Report

Executive summary
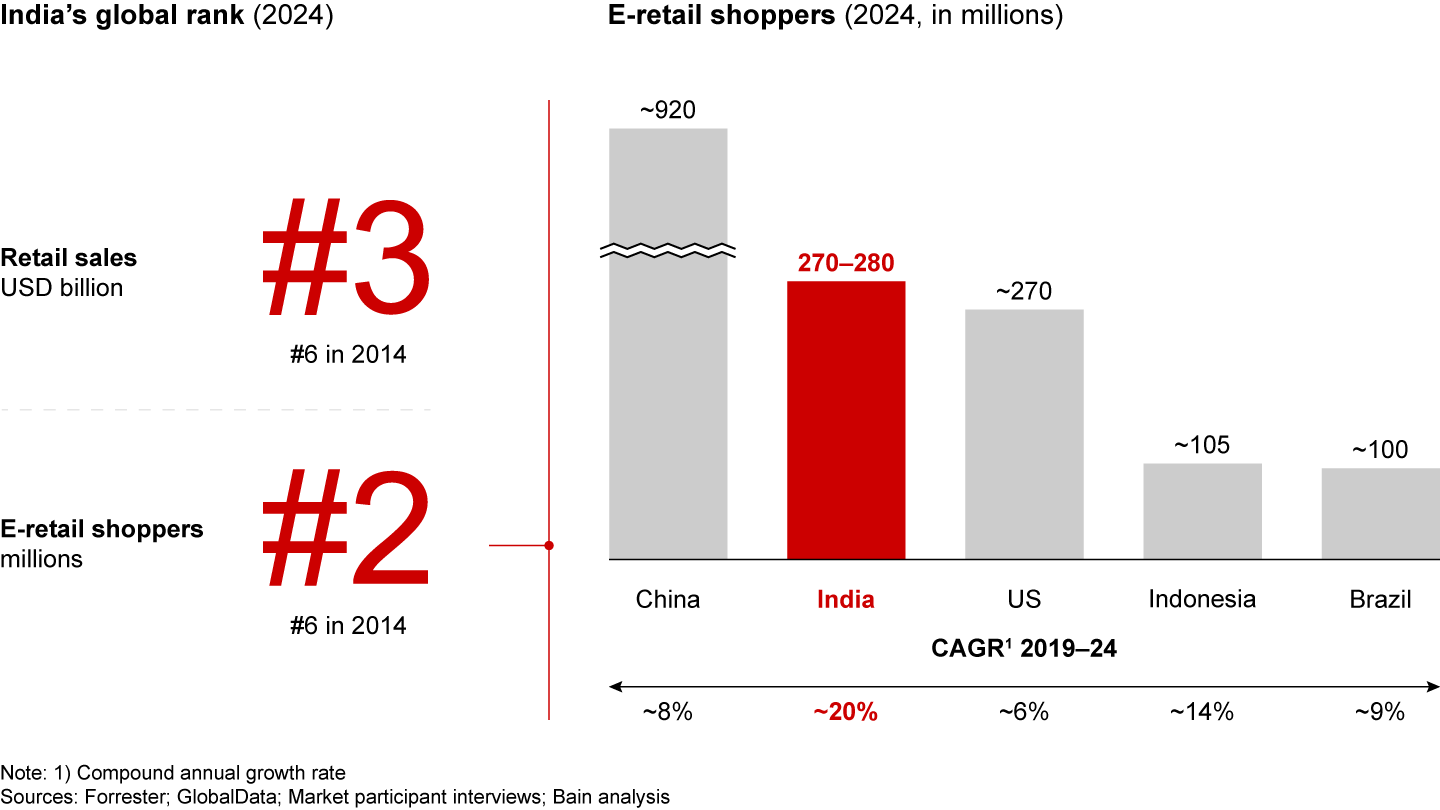
India has become a retail powerhouse over the last decade, ascending to the third largest retail market globally in 2024. The Indian e-retail market has surged to approximately $60 billion in gross merchandise value (GMV), boasting the world’s second-largest online shopper base.
