Report

This article is part of Bain's 2021 Technology Report.
In 2021, if we didn’t open an article about the technology supply chain by talking about the semiconductor chip shortage, you’d wonder why.
Technology executives are well aware that the shortage has made the already-pressing issue of increasing supply chain resiliency even more painfully acute. Indeed, technology companies have been dealing with increasingly disruptive supply chain shocks for years, so it was only a matter of time before one of this magnitude hit. While the breadth and depth of this shortage’s impact on the tech industry and the global economy is unprecedented, the reality is we’re going to see more of these disruptive events.
The hard lessons of the chip shortage have made it clear that navigating future disruptions calls for a more holistic and proactive strategy, one that requires closer collaboration between suppliers and their customers than in the past.
Lesson 1: Major supply chain disruptions don’t have quick fixes.
Despite massive investment announcements from semiconductor makers and pledges of government support, industry stakeholders have been struggling against a harsh reality: There are limited short-term solutions to the chip shortage (see Figure 1). It takes two to three years to build a new semiconductor factory, or fab. Most have been running at full production capacity since the third quarter of 2020, and even adding capacity to an existing fab can take more than a year. It’s also incredibly expensive. We estimate that adding just 5% to 10% capacity across existing nodes in the chip supply chain would cost about $40 billion.
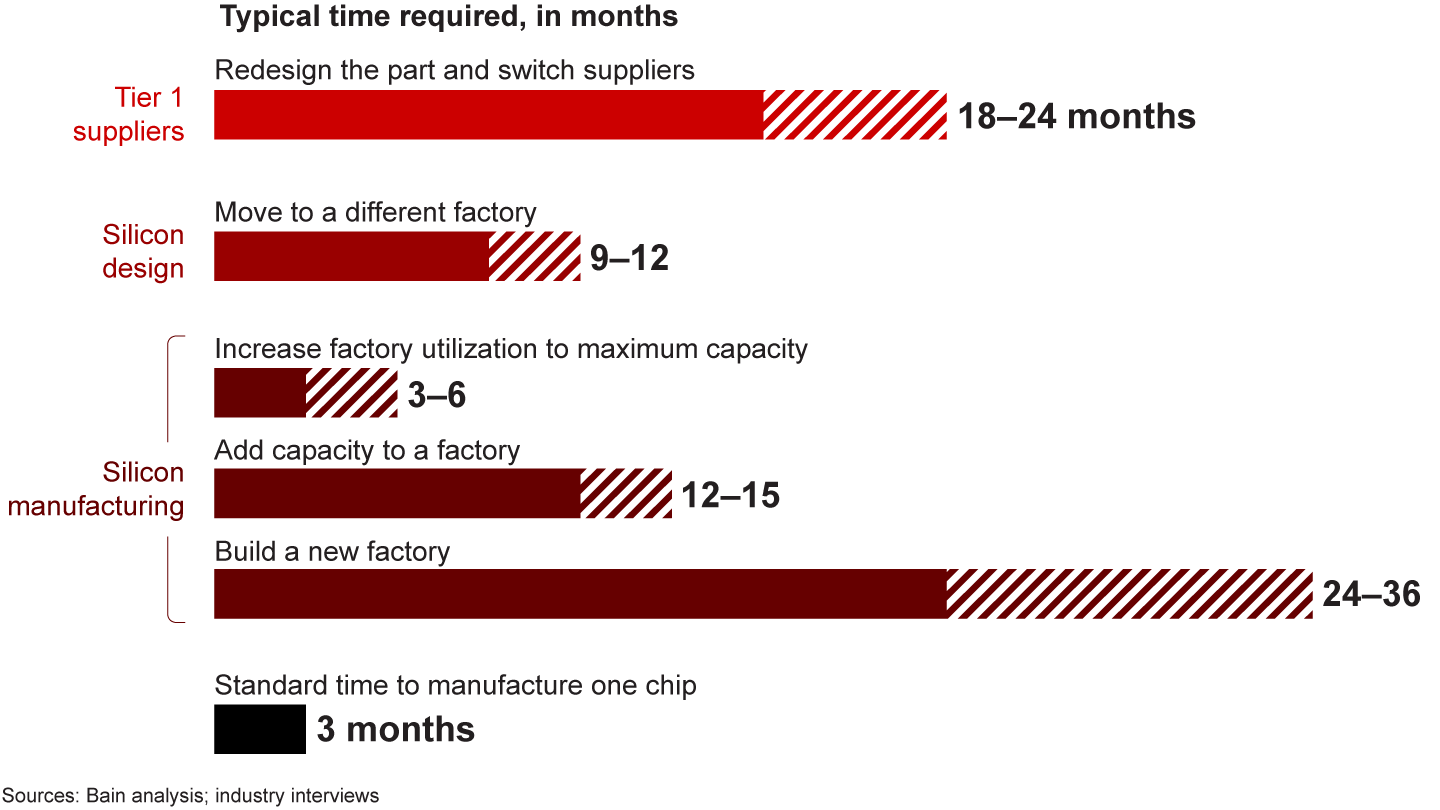

Although some of these dynamics are specific to front-end semiconductor manufacturing, the overarching principle holds for many steps of the tech supply chain. For example, the production of chip components such as substrates and silicon wafers faces similar lead times and disconnects between supply and demand. That’s dialing up the urgency for tech suppliers and their customers to prepare for the next big disruption.
