Brief
 }
}
At a Glance
- EV growth is expected to boost battery demand fourfold by 2030 as OEMs diversify into mass market.
- Key questions for OEMs include which battery technology to use and whether to develop it in-house or with partners.
- OEMs will need to tailor their choice of battery to both the product roadmap and corporate strategy.
Over 250,000 electric cars were sold globally every week in 2023, more than the total sold in a year just a decade ago. As more people buy electric vehicles (EVs), the demand for EV batteries also increases. Anticipated future growth in EVs is expected to boost global battery sales to more than four times the 2023 demand by 2030 (see Figure 1).
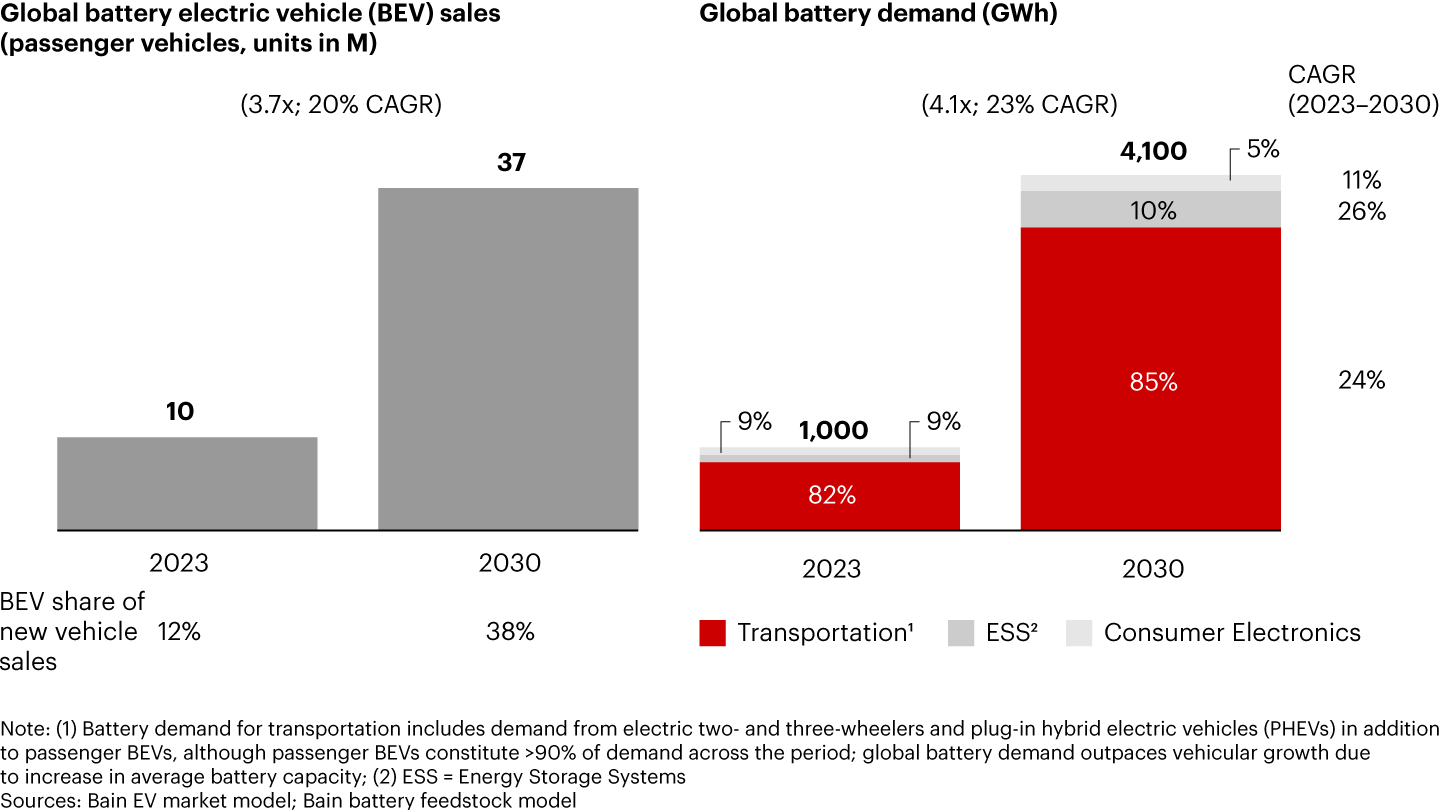

EV makers have reached a critical crossroad. Leading OEMs realize that to sustain recent growth levels, they need to diversify sales from early adopters in the premium segment to value-conscious, mass-market consumers.
