Brief
Is it time to split up?
Investors, bankers, equity analysts and board members all have intensified their efforts to find evidence that a targeted company will be more valuable when split in two. This push to unlock shareholder value by refocusing on a core business has fueled a boom in recent corporate breakups in industries as diverse as financial services and energy, pharmaceuticals and consumer goods—and it shows no sign of abating.
Under mounting scrutiny, executives are taking a closer look at their portfolios and, in record numbers, are choosing to separate. A growing number of management teams and boards of directors, particularly those of multi-business public corporations with lagging shareholder returns, are looking aggressively at this option, in some cases to preempt—or respond to—an investment by an activist investment fund. Separations can take multiple forms, such as divestitures to strategic or financial buyers, carve-outs and outright spin-offs. While these transactions are not new, they increasingly involve related businesses within a corporate portfolio, as opposed to the diversified conglomerate unwinds of the 1980s and 1990s.
The decision to take this big step is not trivial. Such separations are costly, with transaction costs alone amounting to an average 1% of consolidated revenue. They’re time-consuming, too, generally taking 12 to 18 months from decision to close. As anyone who has embarked on a separation can attest, they’re also resource intensive and potentially distracting.
Bain & Company wanted to determine how often such breakups are worth the effort, focusing on understanding the value created when two separate public companies are formed—typically via a tax-free spin-off of one of the entities—out of a portfolio where there had been some level of strategic and operational integration. We studied 40 such transactions involving companies valued at more than $1 billion across a range of industries in the 2001–2010 time frame. Our analysis, including extensive interviews with executives, has shown that the results of the long, complex and costly process are mixed. While the spun-off entity often generates positive returns, the combined equity returns on average do not outperform the S&P in the first 18 months after separation (see Figure 1).
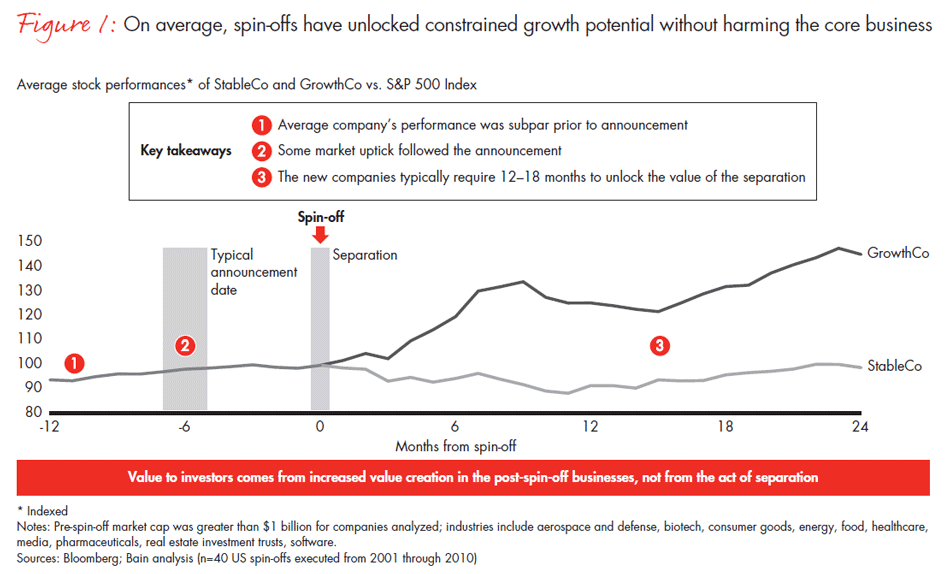
However, looking at average returns is deceiving, as performance varies significantly across separations. Based on our analysis, the top one-third of separations generate significant value, with the combined market cap of the new businesses after separation exceeding the pre-spin value by more than 50%. But in another one-third of the cases, the combined market cap of the new companies 18 months after separation is 40% less than the pre-spin value (see Figure 2).
