Brief

At a Glance
- Managing quality effectively helps avoid operational disruption and associated economic and reputational losses.
- Using advanced analytics can enhance a company’s quality controls in a cost-effective way.
- Generative AI is a game-changer as it can help to find new solutions for quality problems, increasing customer satisfaction.
- Leveraging advanced analytics for quality management requires an organization-wide approach, led from the top.
Advanced analytics is becoming a vital tool in the quest for improved quality. It can help decrease total costs by identifying and addressing the root causes of defects more swiftly, as well as defining more efficient methods to maintain quality. The results of deploying advanced analytics in quality management can be measured in improved customer satisfaction and retention, as well as increased cash flow.
This matters because the total cost of quality has a major impact on economics—costing up to 20% of revenue for a business. This covers the direct resource cost of managing quality—so that substandard items are not produced in the first place—as well as the costs of scrap, rework, or warranty work to correct errors. It also includes another major issue: lost future revenue caused when customers are disappointed by poor quality.
Managing quality effectively starts within production processes and customer service, but goes further. Factors outside a company’s control, such as natural disasters and global instability, disrupt supply chains and can exacerbate production challenges. When these disruptions lead to changes in the value chain—such as the need to set up new manufacturing locations, hire new people, or source materials from different suppliers—the chance of hitting quality problems increases.
