Brief

At a Glance
- Many banks have become more ambitious with applying generative artificial intelligence (AI) to internal operations and customer interactions.
- A new Bain survey found that over 80% of respondents are planning to actively reshape their data architectures soon, anticipating the transformative potential of AI.
- But scaling up generative AI requires shaping a strong strategy, developing the right sequence of use cases, expanding data analytics talent, engineering the appropriate operating model, and adding the most suitable technology architecture.
- CIOs will have to adeptly manage cost, resources, and the bank’s risk profile, all while promoting innovation that will create value for customers and the bank.
Generative AI is starting to transform the banking sector, changing the landscape for traditional operations and allowing banks to deliver services in innovative ways. Given the potential of this technology, it is easy to imagine a future in which financial advisers spend up to 65% less time on mundane tasks and more time on enhancing customer relationships and driving revenue growth. By tapping more sources of unstructured data, the technology creates an opportunity to raise the quality of financial advice tailored to each individual customer.
Currently, some innovative marketing teams in banking and other industries generate personalized content at high speed, producing over a hundred ads in minutes. Coding assistants promise to raise productivity for certain tasks in IT, such as code documentation, by up to 50%. In corporate lending, initial estimates at frontrunner banks indicate process efficiencies of up to 40%. However, as with any new or evolved technology, success is not a given, and generative AI will be most effective within the larger context of business strategy and broader technology capabilities.
As use of the technology has spread, many banks have realized they need a more comprehensive posture than the current siloed proofs of concept. At the same time, the swelling wave of rollouts demands a sharper focus on managing the bank’s cost, resources, and risk profile, without crimping innovation that creates value for customers and the bank.
Mapping out a sequence of use cases, then scaling up