Batteries are the single biggest cost driver for OEMs and greatly influence product performance. However, ongoing flux across battery chemistries and within lithium-ion batteries are affecting OEM product roadmaps. OEMs across the world face the critical choice of which battery type to use and whether to develop batteries in-house or through collaboration with other companies.
Amid market uncertainty, leaders are adopting new strategies to incorporate more flexibility, while managing multiple moving parts that are not amenable to linear planning.
Our five beliefs for the 2030 battery market
1. Lithium-ion batteries will remain dominant for the foreseeable future
Lithium-ion batteries have dominated the global EV battery market and will continue to do so. Emerging technologies such as solid-state and high-density sodium ion are still in the prototype and pilot manufacturing stages, and we expect their market share to stay in the single digit range until 2030.
2. NMC and LFP will be the dominant cathode chemistries
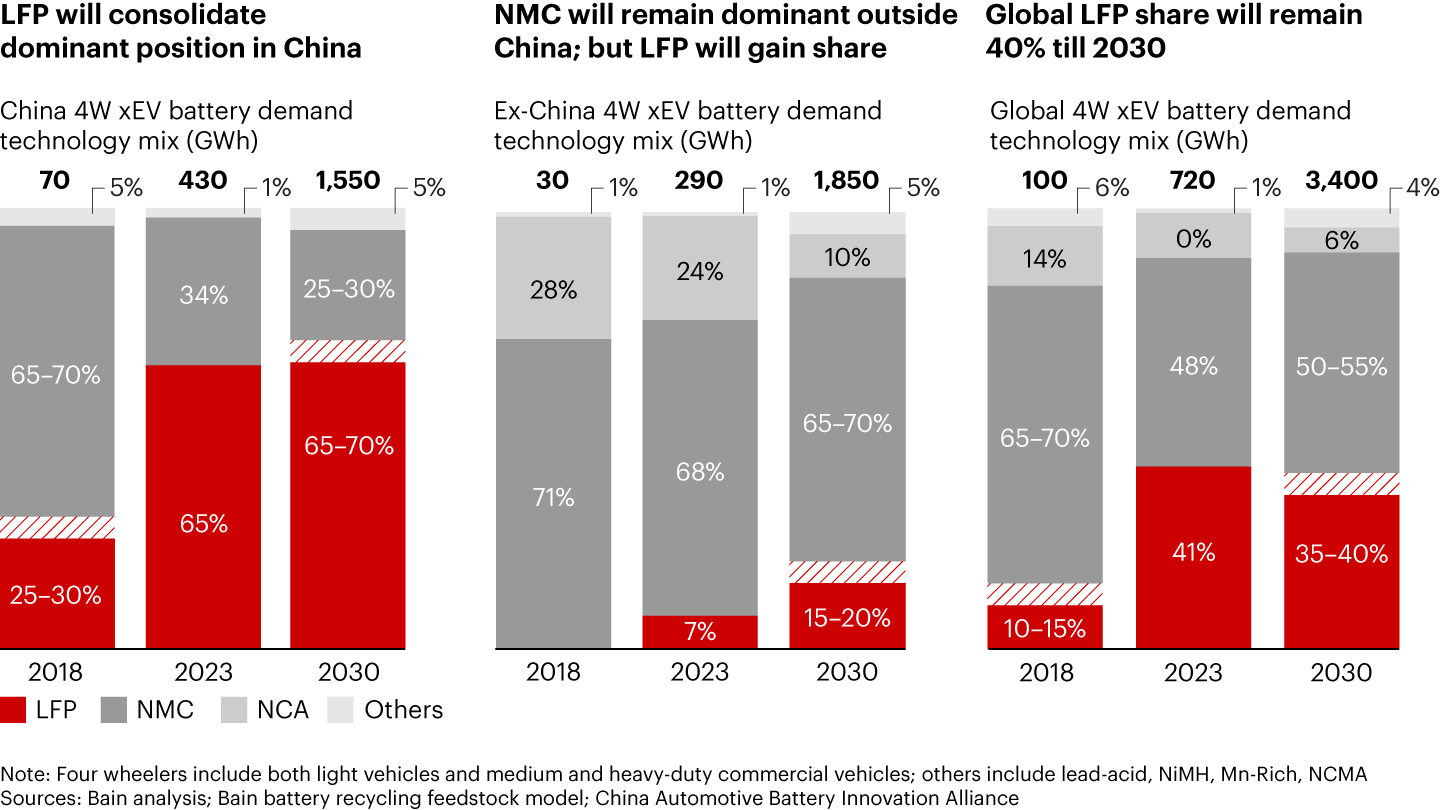
Lithium-iron phosphate (LFP) and nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) chemistries together currently make up more than 90% of lithium-ion battery sales for EVs. Nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (NCA) is expected to remain marginal due to its lack of performance or cost advantage compared to high-nickel NMC.
LFP has taken significant share from NMC since 2018 due to improvements in energy density at sustained lower cost. In China, LFP will become more dominant (see Figure 2) due to robust demand for mass-market EVs and established supply chains, in addition to the emergence of LFP variants with improved energy density (e.g., M3P and lithium manganese iron phosphate [LFMP]).
In the USA and EU, LFP will gain share, although total adoption will still be lower than that in China for multiple reasons. First, domestic LFP production is nearly nonexistent, and existing iron and phosphorous supply chains are significantly less mature in these regions compared to those in China. Consequently, the cost advantage of LFP vs. NMC will be undercut by the costs of importing LFP from China. This will be exacerbated by unfavorable economics