In today’s competitive markets, businesses need to find ways to preempt these issues. Increasingly, that means stepping up how quality is managed across the company (see Figure 1). Advanced analytics, increasingly fortified by the capabilities of generative AI for creating efficiencies, is an effective tool here as it can help crystallize insights and identify future trends by deciphering intricate connections in data that are often invisible to conventional analytical methods.
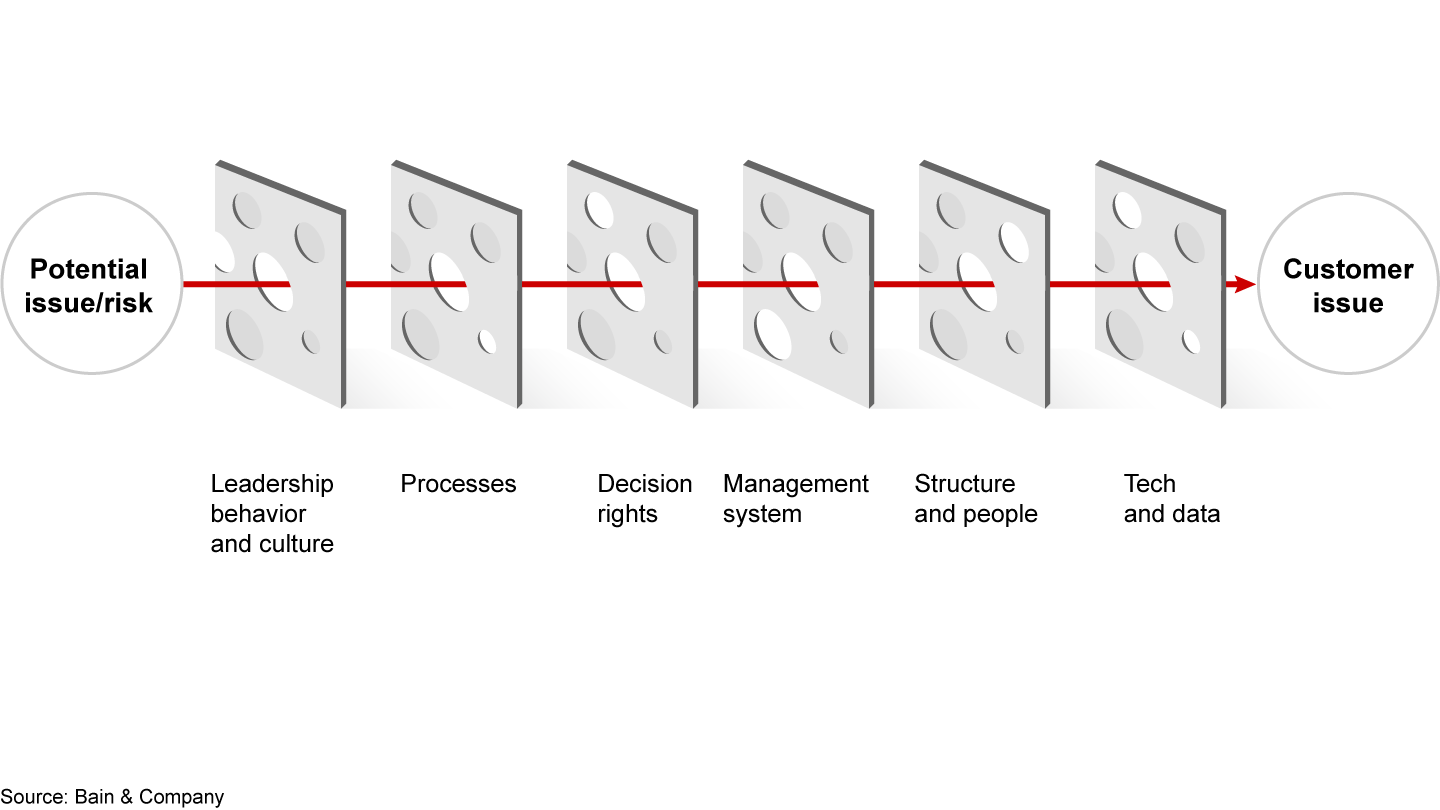

Greater insights through enhanced data analysis
Industries such as semiconductors and pharmaceuticals have used analytics to improve quality for some time, and others are now catching up. Most businesses already use some form of data analytics for tasks such as identifying bottlenecks in supply chains. Advanced analytics uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to examine this data and combine it with other sources of information (such as weather patterns and transport costs) to predict—and therefore avoid—future bottlenecks. More available data, an increased willingness to experiment, and sophisticated new tools are making these processes more accessible and driving significant improvements.
Measuring the right things reduces “black swan” events—major quality issues caused by the stacking of multiple small issues across a process. Without advanced analytics, it can often appear as though these problems couldn’t have been predicted or prevented, so companies write them off as exceptions. However, advanced analytics often uncovers benchmarks that, if measured, would have prevented the problem.
Applying advanced analytics
Measuring everything can be prohibitively expensive, so it is important to select and prioritize.
A common concern is not having sufficient data to start an advanced analytics program, but companies have more sources of data than they think, and useful data can often come from unconventional sources. These include customer rebate claims, quality assurance supervisor shift logs, and even publicly available data about ambient conditions, such as heat or humidity.
