Rapport

This article introduces Bain's 2020 Global Corporate M&A Report. Explore our latest annual M&A report here.
Dear friends,
This is our second edition of the Global Corporate M&A Report. We were thrilled by the response to our perspectives last year on the world of corporate M&A. Thanks to the many of you who provided us with feedback that advanced the dialogue.
Our mission with this report remains the same: We aspire to use our unique position in the M&A world to connect what we see happening in our clients’ executive suites with the larger trends we are witnessing across the globe. The result, we hope, is to make all of us a little better at the craft of M&A.
Many executives adopted a recession footing in 2019, especially early in the year. Economic activity was volatile in 2019. This directly affected the level of M&A activity. M&A deal activity in Europe and Asia was way off in the first half of the year and then started to pick up. The US actually started off strong and then leveled off. Add it all up, and final global corporate M&A deal value for 2019 came in at $3.4 trillion, based on Dealogic data—not a weak year by any count.
Looking beyond the magnitude of deal activity, we see that some of the old norms governing M&A are evolving. Let’s highlight two in particular.
On the geopolitical front, the Brexit specter and trade wars significantly lowered the appetite for cross-regional deals. This was evident from the drop in deal values in and out of the UK, and in outbound deal values from the US and Asia.
On the social front, there was open angst regarding the effectiveness of capitalism itself and specifically the unchecked power of large technology firms. This angst is rapidly expanding M&A regulation. Regulators are increasingly scrutinizing deals for considerations such as access to personal data and the impact on national interest and security as well as the effect deals may have on future competition. This is a trend we will be watching carefully in 2020.
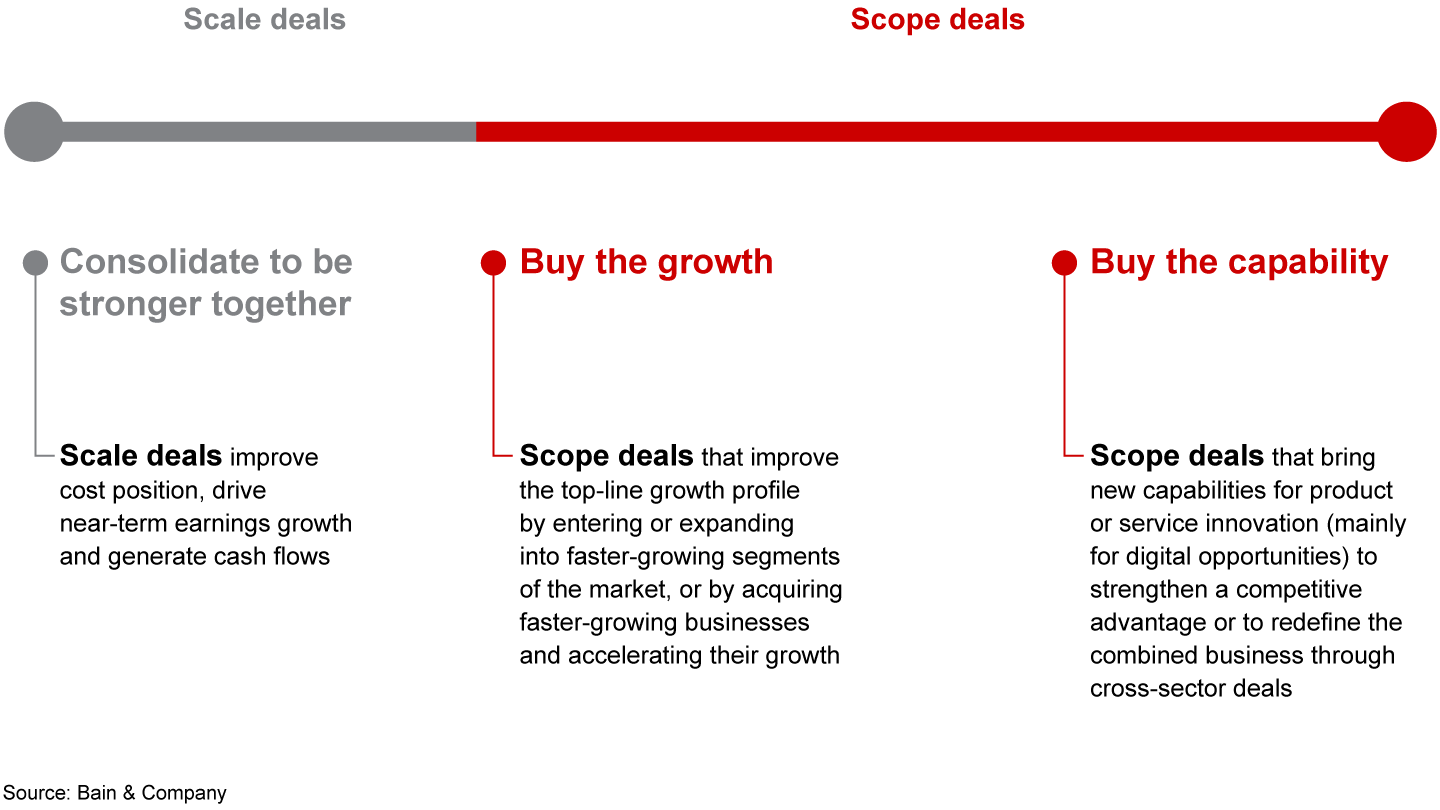
Beyond these macro trends, the shift from scale to scope deals, which we first highlighted in last year’s report, accelerated in 2019. Five years ago, the majority of large deals involved buying assets for scale, market power and getting to a lower cost position. After all, these were the proven routes to success.
Now we live in a world of business model disruption catalyzed by technological progress and the emergence of digital native competitors. Executive focus has substantially shifted to investing in future growth engines. It is no surprise that dealmaking has similarly evolved. Scope deals, which we define as deals intended to enter faster-growing segments or to acquire new capabilities for future growth, now comprise nearly 60% of all deals worth more than $1 billion in value. This is up from around 50% last year and 40% five years ago.