of recycling vs. NMC. In addition, many companies are looking into no- or low-cobalt NMC variants (e.g., NMx, high lithium manganese [HLM], high-voltage mid-nickel), which would further reduce the cost advantage of LFP. Finally, import tariffs (such as those in North America) and broader geopolitical challenges may make LFP less suited for western OEMs looking to build up more resilient supply chains.

3. Lithium-ion technology will continue to decrease in cost and increase in performance
Major developments across the technology stack promise to materially affect the performance and cost of lithium-ion batteries. Specifically, the lithium technology stack will see major shifts across cathode chemistries, anode chemistries, cell form factors, and pack architecture. OEMs are keeping a close eye on multiple innovations such as battery integration via cell-to-chassis technology, where the battery is built directly into the structure of the car; dry electrode manufacturing process, which reduces energy consumption and, hence, manufacturing cost; and AI-powered battery management systems that are increasing the longevity of batteries.
4. Solid state and sodium ion will be the only commercialized emerging technologies by 2030
Solid-state batteries promise significantly higher energy density vs. NMC, along with improved safety, faster charging, and potentially longer life. However, players have only recently been able to demonstrate initial proofs of concept following multiple delays, and commercialization is likely three to four years away.
Sodium-ion cells promise lower cost than lithium ion, along with improved safety and the ability to operate at lower temperatures. However, energy density has historically been substantially lower, constraining EV adoption. There has been progress on this front, with prototypes delivering energy densities comparable with LFP. However, adoption of sodium ion is contingent on the replication of prototype performance at scale and will also be limited by continuing improvements in LFP energy density and decreasing costs. Nonetheless, multiple players have announced plans to scale production by 2025, with commercial deliveries of the first sodium-ion-based EVs having already started.