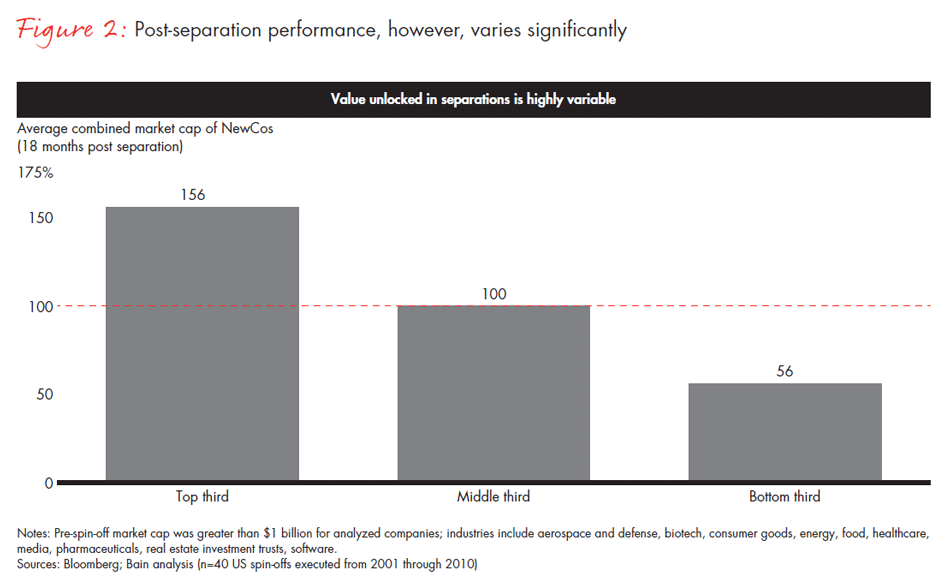
This tells us that separations are “high beta” events, requiring CEOs and boards to thoroughly understand the most important factors that contribute to success—or lack thereof—when considering such an option for their companies. Given mixed performance, it’s important for boards and management teams to take a measured approach to spin-offs, despite external pressures. Based on deep experience supporting major separations, we believe that the following five elements distinguish winning separations from losing ones:
1. A clear and compelling strategic rationale for separating. Will breaking up allow one or both of the companies to do something they can’t do today? It seems like an obvious question but one that sometimes does not garner the objective and rigorous consideration it deserves. Executives and boards must consider and value the specific actions that one or both businesses will be better positioned to take based on both financial independence and strategic and operational independence. Such actions could include gaining access to new markets, capturing significant cost reductions or making strategic investments. For a separation to have merit, the current integrated operating and ownership structure must, to some degree, preclude these actions. Consider the case of the government services contracting industry. Changes in government contracting regulations meant that providing technical services support to government agencies and branches of the military prevented companies from providing other services, such as intelligence support on programs even tangentially related to the technical services support. L-3/Engility and SAIC/Leidos are two examples of recent separations in this sector in which the executives highlighted potential new opportunities enabled by removing potential conflicts of interest.
2. A separation process that sets up both companies for success. A successful split goes beyond the purely transactional and operational elements of separating businesses. It must ensure that both companies will be competitive in their future markets. To meet that objective, leaders must be committed to defining and beginning to implement the strategic, organizational, cultural and operational changes consistent with the strategic rationale for separation. Leadership teams of successful separations view these events as unique “unfreezing moments” for establishing a range of possible new trajectories for both companies. Among the types of changes we see aggressively pursued in successful separations: exiting unprofitable lines of business, initiating major cost reduction programs, revising the role of the corporate center, making major capability enhancements or changing a culture (see Figure 3).
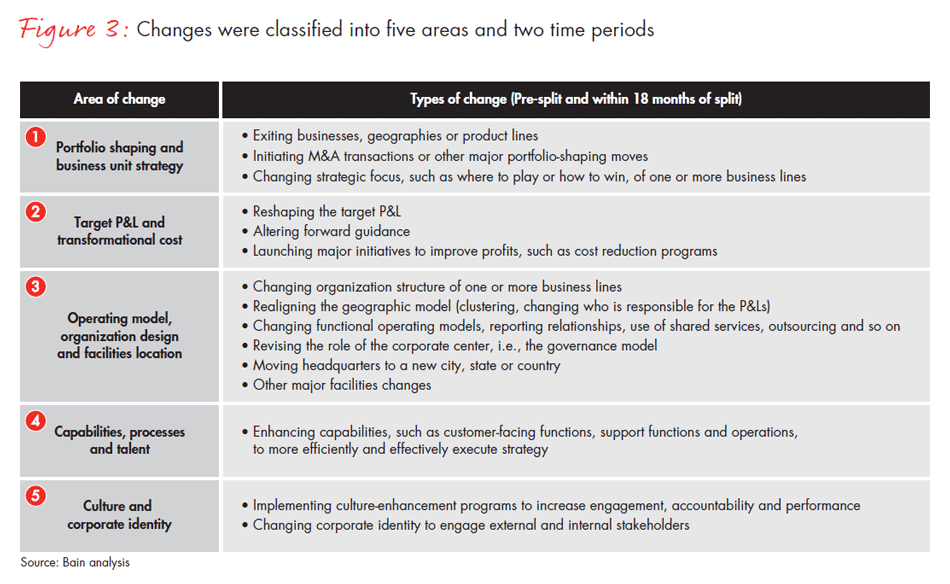
In pursuing changes, companies need to strike the right balance. The risk from too little change is that the new companies will find themselves as smaller versions of the previously combined entity, with stranded costs and no new advantages. The risks from too much change: The separation process falters because it is overwhelmed by complexity, or the new companies stumble in their first few quarters of standalone performance, having failed to digest all of the changes. Knowing how to strike this right balance is critical to a successful separation and must be considered as part of the upfront decision on whether to split.
