Management Tools
What Is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a human-centered, iterative approach to problem solving. It begins with immersion into an opportunity to understand a customer’s wants, needs, pain points, and preferences. From these insights, potential solutions are generated, tested, and refined. Common Design Thinking techniques such as sketching, prototyping, or digital simulations enable ideas to be quickly tested and improved with customers. A Design Thinking framework is ideal for solving ambiguous problems and developing breakthrough innovations through low-risk experimental learning.
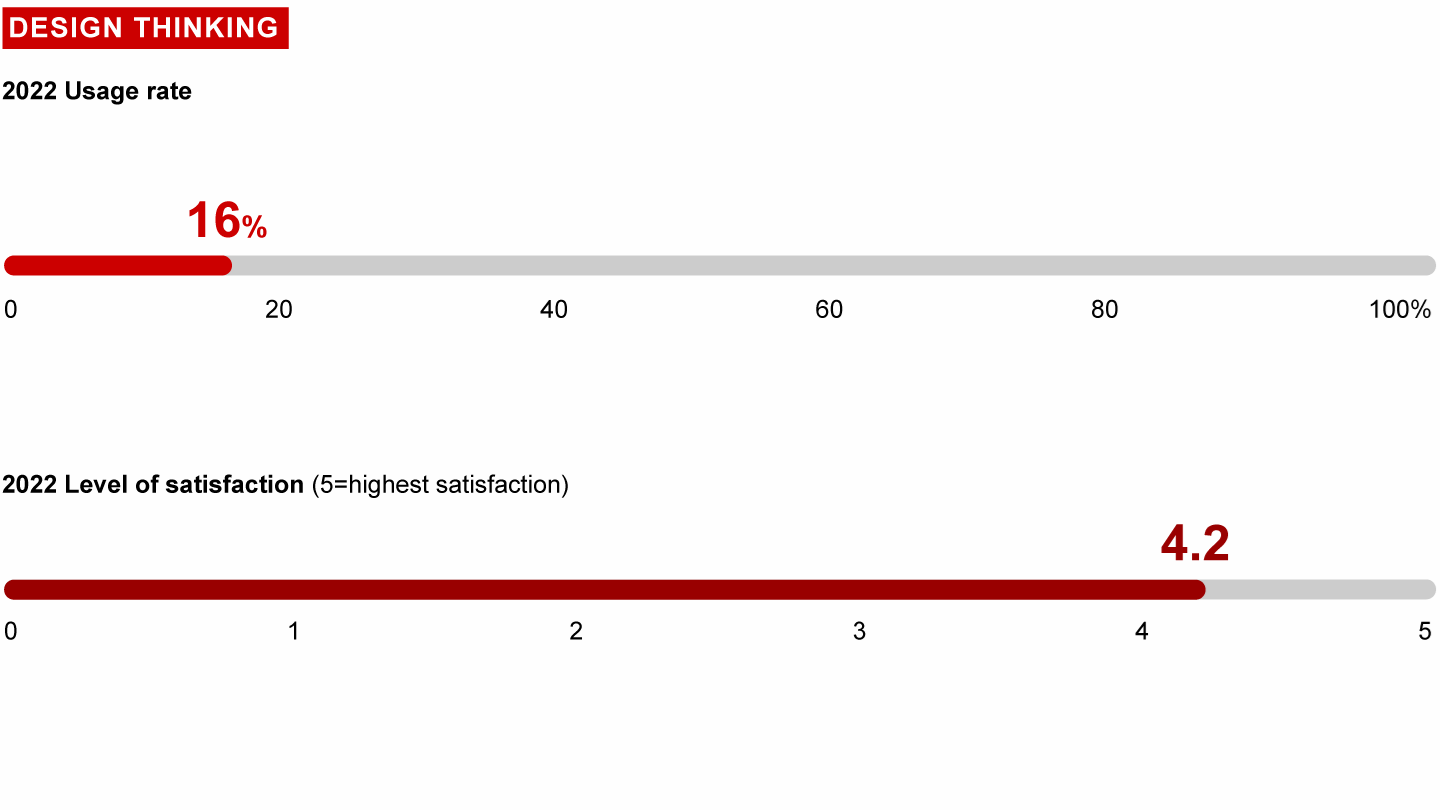
Usage and satisfaction among survey respondents

How Is Design Thinking Implemented?
A successful Design Thinking process requires teams to:
- Empathize—deeply immersing themselves in a problem by observing, interviewing, and engaging with users
- Define—synthesizing insights and defining the problem statement that will drive the remainder of the design process
- Ideate—employing techniques such as challenging assumptions, visualization, or storyboarding to generate multiple ideas
- Prototype—designing fast, low-cost methods to test hypotheses
- Test—testing with users, learning, and modifying solutions
Throughout the Design Thinking steps, the team shifts back and forth between divergent thinking (generating many options), and convergent thinking (prioritizing the highest-value opportunities). During the divergent phases (empathize, ideate, and prototype), the team is open minded, listening, exploring without limitations, and ideating without criticism. During convergent phases (define and test), the team is evaluating ideas based on user feedback and limitations on time, feasibility, cost, or other resources.
Design Thinking is not a linear process. The steps can be taken in almost any order and repeated as often as necessary.
Related Topics
What Are the Common Uses of Design Thinking?
Companies adopt Design Thinking methods to:
- Embrace a user-centered approach vs. a technology-led one
- Promote empathy for those impacted by a problem
- Reduce innovation risks by engaging closely with users throughout the development process to ensure product/market fit
- Visualize breakthrough solutions to problems
- Encourage testing and active learning
- Increase the speed of innovation
- Generate new product, service, and business process solutions

Management Tools & Trends 2023
On the 30th anniversary of our survey, managers seem surprisingly upbeat.