To be sure, generative AI will not solve all challenges by itself. The technology works best when orchestrated with other machine learning processes and systems, and it raises its own organizational, technological, regulatory, and ethical challenges. That’s why it is critical to draw up a use-case roadmap, including the capabilities shared across use cases and the bottlenecks that might emerge during development and rollout. Some banks that began their generative AI journeys by integrating the technology into lower-risk initiatives that still involve humans are now becoming more ambitious, implementing solutions with greater scale (see Figure 1). For instance, Morgan Stanley conducted a pilot phase of its AI@Morgan Stanley Assistant and subsequently rolled out the offering to financial advisers and support staff.
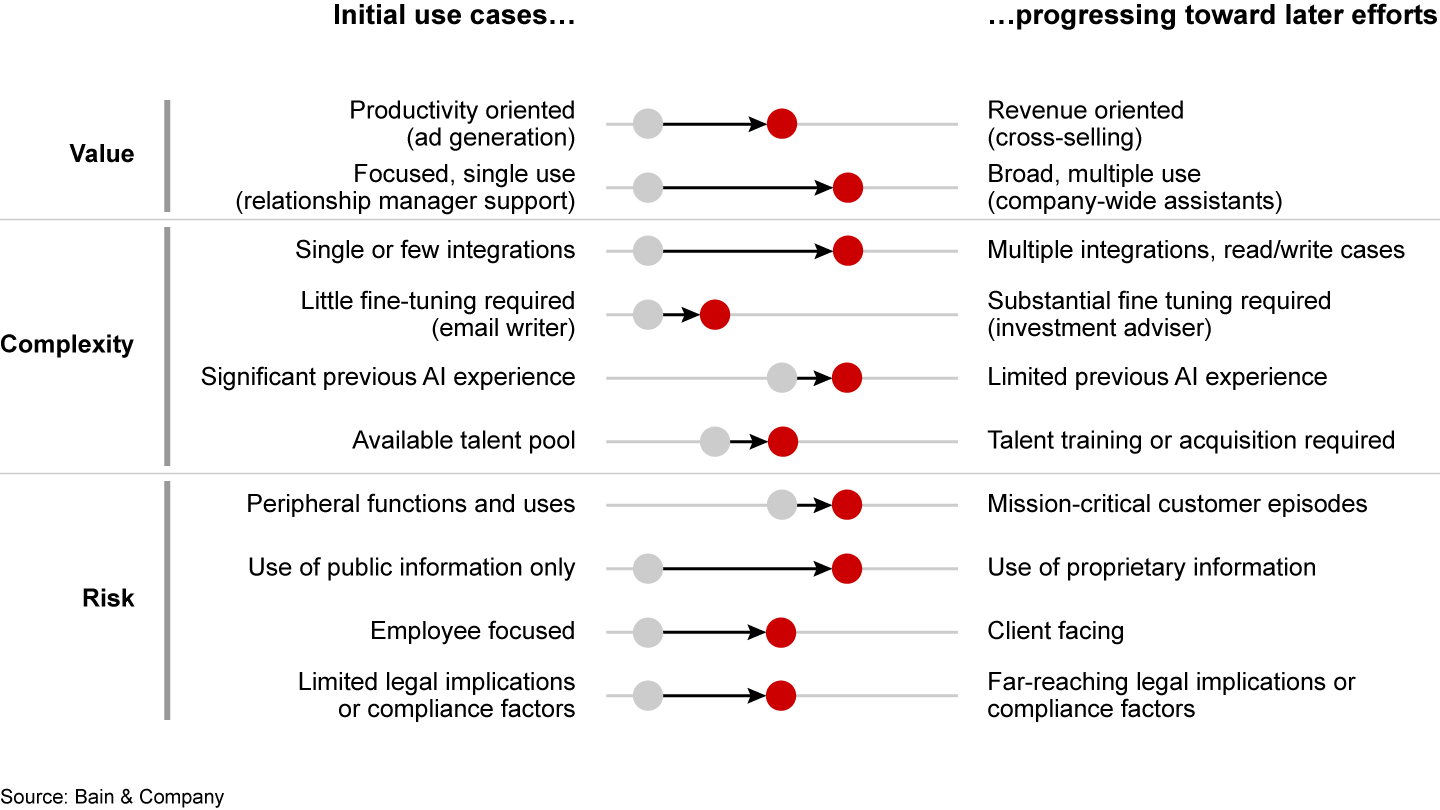

Deploying solutions at scale requires consideration of the supporting capabilities in such areas as user interfaces, data integrations, process design, and training. Selecting the sequence of use cases will depend not only on data-driven scenario planning around industry trends but also on customers’ priorities and behaviors.
Once the roadmap has been drawn up, the ability to deliver use cases through a streamlined and scalable approach typically relies on five steps, from the initial design to continuous monitoring and improvement (see Figure 2).
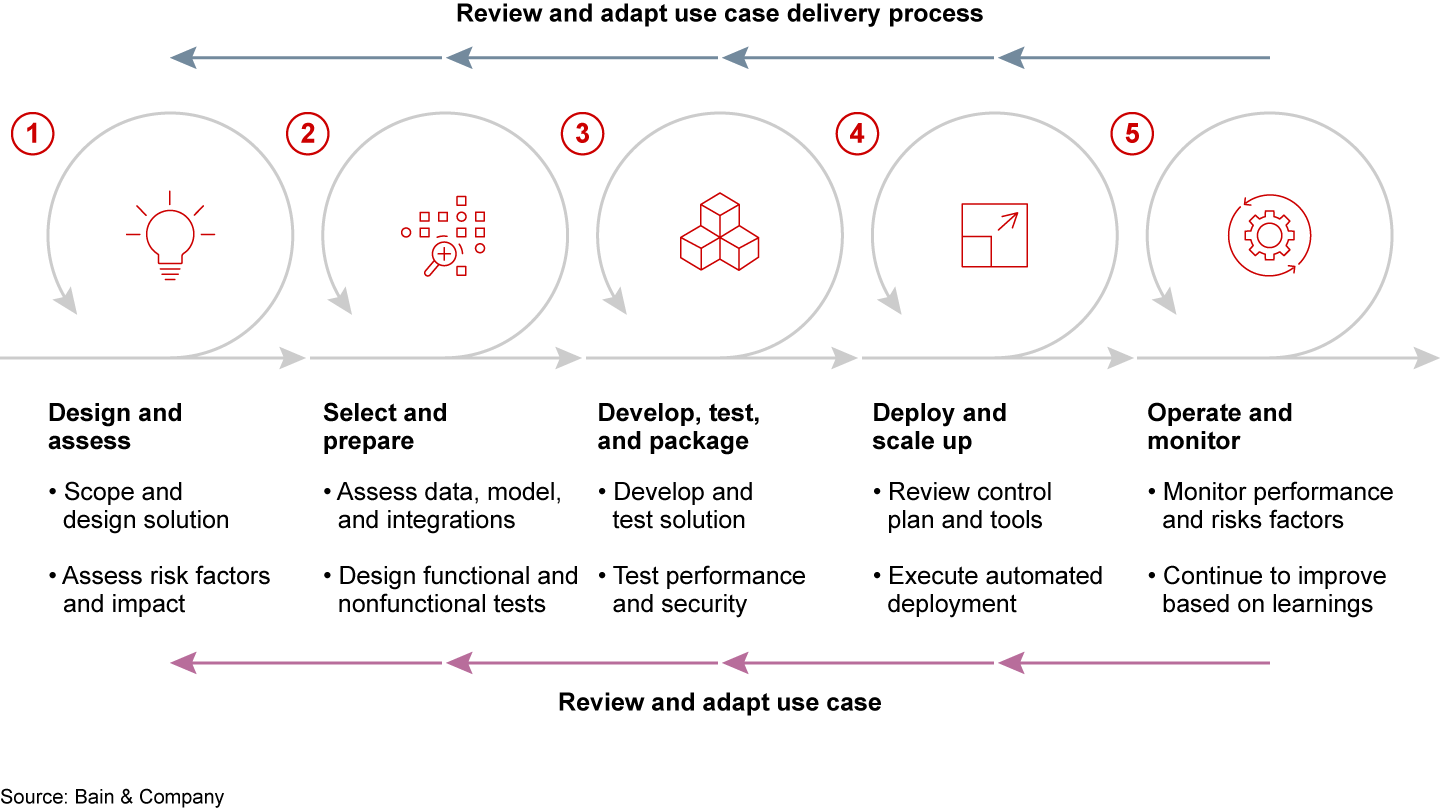

What’s required behind the scenes
Given how broadly generative AI may change both internal operations and customer-facing interactions, banks will need to develop a broad view of the underlying systems and data that enable the technology to make a difference. Most banks will not be laying the bricks and mortar of their AI foundations from the ground up, but rather will make incremental advances and upgrades that align with their ambitions. Let’s review each of the dimensions that will be affected.
Applications and systems. Early adoption of cloud-based systems and state-of-the-art application programming interfaces (APIs) provides a distinct advantage. Access to cloud-stored data offers an edge in deployment of generative AI solutions, in terms of both practical and regulatory aspects.
The global market value for generative AI technologies in banking and financial services institutions could increase from $20 billion in 2022 to more than $100 billion by 2032, according to Global Market Insights.