Lesson 2: This is unlikely to be the last tech supply chain disruption that affects multiple industries, as more products across sectors rely on components that share the same manufacturing capacity.
Automotive was the canary in the coal mine. But the impact of the chip shortfall soon spread to other sectors, even hitting blue-chip tech companies such as Apple, Nintendo, and Cisco. The crisis disrupted even the best-prepared companies that had been investing in supply chain resiliency for years.
Why did the shortage spread? Most investments in semiconductor R&D and capital expenditures for new fabs go into the “bleeding-edge” technology needed to produce the advanced chips in smartphones, laptops, and servers. But "lagging-edge” chips have been the major pinch-point in the shortage. These chips, though based on technology developed more than a decade ago, play fundamental roles in automotive and industrial goods like cars and washing machines, as well as tech products such as laptops and smartphones (see Figure 2).
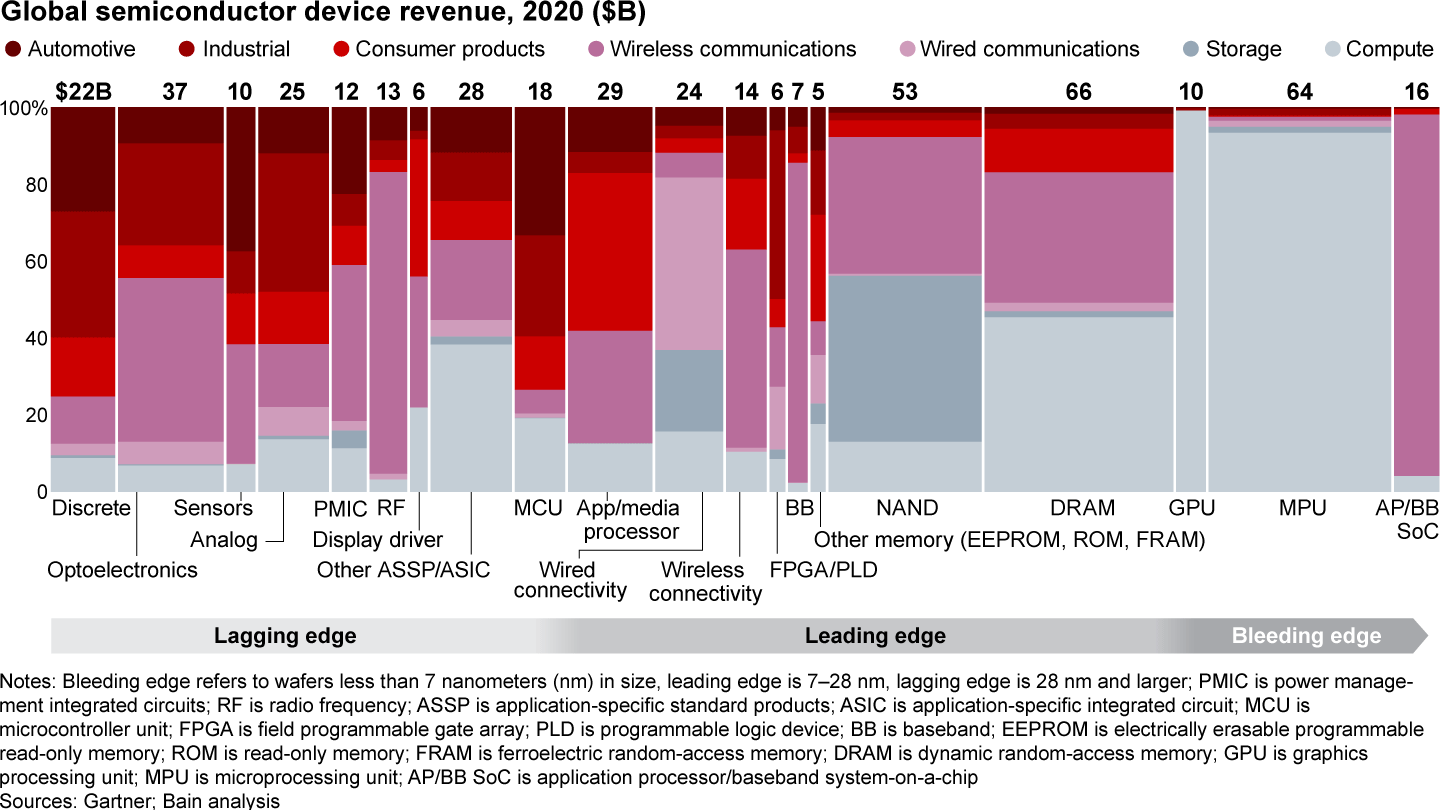

However, chip makers have had limited incentive to invest in additional production capacity for these less-advanced chips, which typically sell for a dollar or two apiece, compared with $100 or more for higher-end semiconductors. Unlike their bleeding-edge cousins, the fabs that produce lagging-edge chips tend to be older and fully depreciated, and have historically been run at full capacity for maximum efficiency. When demand spiked last year, lagging-edge fabs had no excess capacity to give.
Where might the next supply chain disruption hit? It’s possible that other components shared across industries could spark a similar event. For example, tech firms have been the largest consumers of lithium-ion batteries for years, but they’re quickly being overtaken by the automotive sector as it shifts to electric vehicles. In a battery shortage, tech vendors may find themselves the smaller, lower-priority customer losing access to a vital component.
Governments are already bracing for the possibility of a battery shortage. The European Union and India this year announced subsidies for domestic battery production, and the US has also signaled increased support for the sector.
A holistic strategy
As supply chain resilience has risen to the top of the CEO and board agenda, here are the investments leading companies are prioritizing.
- Developing a segmented strategy. Leading companies rank and prioritize components based on the probability of whether and how much they’ll be disrupted. Companies assess risk across several areas: lead time to add capacity; concentration of the supply base; geographic concentration (considering weather risk and geopolitical tensions); and multiple industries competing for supplies from the same producers.