Other emerging chemistries are unlikely to be commercialized in EVs by 2030. The two front-runners, lithium-sulfur and metal-air batteries, are still in the early stages of development. Companies are developing initial proofs of concept but have not yet validated concepts at scale with OEMs. This means it will be at least six years, if not longer, until they can commercialize these batteries.
5. Demand for recycling will increase
Recycling of EV batteries is expected to grow significantly, led by expansion in feedstock volumes. A rising number of new global regulations around collection, recycling, and the use of recycled content will further promote recycling.
Currently, no recycling technology holds a clear advantage, and the technology and roles of companies in the recycling process are evolving. Battery manufacturers and OEMs are exploring new business models (e.g., battery rentals) to maintain ownership of batteries and take responsibility for recycling. The top priority for most companies today, however, is getting access to the right battery cost and infrastructure. Once that is in place, they can refine their recycling strategy down the line.
Top priorities for OEMs
Tailor battery strategy to both the product roadmap and corporate strategy
Historically, the choice of battery technology has been straightforward: LFP for lower-end mass-market models and NMC for high-end performance models. This choice is becoming increasingly complex with the evolving technologies making new options available for OEMs. OEMs need to invest in understanding both the rapidly changing battery landscape and evolving customer buying patterns to ensure they deploy the right technology.
The choice of battery will also have supply chain implications depending on where it is manufactured. Leading OEMs are aligning their battery strategy with their product roadmap and their overarching corporate strategy. This comprehensive approach includes supply chain setup, vertical integration, and resource allocation.
These choices also depend on which market segments the company serves. Catering to a premium market with long-range and higher-performance requirements would dictate different choices than serving mass segments focused on urban mobility. BMW, for example, is well known for offering a premium driving experience. The automaker has taken a large role in designing and developing its batteries, which directly affect the core driving experience. General Motors, in contrast, has partnered with LG Energy Solutions (LGES). LGES designs and manufactures the batteries while GM focuses on the integration of batteries into its vehicles and systems.
Choose the mode to access these technologies
Leaders are generally accessing these technologies in two ways. Some companies are developing designs internally so they can manufacture batteries in-house. With this approach, they do not depend on external partners for knowledge, and they have a stronger position to reduce battery costs and increase productivity in procurement. Other companies rely on external sourcing to varying degrees. They partner with either incumbents that already have scale in the market or with start-ups that have breakthrough technology.
Strategies will vary by player and should be based on an evaluation of financial factors (e.g., capital requirements, return on investment), strategic factors (e.g., cost, performance, degree of customization, future technology roadmap), and the risk (e.g., supply chain resilience, risk to brand perception, regulatory requirements).