A growing number of vendors have incorporated generative AI functionality into their off-the-shelf solutions. Examples include tools for project managers and software developers, such as Atlassian, and customer experience products, such as those by Genesys. Major cloud service providers are also integrating generative AI into their offerings, featuring integrated development environments and office productivity software.
To be sure, generative AI will pose new challenges around managing requests, compute capacity, and token charges (which are based on the number of words). Banks will also have to build a service layer acting as an interface between large language models (LLMs) and generative AI-based applications. These will involve a significant investment, so it is vital to allocate funds strategically, which will require meticulous decision-making around whether to build, partner, or buy individual technology solutions.
Data architecture. The evolution of generative AI turns data into an even more remarkable and valuable asset. Unstructured data, both inside and outside the bank, can now be incorporated to yield valuable insights about customer behavior if banks manage the data effectively. One challenge is making sure that data, such as new product brochures and country or sector reports, moves quickly into a bank’s systems. Consequently, data architecture—the management of data from collection through transformation, distribution, and consumption—has risen to strategic prominence. More broadly, banks will need to invest in technology architecture to build common generative AI services. The architecture should allow a bank to monitor the cost and latency of the system, provide traceability for a query or conversation, moderate content, and help decide which foundation model to access for diverse use cases.
A recent Bain & Company survey of banks indicated that over 80% of respondents plan to upgrade their data architecture in the next three years. More than 40% of respondents seek to harness “data as a product” as the architectural paradigm. This stance stems from a desire to meet regulatory requirements related to data handling, and to expedite progress toward advanced analytics.