Putting advanced analytics to work starts by focusing on major pain points to find those that can be improved by AI and ML or by automating processes entirely (see Figure 2). For example, metrics such as noise, temperature, and vibration can help identify malfunctioning or poorly maintained equipment. Feeding these metrics into an AI model can help companies determine when a machine needs maintenance.
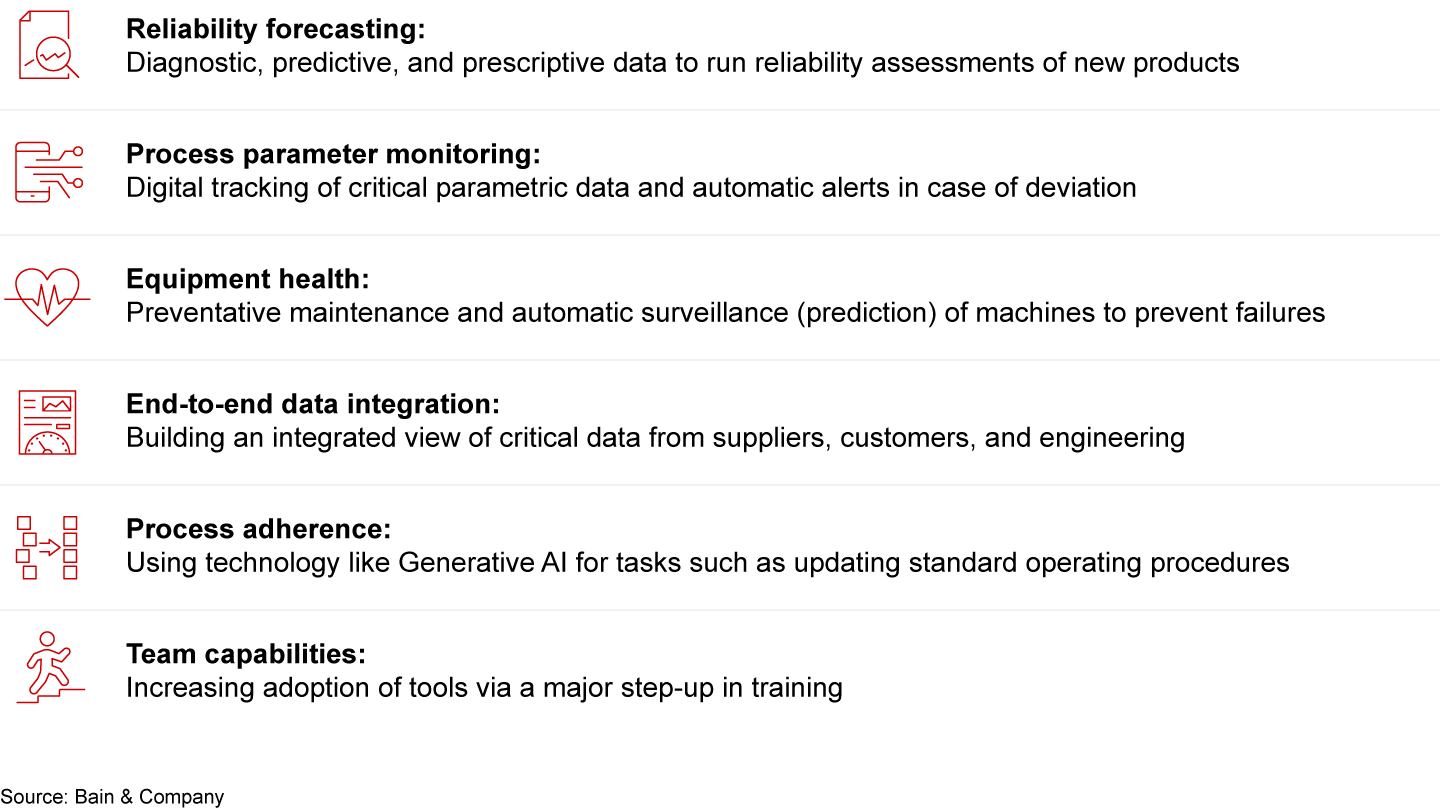

In addition to predictive maintenance, advanced analytics can help prevent other potential problems: it can be used to detect changes in the quality of material inputs and alert manufacturers to the need to adjust production processes; and it can be programmed to identify material defects, such as variations in dimensions or composition.
Understanding customer needs
Some pain points will be obvious, while others will require a deeper understanding of customer needs. One useful tool for this purpose is generative AI-driven sentiment analysis, which can help categorize and quantify different causes for customer complaints.
A specialty chemicals company, for instance, decided to include a dataset of customer complaints in an analysis of the quality of different product batches to identify the factors shaping good and bad production. Combining more than 250 variables from six different sources including structured data (the quality of different batches) and unstructured data (customer feedback), the company discovered that complaints increased when the acidity of the process fell outside a certain range—an important insight that would not have been achieved without the right dataset and advanced analytics capability.
This led to improvements that brought about a 50% reduction in production defects from contaminants and significant cost savings (see Figure 3).