Winning OEMs will stay flexible, watch the market, and adapt their strategy
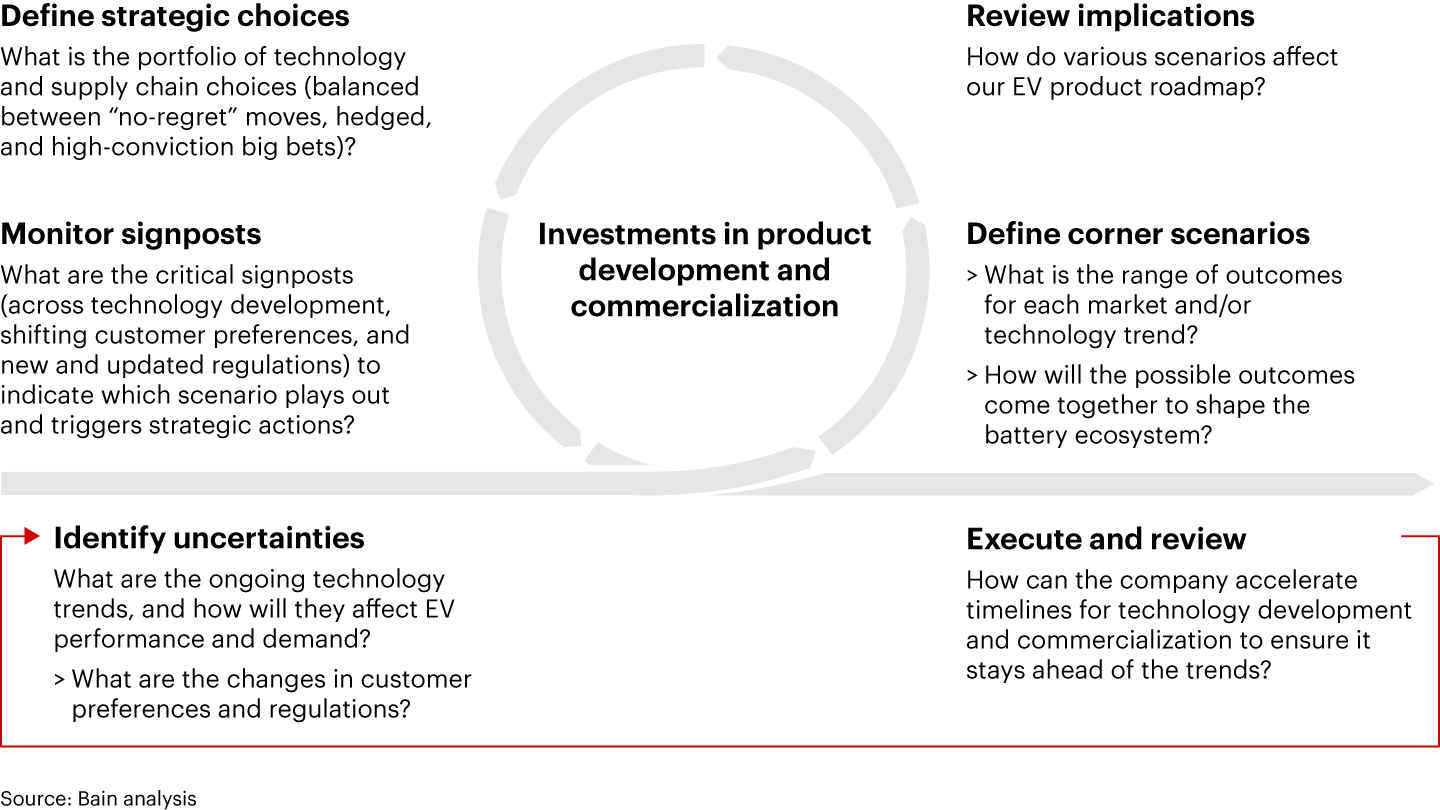
EV OEMs are navigating a landscape in which frequent nonlinear disruptions greatly influence the return on their large investments. For instance, timelines for commercialization of certain battery types can accelerate or decelerate. New technologies or variations can also emerge, such as new cell form factors and module or pack designs. In addition, the evolution of one technology can affect demand for others and influence supply chains. For example, a sustained drop in LFP prices will adversely affect demand for sodium ion. Also, the emergence of silicon anodes will affect demand for solid-state batteries. In this landscape, players must adopt a new way to establish strategy amid uncertainty, creating a portfolio of choices that combine commitment with flexibility (see Figure 3).

Beyond the battery
In the coming years, various factors, from evolving technology to shifting geopolitical tensions, will continue to affect battery strategy. Leaders must assess what assumptions they can safely make now and what decisions they should keep open. Furthermore, many elements of EVs, from autonomous driving to increased passenger connectivity, may ultimately matter more to customers than the vehicle’s batteries, which would in turn shape OEM investment. Ultimately, OEMs will need to make big-picture trade-offs between what is required and what the customer wants and assess how this influences the choice of battery and the overarching corporate roadmap.