Banks that are advanced in data and analytics have leveraged data architecture as a primary means of creating value (see Figure 3). JPMorgan Chase, for instance, has adopted a two-pronged approach: defining data products, curated by those who understand the constraints and value of the data, and implementing a data mesh architecture. This aims to align data technology with data products, ultimately enhancing the enterprise data platform.
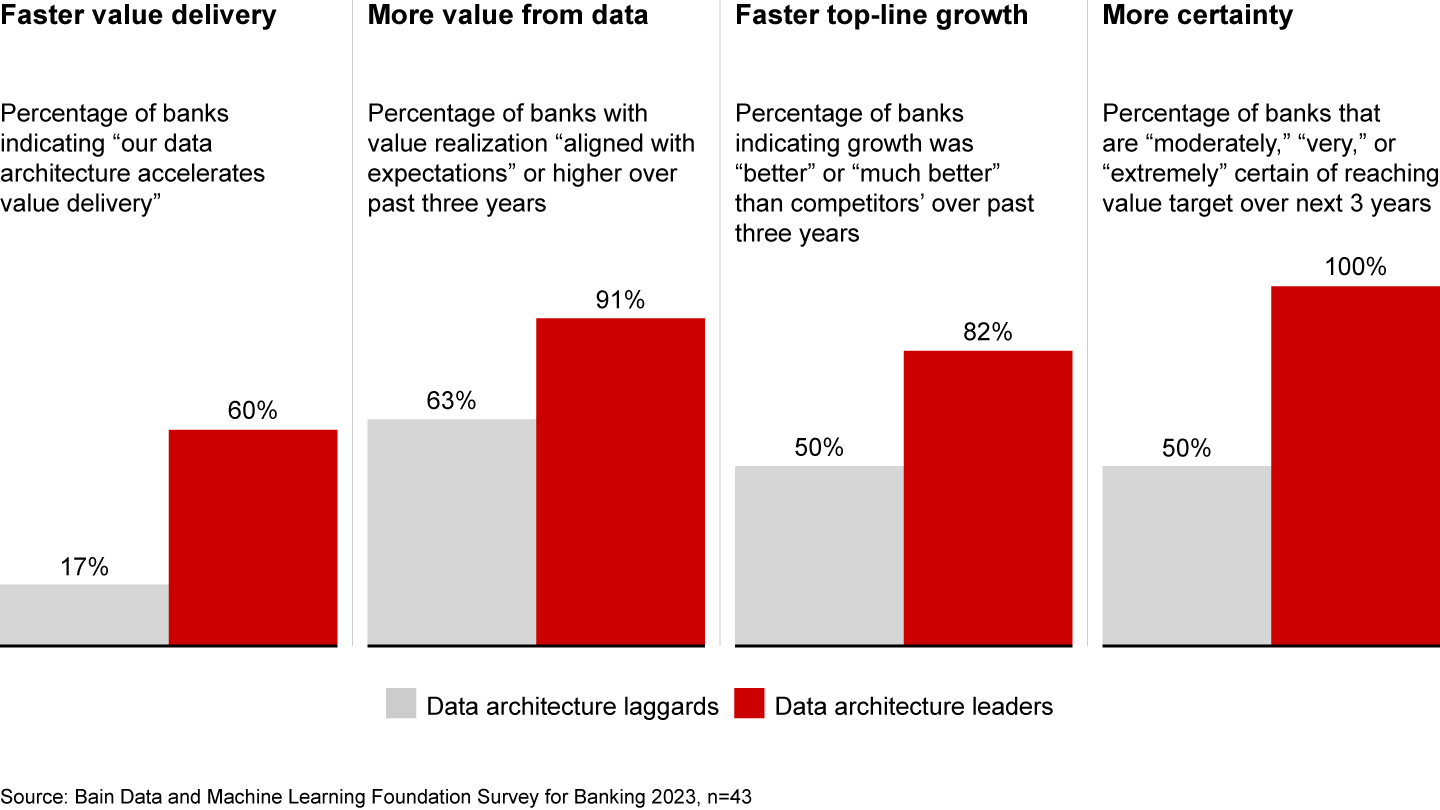

Upgrading data architecture is a complex endeavor, and numerous banks, such as Deutsche Bank, have formed partnerships with cloud service providers. Such partnerships acknowledge the symbiotic relationship between cloud transformation and data architecture.