We were asked repeatedly after last year’s report: “Are scope deals successful?” We decided to pose this question to a group of nearly 250 senior executives. They were asked to rate their perception of success with scale and scope deals. The response? Scope deals are considered at least as successful as scale deals—and among scope deals, those aimed at acquiring new capabilities were rated as most successful.
That said, this finding comes with a caution. It is based on the respondents’ self-assessment, not backed by an analytical study or other tangible proof points. We are starting to see that some of these deals are successful, but we’re still in early days. In fact, in 2019, some scope deals got substantially larger than usual and started looking like one-off big bets. This is dangerous, for the history of large, big-bet acquisitions has often not been pretty.
We have been writing on the topic of success in M&A for more than two decades, and the bottom line is this: Companies that develop a repeatable capability for M&A through frequent acquisitions outperform all others.
Remarkably, frequent acquirers don’t only acquire the most, they also divest the most. Scope deals help companies expand into new growth segments and add new capabilities, scale deals help to build leadership positions, and divestitures release the time, talent, energy and capital that is locked up in nonstrategic businesses.
Experienced acquirers show us that doing scope deals, especially for technological capabilities, requires a different mindset and approach than those used for scale deals. In the second half of this report, we outline an approach to M&A capability building that is adapted for the changing times. A few things should and will feel different.
- A traditional target-screening approach within a defined industry boundary is barely adequate in today’s environment. The best acquirers are rapidly developing broader market-sensing capabilities to identify and track new technologies and new business models.
- We know that most deals fail in the beginning, at diligence, and this has not changed, even if the deal mix has. Many acquirers are improving the odds through earlier cross-functional team involvement, longer diligence horizons and more robust relationship building to really understand the people, culture and talent. After all, that’s where the value often is.