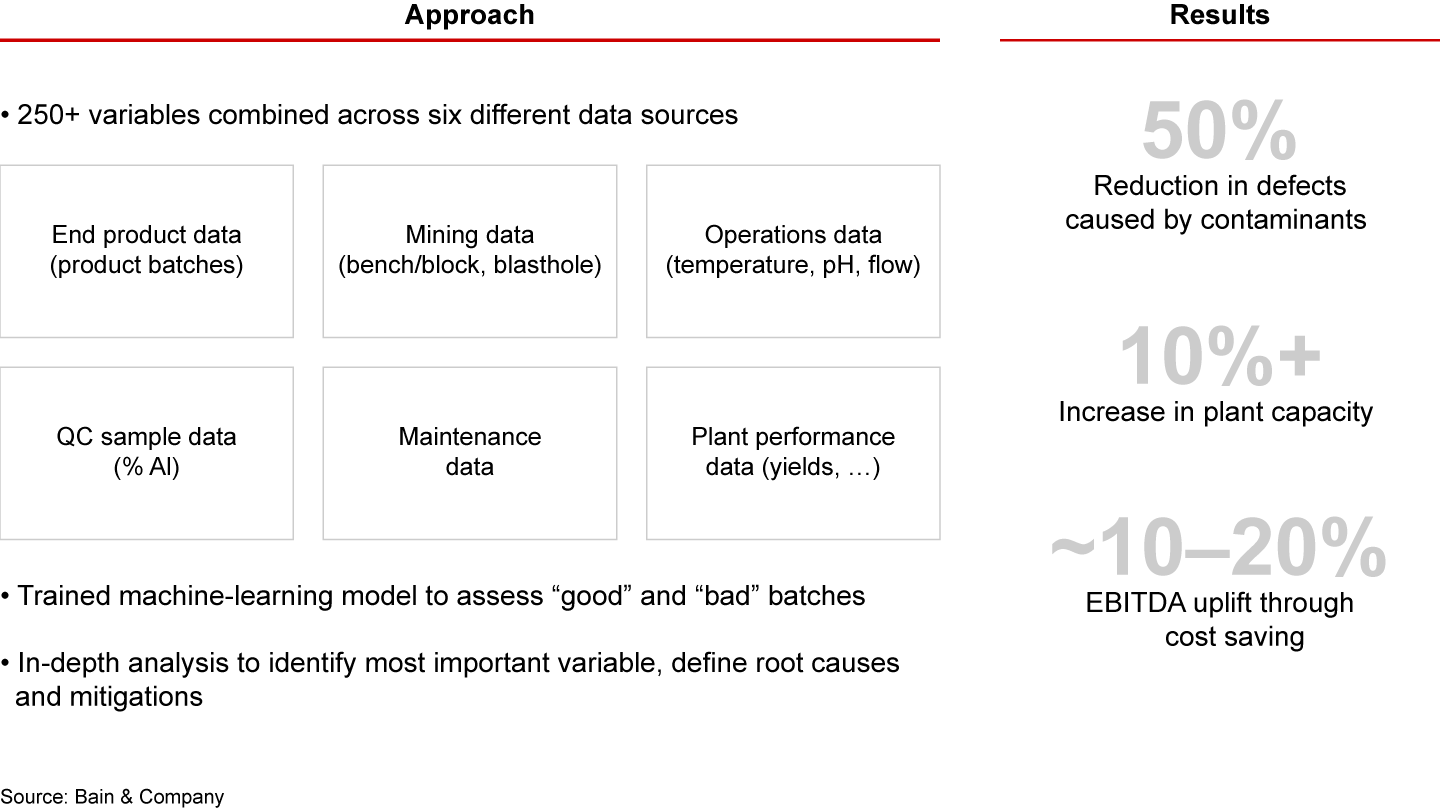

Companies can also aggregate datasets to gauge the difference between real and reported behavior. Customers often say they spend a certain amount of time using an app, for example, but sanitized data captured from devices might show that customers under- or overestimate their usage.
Generative AI opens up a new dimension
Creating advanced analytics models used to require not just data, but significant amounts of time and compute power to train the model on the datasets. But that is changing.
Today’s AI computer vision tools, for example, can make a major contribution to implementing quality. Automated visual inspection used to be relatively crude, but the most up-to-date vision tools can spot tiny defects on, for example, steel welds, vials, syringes, and even microchip wafers. They can do this more quickly, more accurately, and at lower cost compared to visual inspection by humans.
In addition, “few-shot learning” or “visual prompting” techniques allow manufacturers to begin with only a small set of their own examples. These are then fed to a powerful pretrained algorithm, resulting in usable insights related to visual inspection without the need to spend time and money training a new AI model.
The rise of generative AI, meanwhile, brings wholly new capabilities to managing quality, opening up a variety of current and future use cases (see Figure 4). For instance, it can conveniently update risk assessments in real time as variables change, predict potential manufacturing bottlenecks, and suggest necessary solutions, such as identifying alternative suppliers to prevent a production halt. Additionally, it can synthesize learnings to automatically generate, for example, the standard operating procedures needed for each production activity from recognized patterns in quality control. And it can do this at a speed and cost that is transformative.