Data privacy, security, and risk management. Generative AI has shifted the perception of age-old risks around data privacy and security, so it’s critical to develop a responsible AI strategy. How, for instance, should a bank identify and mitigate risks around “hallucination”—the tendency of some LLMs to generate content that appears factual but is, in fact, ungrounded?
Three elements come into play here: the democratization of AI tools, which can inadvertently lead to mishandling of data; the transition of data stored by or transmitted to third parties, particularly under software-as-a-service models; and the greater scrutiny caused by more use cases and data sources. We have begun to see corporate responses to the various risks posed by AI. For instance, leading banks including Citigroup and Goldman Sachs decided to ban the use of third-party chatbots for business purposes. Other banks have taken similar steps to comply with data regulation within their jurisdiction. BNP Paribas and Daiwa Securities Group have been developing proprietary chatbots for both internal and external users.
Banks that have had the greatest success with their AI implementations have addressed privacy and security challenges from inception, treating them as fundamental components of a “built-in compliance” policy, as opposed to dealing with them as afterthoughts.
Operating model and governance. The surge of generative AI calls for banks to revisit their operating model, especially to foster cross-functional collaboration and knowledge sharing across business units.
AI operating models can vary by the degree of centralization, particularly when prioritizing use cases and setting ethical standards (see Figure 4). Most banks are using a centralized model to kick-start generative AI, promote transparency, align on roles and priorities, and extract the most value from scarce resources. Later, they can shift to a hub-and-spoke model in which individual business units maintain ownership of specific use cases.
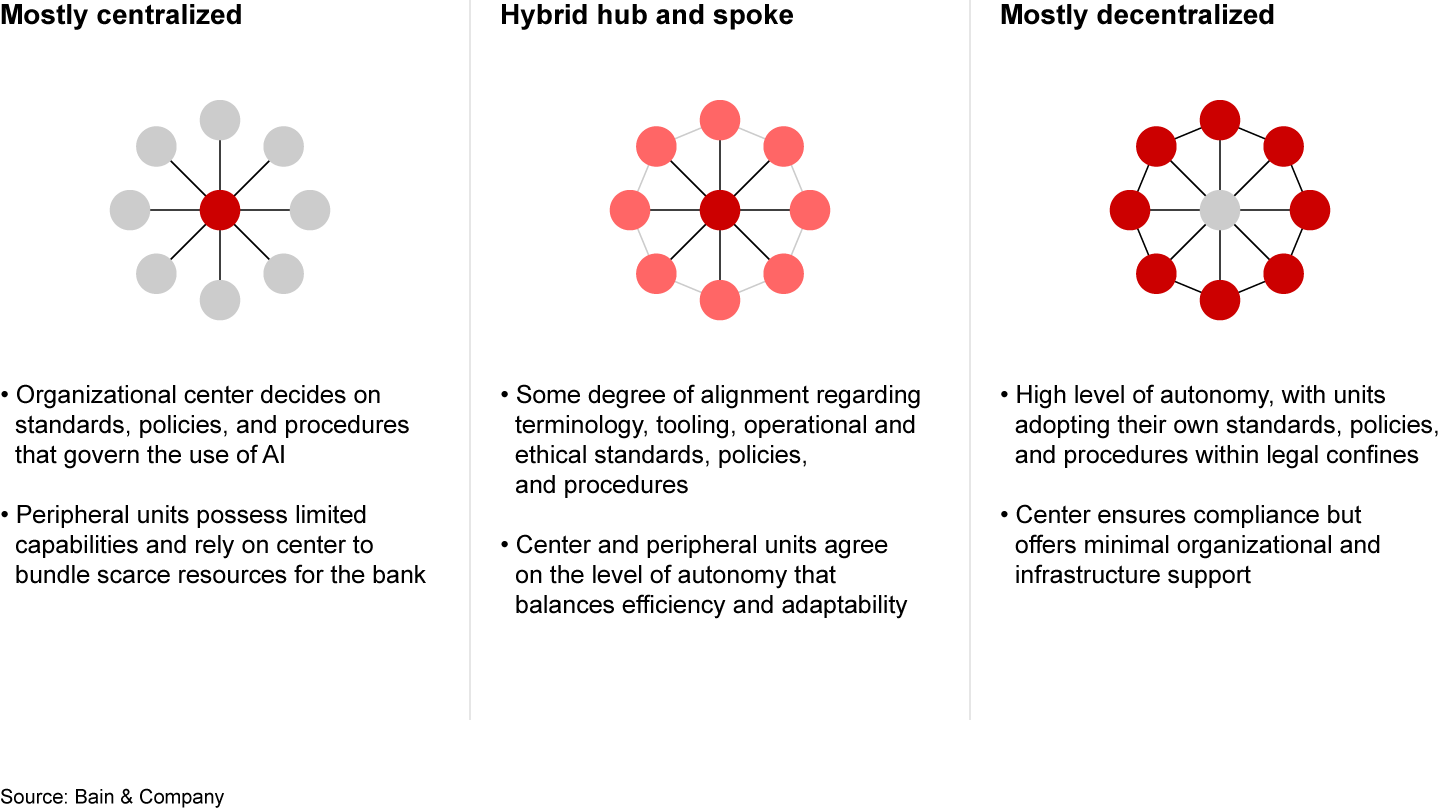