- We are seeing a real interest in acquiring new capabilities, whether digital or otherwise, to strengthen the existing business or for innovation. Clearly, traditional scale integration playbooks won’t help to capture the value in capability deals. In a major departure from traditional approaches, successful acquirers are leading with joint value-creation plans, not functional integration.
- Finally, there is no way to invest in new growth engines without divesting businesses that no longer fit the future strategic agenda, but there is also no reason to lose value in the process. The best companies divest without needless delay, and they prepare ahead of time to get their fair share of value.
Will we experience a recession over the next couple of years? Whether or not we do, the most successful companies will take advantage of any opportunity to strengthen their structural positioning in the market through preplanned M&A and divestiture action.
We hope you enjoy reading the rest of this report. As always, please feel free to reach out to us to share your views and advance the dialogue.
Sincerely,
The Bain Global M&A team
This article is part of Bain’s 2020 Global Corporate M&A Report. Explore the contents of the report here or download the PDF to read the full report.
-
About the methodology (Click to expand)
About deal classification—scale and scope deals
To understand the nature of M&A activity, we first identified the top 250 strategic deals of each year (top 165 strategic deals for 2019 year-to-date until September, since the analysis was concluded in October). From the initial list of deals with deal values greater than $1 billion, as reported by Dealogic, we excluded nonstrategic deals. These include asset or property acquisitions, financial investments, internal reorganizations, and minority stake acquisitions.
We then classified the strategic deals into scale or scope deals based on a proprietary framework applied consistently across the years. The proprietary framework uses the stated strategic rationale by the acquirer at the time of announcement to identify the key elements of the deal thesis. Based on these elements, the deals were categorized as scale or scope deals.
Scale deals are intended to strengthen market leadership and lower cost position through the benefits of scale, such as cost synergies. Scope deals are intended to accelerate top-line growth by entering or expanding in faster-growing market segments or bringing in new capabilities. In reality, some deals are a blend of both scale and scope; however, the vast majority lean toward one or the other (see chart).
About the M&A and Divestitures senior executive survey, 2019
In partnership with the Gerson Lehrman Group, we conducted a survey of 247 senior executives on the topic of corporate M&A and divestitures. The survey ran throughout July 2019 in the US, UK, Germany, France, China, Australia and Japan. Survey participants belonged to companies with greater than $500 million in annual revenue and held senior executive roles in the capacity of CEO, CFO or head of strategy/business development/M&A.
The survey covered the topics of portfolio management best practices, divestiture decision making and keys to success as well as M&A success drivers for scale and scope deals.
-
Acknowledgments (Click to expand)
This report was prepared by Les Baird, who leads Bain & Company’s Global M&A and Divestitures practice; David Harding, an advisory partner with Bain based in the Boston office; Andrei Vorobyov, a Bain partner in the Copenhagen office; and a team led by Shikha Dhar, a practice manager with Bain’s M&A and Divestitures practice.
The authors thank Dale Stafford, Peter Horsley, Phil Leung, Arnaud Leroi, Jim Wininger and Suzanne Kumar for their contributions. They are also grateful to Josef Ming, Lars Dingemann and Bhavya Nand Kishore for their perspectives on corporate strategy and portfolio management; Alexander Dahlke for his perspectives on M&A strategy and regulatory trends; Simon Heap, Jay Bhatnagar and Daan van Ginneken for their perspectives on new approaches in M&A strategy and screening; Dalton Maine, Adam Haller and Mark Capeless for their perspectives on capability deal integrations; Martin Holzapfel, Magnus Konberg, Henrik Bergh, Markus Illukka and Daphné Vattier for their contributions on emerging due diligence approaches; Jorge Rujana for his thoughts on divestitures; Oron Amsalem, Saskia Versteeg and a team led by Garima Aggarwal at the Bain Capability Network for their analytic support; Mateusz Kaminski, Jan Trawinski, Mateusz Firlej, and Emily Lane for their research assistance; and David Diamond for his editorial support.