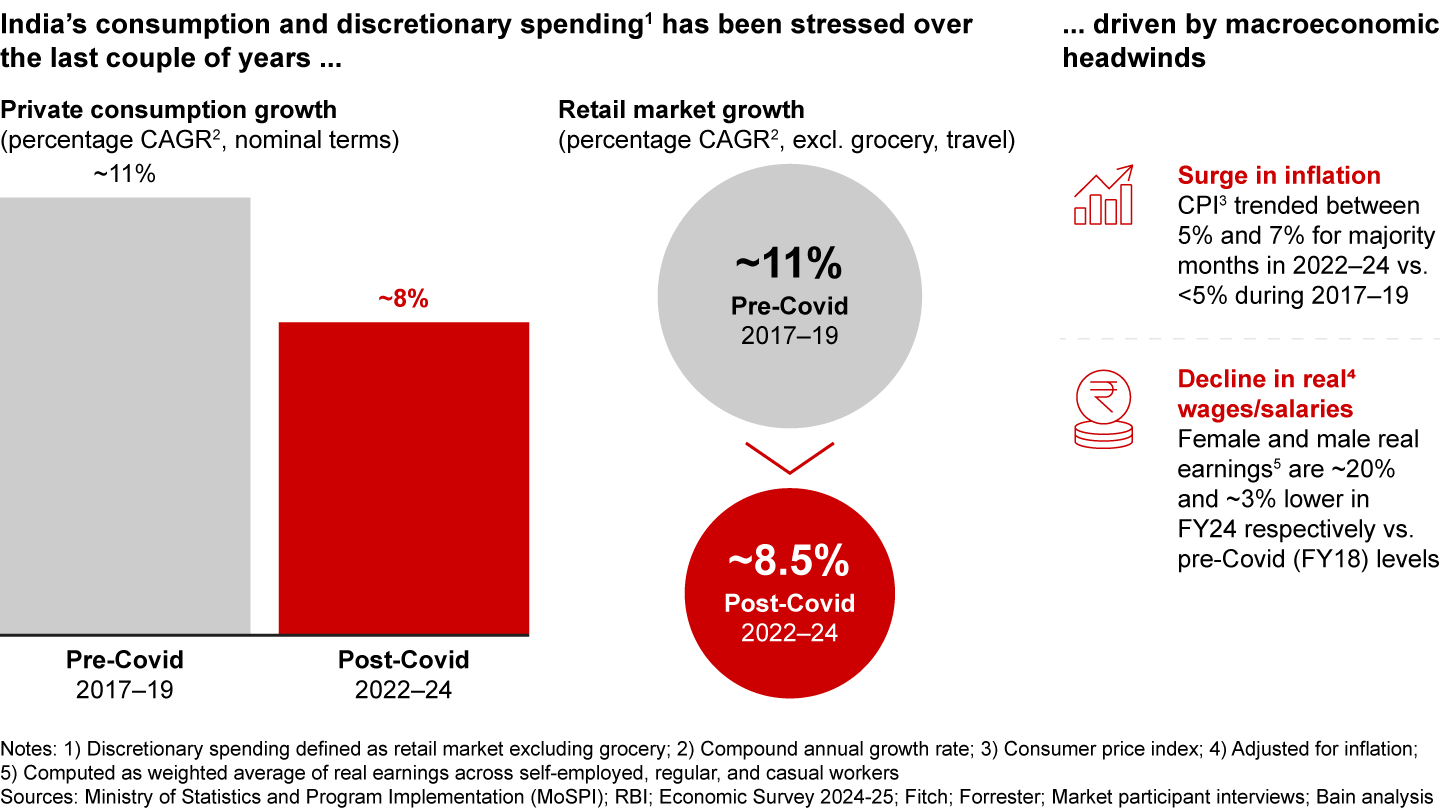
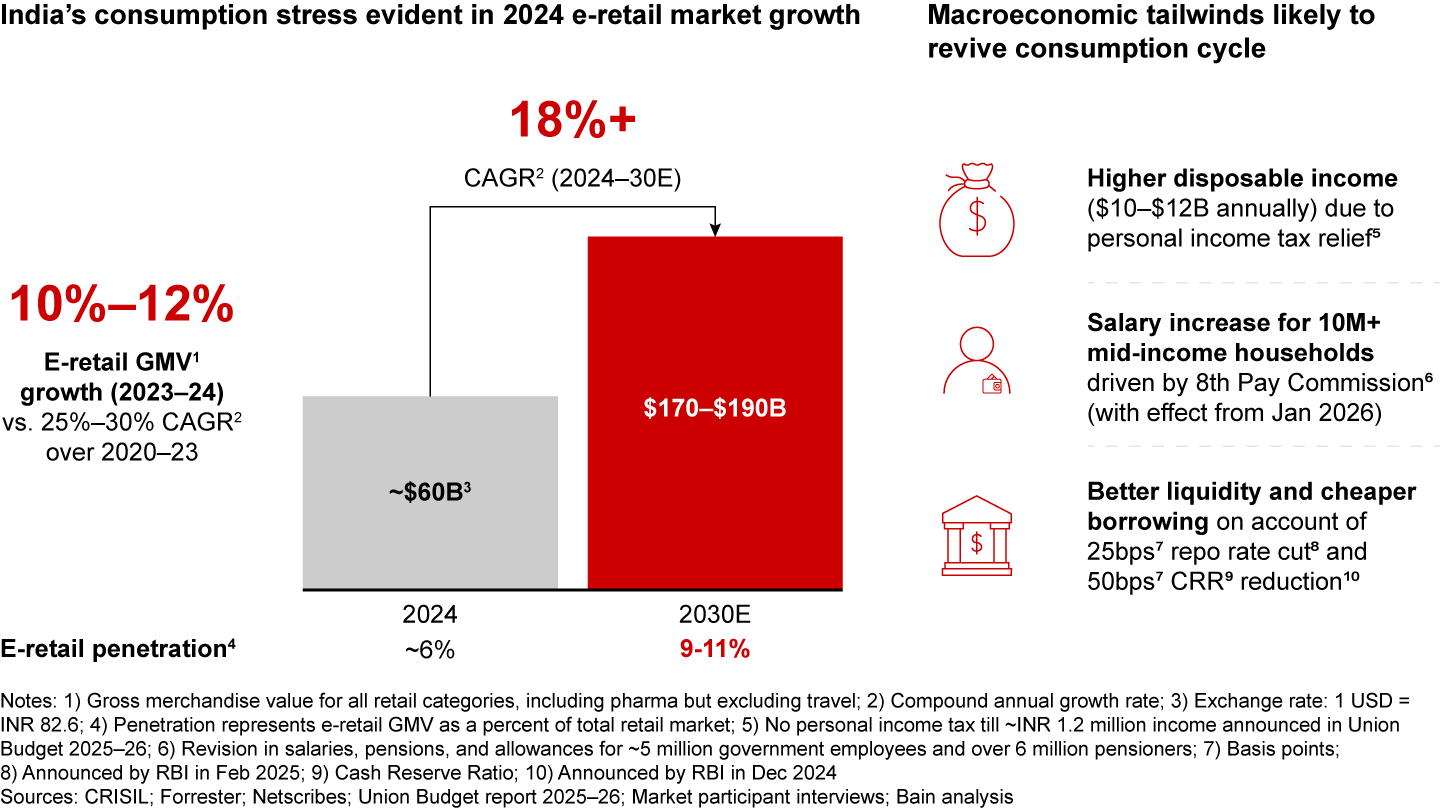
India’s consumption and discretionary spending have faced headwinds in recent years, with private consumption growth slowing from 11% pre-Covid (2017–19) to ~8% post-Covid (2022–24). This decline is driven by higher inflation and a stagnation of real wages. The stress in consumption is evident in e-retail growth in 2024 being 10%–12%, compared to historical growth rates of over 20%.
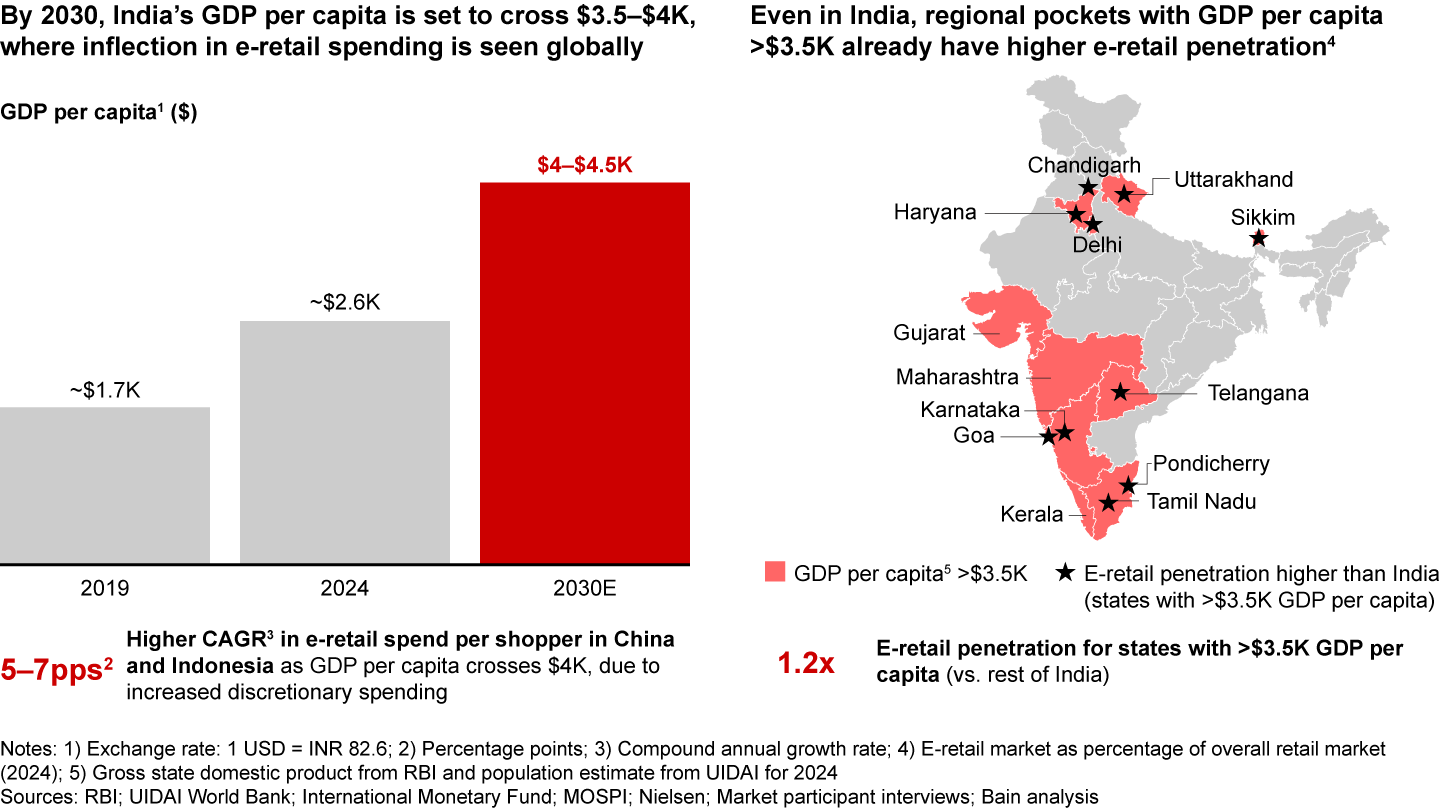
However, the recent fiscal and monetary policy interventions are expected to drive a rebound in e-retail growth, especially from the festive period of 2025, on account of revival in the consumption cycle. Long-term market fundamentals remain robust, with e-retail projected to exceed 18% growth over the next six years, reaching an estimated $170–$190 billion in GMV, with nearly 1 in 10 retail dollars spent on e-retail by 2030. This growth will be fueled by increased discretionary spending as India’s per capita GDP surpasses $3,500–$4,000—a crucial tipping point unlocking discretionary and e-retail spending globally. States in India with per capita GDP above $3,500 already exhibit 1.2 times higher e-retail penetration than other regions.
