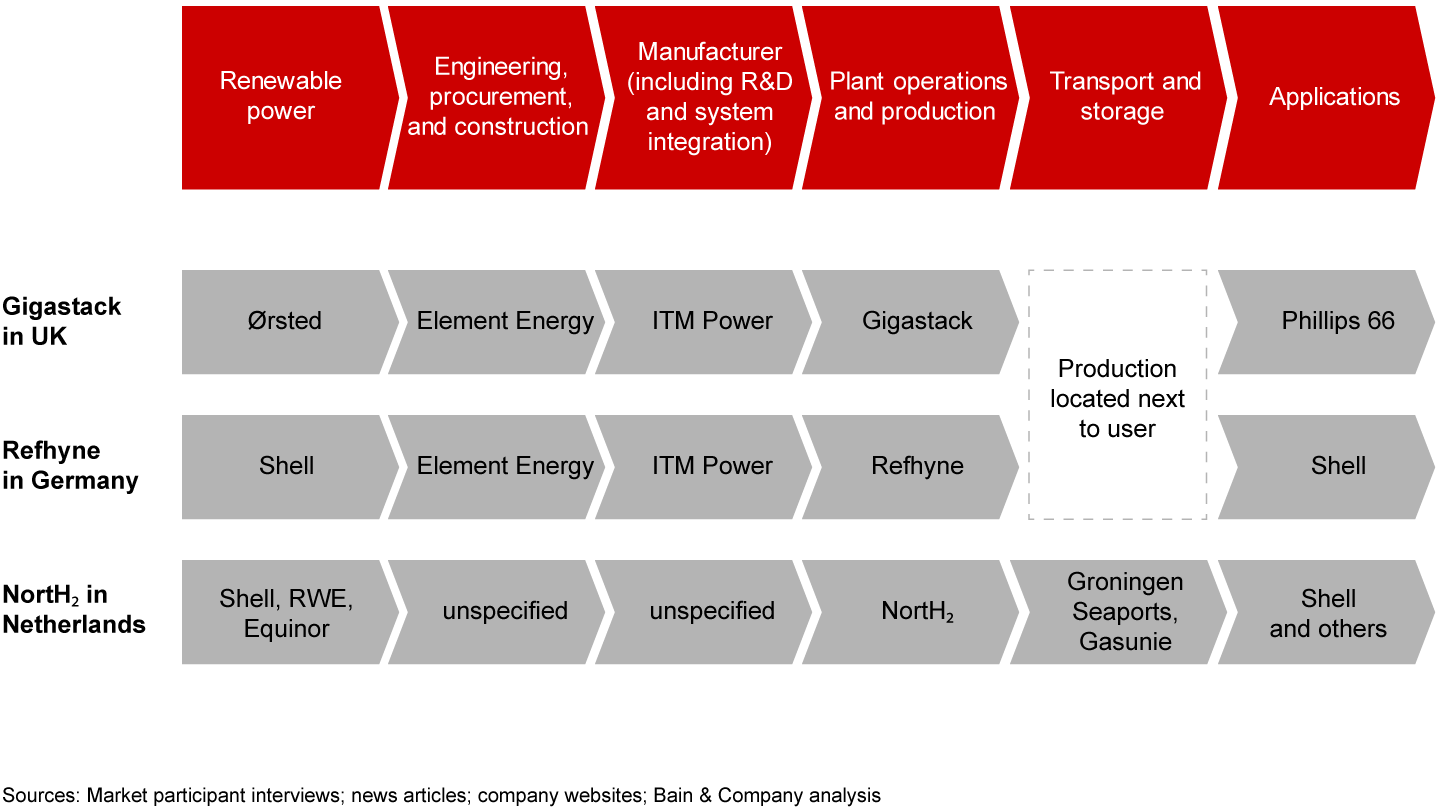
The pipeline for announced hydrogen projects grows nearly every day. Many of these involve consortia of companies teaming up to meet demands along the value chain, from development of facilities through production of hydrogen and consumption in the making of ammonia or methanol (see Figure 2). Although low-carbon hydrogen still costs more than gray hydrogen, these industrial companies are gaining experience that their competitors lack. At the North-C-Methanol project in Belgium, for example, hydrogen produced with renewable energy is consumed in methanol production along with captured CO₂, greening the process. Japan’s power sector represents another set of hydrogen customers with environmental, social and corporate governance commitments, high alternative fuel costs, and limited options to decarbonize.