- Instilling smart resilience. Companies are embedding more resilience in their supply chains through a custom blend of investments. They run numerous scenarios to pressure-test supply chain resilience and identify the relative return on investments in addressing weaknesses. The most effective strategies emphasize three capabilities:
-
- Adaptability. Companies are revising their component qualification process to emphasize standardization of hardware where possible. Electric vehicle maker Tesla uses standard semiconductor hardware, but is developing the software running on those chips in-house. That has given the company more flexibility in the components to manufacture its cars.
- Redundancy. For select areas, companies are building a supply buffer by buying up extra product inventory and, where possible, purchasing from multiple vendors.
- Real-time feedback. Leading companies build a real-time market monitoring system with a dynamic heat map of potential supply chain failure points. For example, BMW is working with Amazon Web Services to use machine learning and blockchain technology to improve supply chain visibility.
- Deploying a cross-functional operating model. Efforts to boost supply chain resilience can’t be confined to the supply chain team alone. The most effective approaches involve all key stakeholders, including supply chain planning, engineering, procurement, and sales. This can head off supply chain disruptions or shift customer demand toward products with larger inventory. More companies are looping the supply chain team into the product design phase to highlight potential risks and trade-offs. Germany-based automotive parts maker Continental established an advanced buying process increasing the purchasing department’s role in the engineering of parts. This streamlined component use and reduced the number of parts in Continental’s end products, thereby cutting costs and limiting the company’s exposure to supply chain shocks.
- Collaborating up and down the supply chain. Companies increasingly recognize that complex, specialized supply chains, like those involving semiconductors, require strong collaboration between customers and suppliers. What does this look like?
-
- More industrywide data sharing and negotiation for manufacturing capacity, both to improve transparency and avoid the bullwhip effect we saw with the chip shortage
- Integrated planning teams to jointly assess the market situation and develop aligned strategies
- Teaming up to appeal for government subsidies to locate manufacturing in home countries or diversify production capacity
The current chip shortage will pass eventually. The companies that act decisively now to build supply chain resilience will be best positioned to weather the next storm, wherever it comes from.