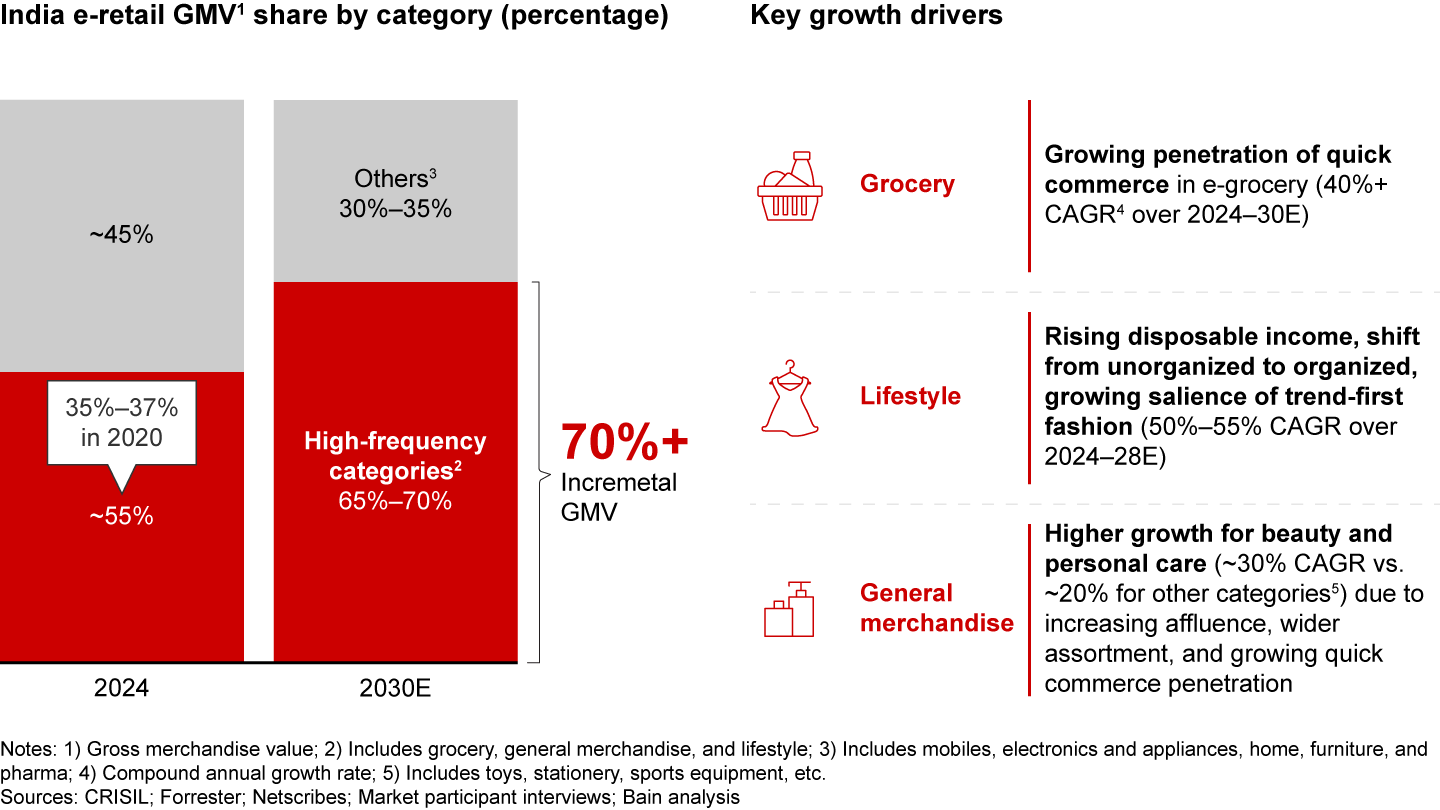
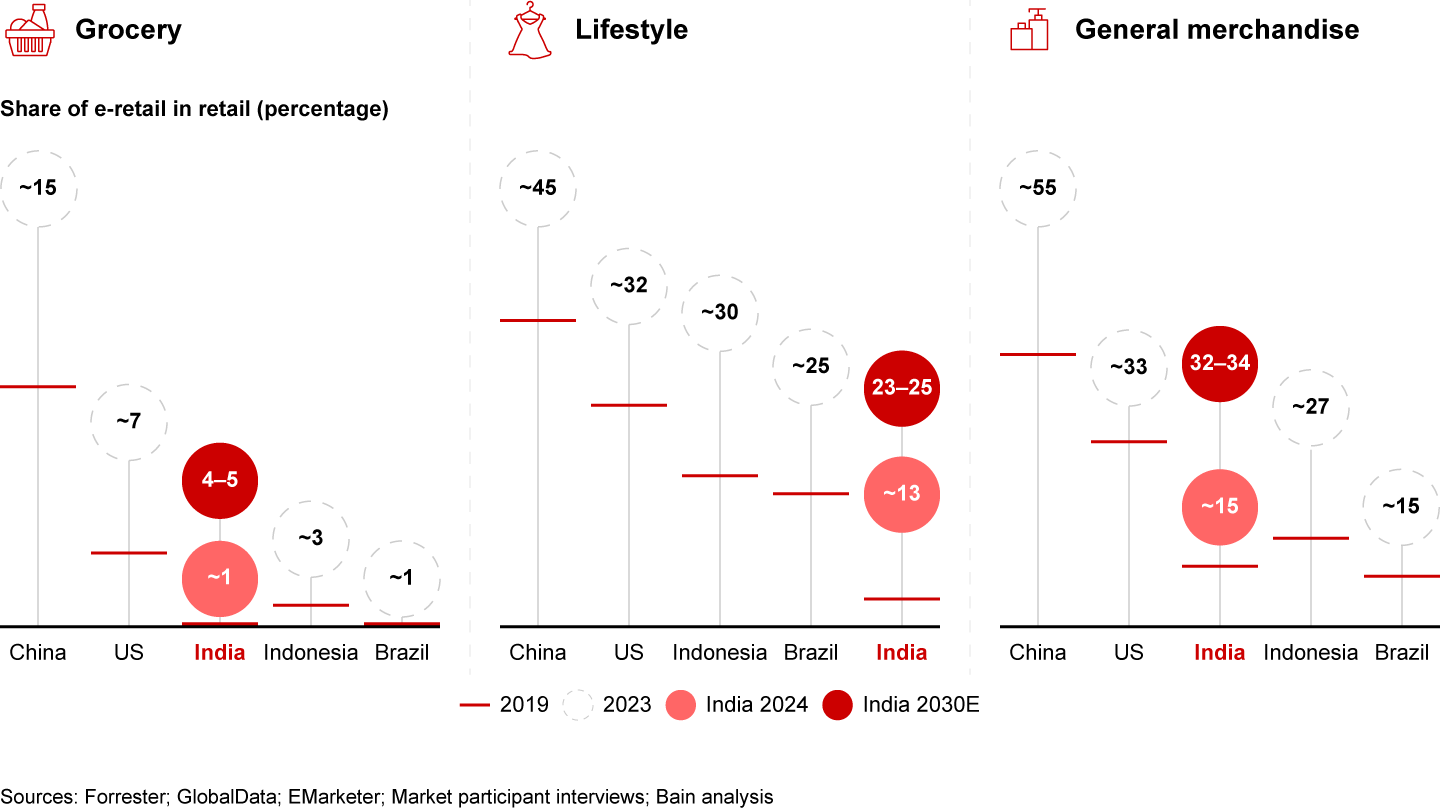
High-frequency categories such as grocery, lifestyle, and general merchandise will drive e-retail growth, accounting for two out of every three dollars spent on e-retail by 2030. These categories are set to see a two- to fourfold increase in e-retail penetration over this period.