An effective operating model should enable a bank to capitalize on potential synergies through, for example, the joint development of reusable components or the consolidation of learnings across the organization. Ideally, the model promotes operational efficiency while fostering innovation and adaptability.
AI and ML operations. While proofs of concept might work initially, the widespread application of use cases requires enhancements consistent with a larger scale, echoing DevOps principles. Generative AI also introduces novel requirements, from API management to vector databases to application hosting. As a result, an ecosystem of vendors tailored to address specific elements of the tech stack enabling AI and machine learning (ML) operations is taking shape.
Policies and regulation. Regulatory bodies and policymakers are closely monitoring generative AI in banking with an eye to responsible, transparent use of data and analytics. Regulations in the European Union have evolved to address the risks associated with certain use cases, with the EU AI Act providing a framework for four risk-focused categories (see Figure 5).
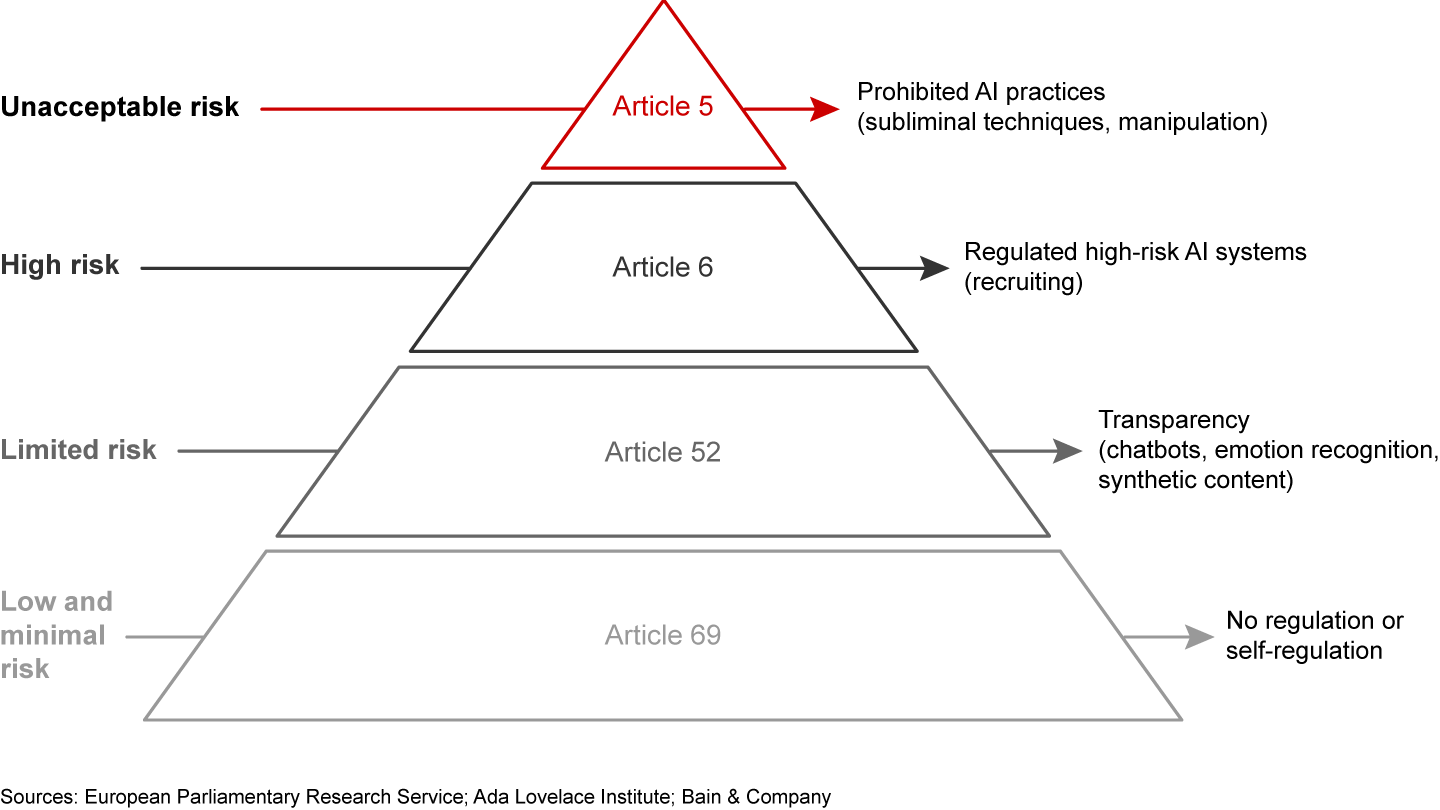

These regulations will likely influence related initiatives and practices globally. Multinational banks now find little room for regulatory arbitrage due to an equivalent increase in scrutiny from other regulatory bodies and intense international surveillance around AI usage. Greater scrutiny demands that banks align themselves with responsible AI practices.
Cost and resource management. The overall cost associated with implementing generative AI depends on the use case’s complexity—a factor that varies markedly from standard off-the-shelf initiatives to transformational endeavors.
Recurring costs constitute a greater proportion of the total outlay for simpler setups, whereas more complex deployments require substantial upfront investments that may dwarf ongoing expenditures. Irrespective of the exact use-case scenario, maintenance, including continued LLM API usage, accounts for a significant portion of the cost.