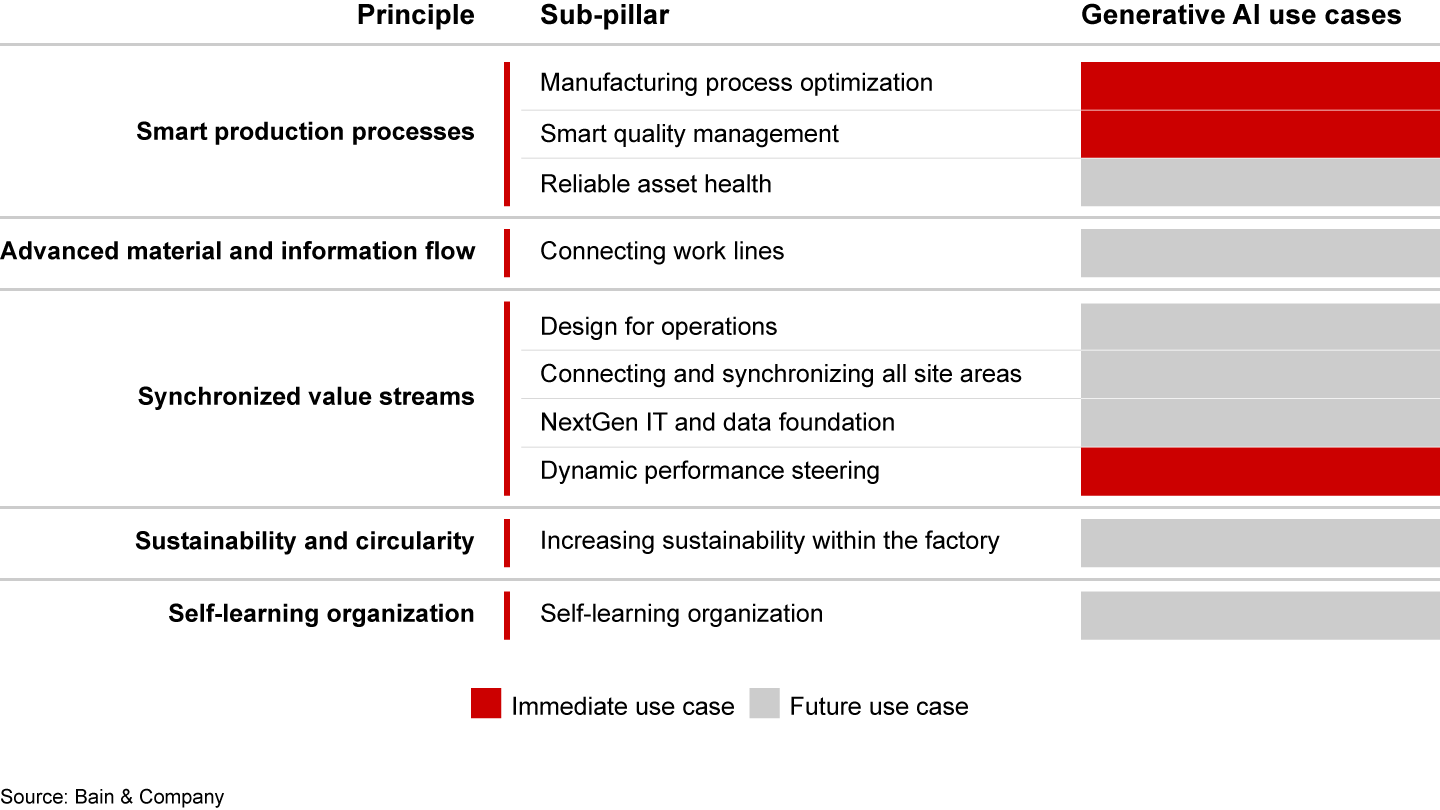

Six crucial steps to success
While advanced analytics offers remarkable benefits, realizing them requires a strategic and cross-functional push. Leaders must not only articulate their vision, but also foster a data-driven culture where teams are emboldened to experiment and develop expertise. This, coupled with investments in digital infrastructure for data integration, speeds the integration of advanced analytics into organizational thinking, converting apparent complexities into strategic advantages.
There are six crucial steps that companies need to work through to gain the full benefits of deploying advanced analytics:
- Define a clear vision and supporting culture: This requires a top-down commitment to embedding data-driven decision-making and strengthening a culture of continuous improvement. Nominating a senior executive to spearhead the effort is crucial to ensuring tangible changes are achieved.
- Focus on priority areas and major pain points: Identifying the areas or quality defects that have the biggest effect on customer satisfaction, operational performance, and business outcomes is crucial to prioritizing resource and effort.
- Establish a cross-functional team: Form a diverse team of analytics experts, quality leads, and relevant team members from operations and manufacturing, customer management, IT and digital, marketing, and finance. This team should be directly responsible for designing and implementing any future solutions.
- Explore data sources: Creatively consider which existing data could be used as part of analytics-led approaches—companies often have access to more than they realize and it might not be stored in obvious places.
- Invest in infrastructure, training, and change management: Ensure the organization has the necessary digital infrastructure, tools, and skills to effectively use advanced analytics. This includes investing in training and development, as well as addressing any barriers to change, such as resistance to new technology or the latest ways of working.
- Implement analytics use cases and track results: Iteratively implement advanced analytics measures to identify true root causes and generate palpable process improvements. Actively track outcomes and metrics and continue to add capability as the business case warrants.
Innovative quality solutions
A focus on quality is business-critical for any company that wants to stay competitive. Advanced analytics alone won’t be enough to solve quality problems, but using it is the foundational piece of a broader organizational approach.
A well-articulated vision, combined with a program that addresses key business pain points, will ensure that deploying advanced analytics quickly demonstrates value by delivering innovative quality solutions while keeping costs under control.
The authors would like to acknowledge the contributions of Gregory Bandak to this brief.