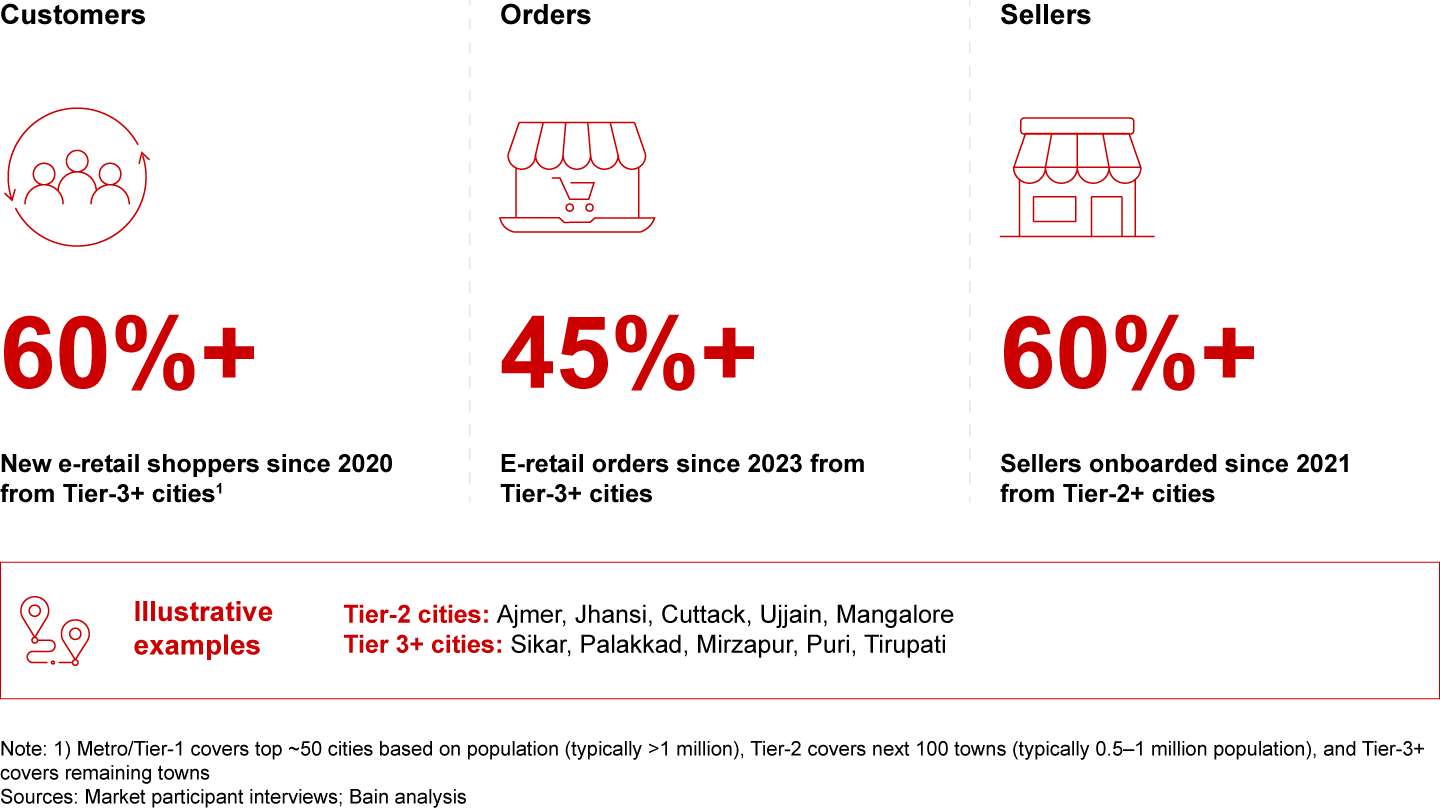
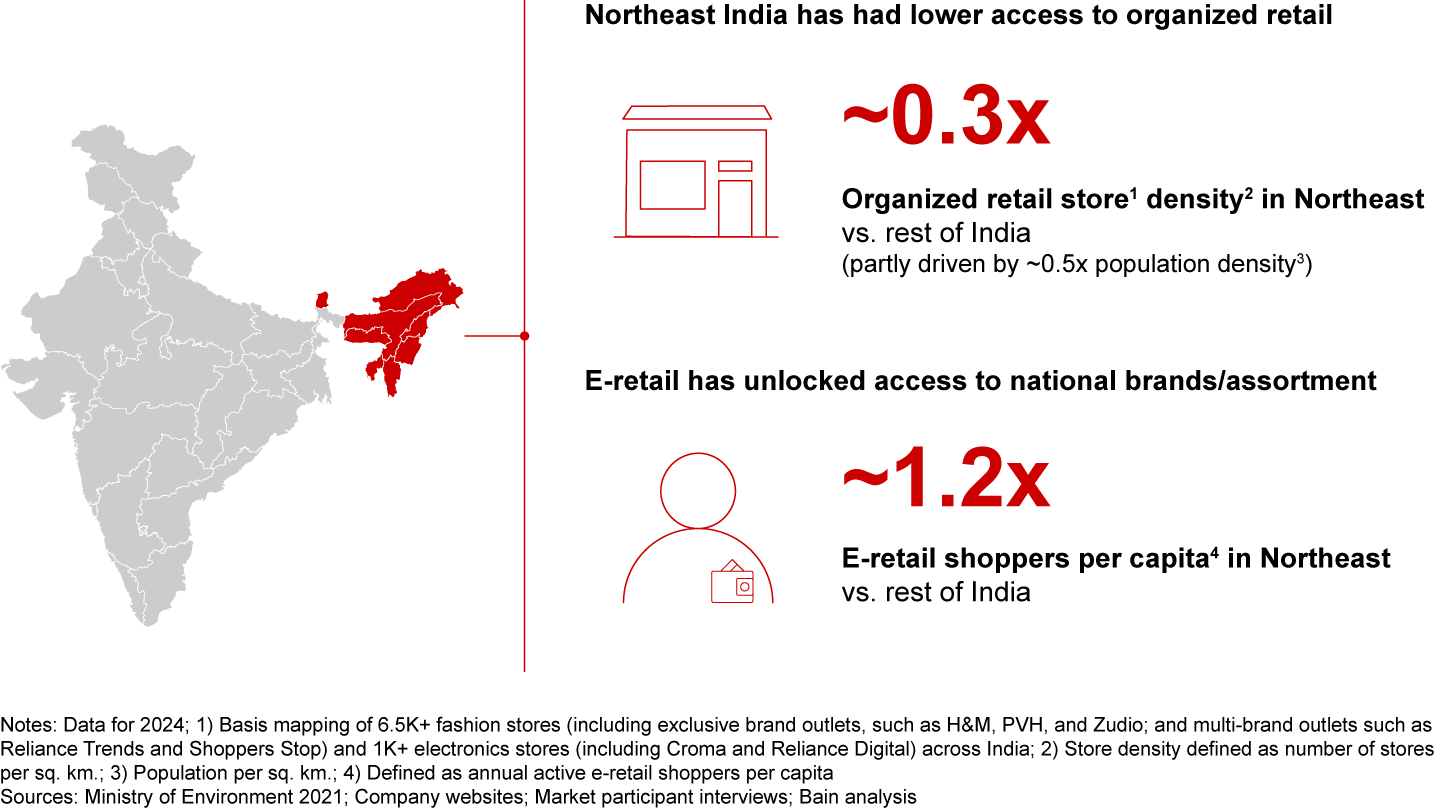
Growth will continue to reshape India’s shopping landscape. User adoption is already spreading from Tier-2 to Tier-3 cities, with three in five new shoppers since 2020 coming from cities designated Tier-3 or smaller. This growth is unlocking access for consumers in remote, brand-starved areas, as evidenced by the 1.2 times higher e-retail shopper penetration in the Northeast compared to the rest of India. The