Projects are also underway in regions with lots of wind and solar energy but limited domestic consumption of hydrogen. Neom, an experimental city of the future under development in northwestern Saudi Arabia, is one such location. A $5 billion collaboration between Neom, Air Products & Chemicals, and Saudi Arabia’s ACWA Power will produce green hydrogen with electricity generated by solar in the day and wind at night, to gain experience, develop the market, and scale production as demand rises to meet it. In the near term, this systems approach will produce hydrogen for use locally in Neom, with the long-term goal of scaling to support exports. Australian production follows a similar model and is the global leader in announced green hydrogen projects (see Figure 3).
Finding your place in the value chain
The market for low-carbon hydrogen is new and likely to remain in flux for a while. As players consolidate their views and experiment with business models, many are struggling to get started and find their focus. The most effective way to avoid dead-end experiments and to gain a leading position is to develop a clear view of the value chain, potential profit pools, and what it takes to win in these future profit pools.
As in any new market, companies should assess which current capabilities might give them a competitive edge in hydrogen (see Figure 4). A European manufacturer in the renewable energy space considered its strengths in engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC); electrical systems; power controls; and system integration. Geographically, it has a strong presence in several locations with potentially high demand. Executives decided that it could use these capabilities to design power-generating assets and production sites for low-cost hydrogen and help scale production in the electrolysis industry.


Closing capability gaps
In the emerging hydrogen project consortia, companies are combining their strengths to complete the value chain. In many cases, oil and gas majors or utilities are taking on the role of project developer, with the output often used within refining, ammonia production, or blending into existing natural gas networks. Securing such offtake partnerships is critical for these early consortia, because a significant merchant market isn’t expected to develop before 2030. In the current project pipeline, some oil and gas companies are taking both the project developer and offtake roles.
Over time, the value chain is likely to consolidate as companies integrate forward or backward. For example, manufacturing and EPC companies in oil and gas or renewable energy could extend their core capabilities into optimizing electrolyzer production, taking out weight, applying a modular approach, and procuring components at lower cost. At the same time, these companies may need to close gaps in stack and electrolysis design, where there are many partnerships with electrolysis pure players.
New partnerships will be essential. Consider a renewable energy original equipment manufacturer (OEM) seeking a larger role in the value chain, which might include electrolysis design and access to end customers. It would make sense to seek out an electrolysis partner to combine capabilities to design and scale production. To cover its gaps in the gas and end-consumer markets, it could partner with strong midstream and downstream partners, such as oil and gas majors. That would help the OEM focus on taking market share and developing repeatable models that will enable it to expand to other geographies.
Moving forward to execute
The hydrogen market is moving quickly. A year ago, most executives were just beginning to consider where hydrogen would play a role in their industry’s value chain. Today, companies have started deploying strategies for using hydrogen, all while maintaining the flexibility to adjust as the market evolves and conditions change.
Winners in this market will be companies that can develop a keen understanding of hydrogen’s potential and economic feasibility, as well as a determination of their place on the value chain. Setting long-term strategic goals will be essential, with progress measured against short-term milestones.
Finally, no new program will gain much traction without strong support from senior management. Some companies will invest in hydrogen as a second engine of growth (see “Engine 2: How to Grow a Sustainable New Business”). Only by guaranteeing continued support, and securing the resources to make it happen, can companies ensure that their investments in hydrogen will have a chance to succeed in the developing energy economy.
Read our 2021 Energy and Natural Resources Report
More from the report
-
Two out of Three Won’t Do
-
Harnessing the Energy and Resource Transition
-
Net Zero: From Political Targets to Industry Action
-
Energy Is Only One Part of the Sustainability Transition
-
Redesigning Value Chains to Deliver More Sustainable Goods
-
Time for ESG Investors and Energy and Natural Resources Companies to Work Together
-
Business Opportunities in Low-Carbon Hydrogen
-
Raising Productivity in Energy and Natural Resources Capital Projects
-
Creating Resilience, Sustainability, and Accountability in Supply Chains
-
Engine 2: How to Grow a Sustainable New Business
-
Accelerating the Journey to Net Zero
-
Four Ways to Scale Digital in Energy and Natural Resources Companies