The size of the investment required and the potential of operating expenses to escalate rapidly, unless carefully controlled, raise the importance of cost control. Successfully navigating an AI transformation entails an evidence-based understanding of costs, along with assembling the capabilities to monitor, influence, and actively manage costs following rollout.
Data talent and culture. The expanding use of AI has raised demand for specialized abilities that extend beyond the standard repertoire of most data scientists and engineers. These include skills such as prompt engineering, management of vector databases, and command of a toolbox dedicated to AI and ML operations. A recent industry study found that current hiring trends suggest more than 30% of job ads by prominent European banks, including Barclays, ING, and NatWest, now encompass AI-related roles. Moreover, generative AI puts a greater premium on business domain knowledge.
Addressing the talent issue goes beyond merely employing AI specialists to identifying the groups that will be most affected by this shift and encouraging behavioral changes. Mobilizing change agents at all levels of the organization will help establish a “sponsorship spine” to promote behaviors aligned with the bank’s AI strategy.
With the uses and power of generative AI expanding exponentially, banks will want to master the technology soon if they hope to thrive, not just survive. To do that, a bank will, of course, need a detailed, coherent strategy that incorporates scenario planning and a deep understanding of retail and commercial customers’ priorities. A bank must also execute well, notably by delivering use cases that can be easily scaled up and encourage test-and-learn adjustments. The components to support such a process include specific applications as well as a deeper bench of data analytics talent.
There is no question that generative AI will disrupt many banking processes and how banks interact with their customers. However, if the technology is deployed in smart ways, it will allow banks to serve customers better while also improving their economics.