seller base is also diversifying, with 60% of new sellers since 2021 hailing from Tier-2 or smaller cities.
Written in collaboration with
Written in collaboration with

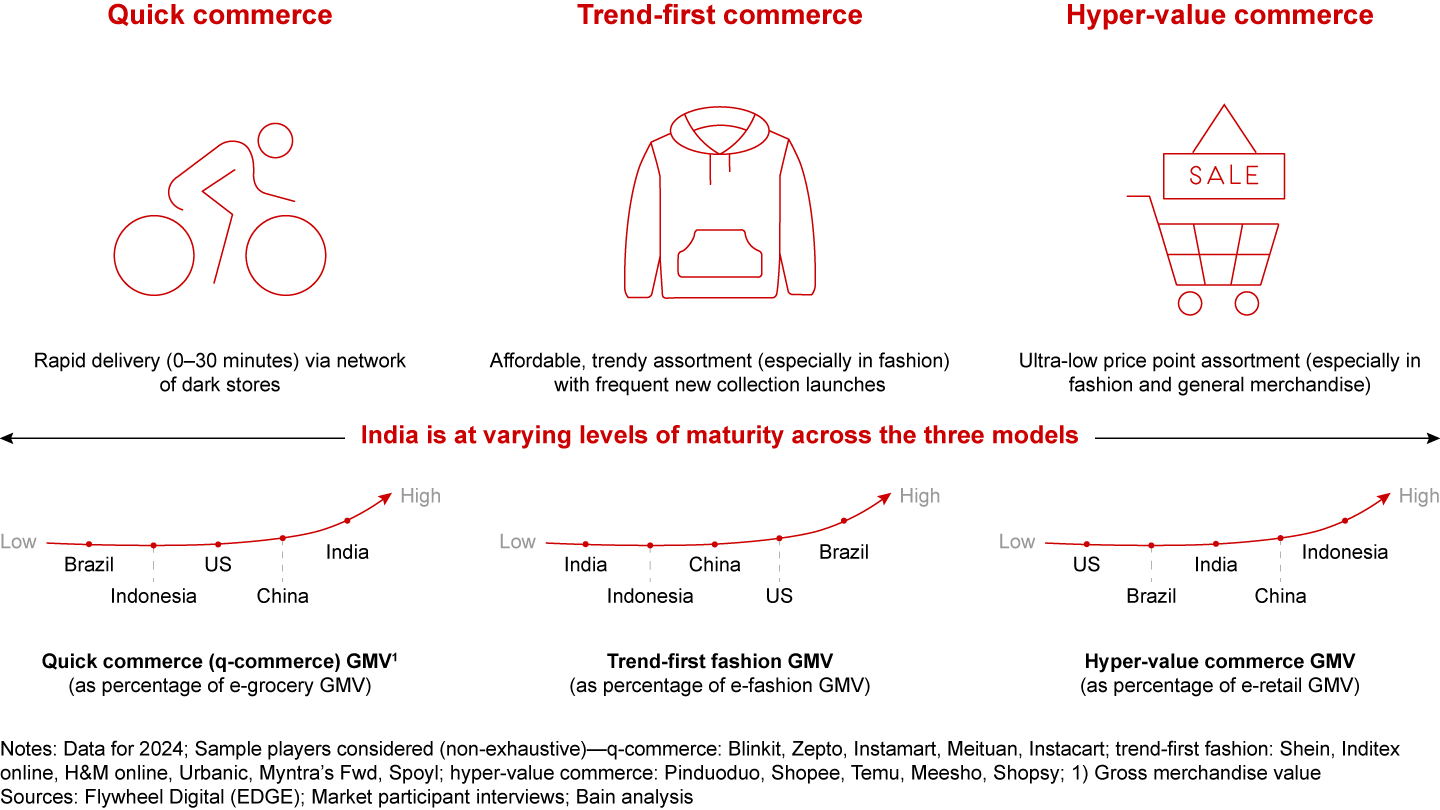
Three disruptions—quick commerce, trend-first commerce (especially in fashion), and hyper-value commerce—will define the next chapter of growth. Each of these models is at a different level of maturity. Together, their evolution will shape the future of India’s e-retail landscape.