3. A plan to offset dis-synergies over an appropriate time frame. Winning companies create a cost-mitigation plan for offsetting the incremental costs that result from a duplication of activities and personnel, or the loss of economies of scale. Those dis-synergies tend to be higher for companies that are tightly integrated before the separation, and the cost structures typically are highest in the months immediately following the split, during the period before profit improvement programs can offset these incremental costs. Well-run separation processes strive, where possible, to design their spin-offs to mitigate some of the potential dis-synergies. Less successful separations fall into one of two traps. They apply a simple carve-out “cut and paste” approach where they duplicate all currently shared roles—often those at the management or corporate level. Or they establish overly aggressive cost-reduction objectives for day one that are not achievable and would adversely affect the post-spin trajectory of the businesses.
On average, companies can expect to see selling, general and administrative costs rise by 5% in the first year of a separation. In successful separations, those added costs are typically more than fully offset 12 to 24 months after separation, as both companies begin reaping the benefits of performance improvement efforts. It is important to help investors understand how those added costs will be more than offset over time. For example, in investor conferences, Kraft described end-to-end cost-reduction efforts and overhead cost-management actions that were under way as it was in the process of spinning off Mondelez. When such plans are communicated in a compelling and well-articulated equity story, investors and analysts focus on the additional value being created by the new entities rather than the short-term change in cost position.

Breaking up is hard to do
The risks of a separation are abundant, but companies that get it right will reap big rewards for investors.
4. A continuing focus on current business priorities during the separation process. As we mentioned, a separation typically takes 12 to 18 months, depending on the circumstances, and can create a high degree of inward focus for an organization. Given ongoing market and competitive changes, such a diversion can be problematic. During that time, competitors may attempt to disrupt customer relationships, and employees can become distracted. Further, facing an uncertain future, an organization’s best talent may choose to leave. Without a carefully structured process that enables the vast majority of the company to remain focused on day-to-day execution, management runs the risk of diverting its attention from the base business. In the upfront deliberations on separation, important questions need to be asked and answered:
- Will this separation create an opening for a competitor to attack our position? Can we ensure our customer relationships and service will not be disrupted?
- What critical initiatives do we need to insulate from the distraction of a separation process? Can we execute those while conducting this separation?
- Given the potential disruption, are we going to be able to effectively retain our key talent?
5. Active management of leadership talent through—and after—the separation. Some companies fail to anticipate a basic need: the leadership depth required to pull off a successful separation. Strong leaders are required for both new companies—during and after the separation. We find that at least 75 senior and midlevel full-time employees are needed to execute most separations. And separations are particularly demanding of resources in IT, finance and HR. In addition, many more employees are partially involved as experts.
After the separation, both companies will need full executive teams with public company capabilities and credibility. The trouble is, few companies have that level of leadership talent on their bench. Companies must make decisions as early as possible about which future senior leadership roles they can fill internally and which would require new talent. Tackling those decisions early allows sufficient time for external searches. It also improves the odds that external hires can be on board before the split and can take part in the process of designing the new companies.
As the debate over separating intensifies, one thing is clear: The decision about whether to split can be a make-or-break career bet for most CEOs and boards. The companies and executives most likely to succeed will be those that focus on these five priorities after first carefully considering and discussing them in deliberations on whether to split. They know exactly how they’ll create value from the split, set both companies up for success, have a plan for mitigating incremental costs, keep a focus on core priorities and ensure they have leadership depth. It is also important that they run a highly disciplined program (see below, “Is the process set up for success?”). Boards and CEOs that apply a rigorous approach based on these principles increase the odds of making it a winning move.
Bain & Company Partner Andy Pasternak outlines some of the challenges of spin-offs and suggests strategies that can help companies succeed in these make-or-break moments.
Is the process set up for success?
When the evidence shows that a split makes sense, the best companies boost their odds of success by establishing a disciplined and well-resourced program structure. Key success factors include:
- Making clear to all individuals working on the separation that they need to focus on the best interests of current shareholders, who will own shares of both companies on the day of the spin-off, as opposed to becoming captive to the interests of their future company.
- Establishing clear guiding principles and decision rights for the program at the beginning of the process. These will be critical to offset the potential blurring of governance roles with current organizational reporting relationships as the pace of difficult decisions increases.
- Creating a separation program organized around three distinct and parallel sets of activities—transaction, separation and design—and an acknowledgment that each requires different resources.
- Mobilizing and tracking the program around the hundreds of decisions that must be made to affect the separation and set both companies up for success, rather than using a traditional Gantt chart or task-based approach.
- Paying special attention to IT and to existing shared services. These typically are critical path elements, and it’s crucial to have dedicated people who know the organization well.
- Developing organization designs that meet two stringent requirements: aligning with the strategic intent of the newly independent companies, and being robust enough to function effectively on their own by day one while putting in place a plan to fit within the desired cost envelope needed for market competitiveness within one to two years of separation.
- Establishing clear communications and change management support to the organization at large.
- Managing readiness for both companies to operate successfully on day one across people, process and system dimensions. This demands a robust approach to readiness testing, which often requires that the critical organizational, process and system changes are practiced before separation.
Andy Pasternak is a partner with Bain & Company’s Chicago office, and Jim Wininger is a partner with Bain’s Atlanta office.