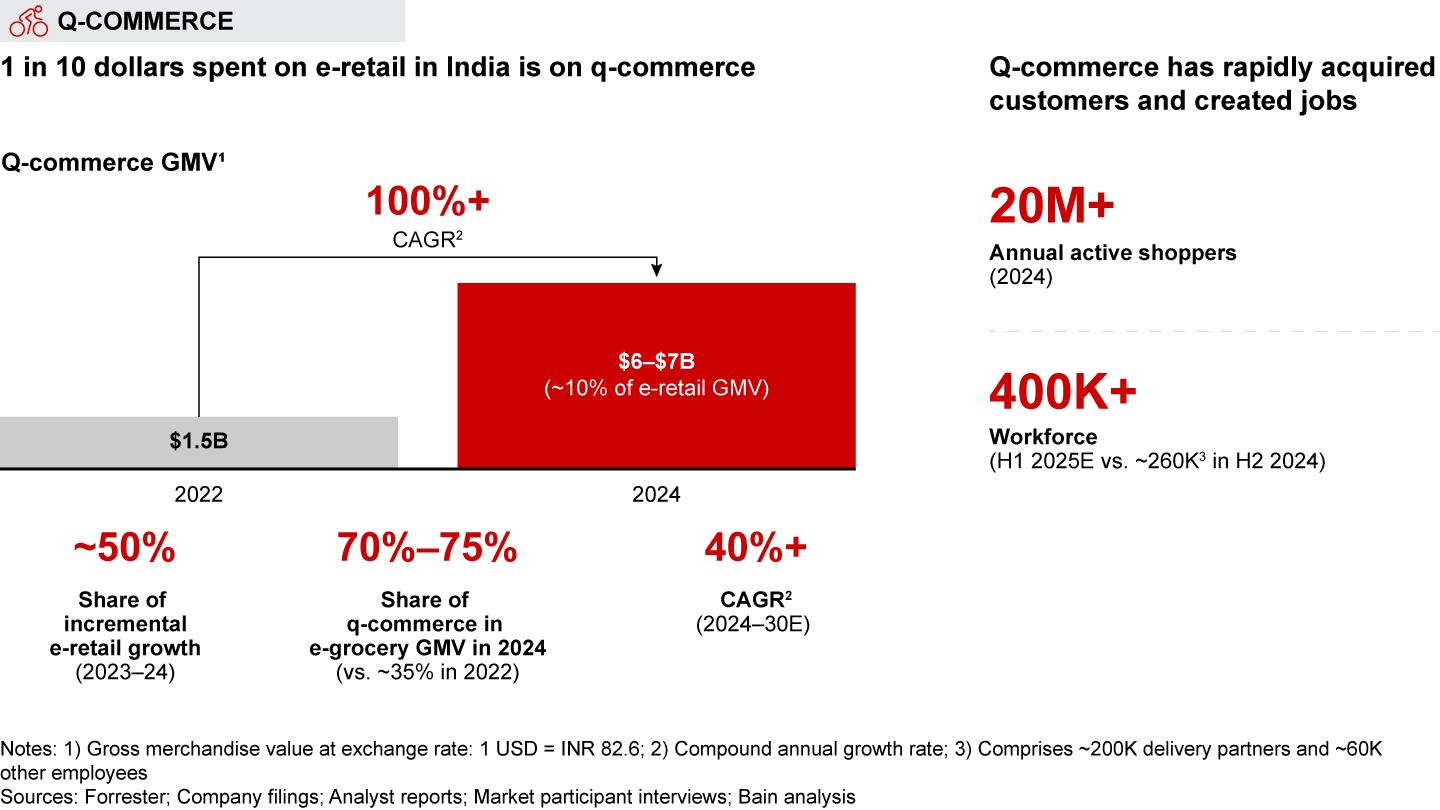
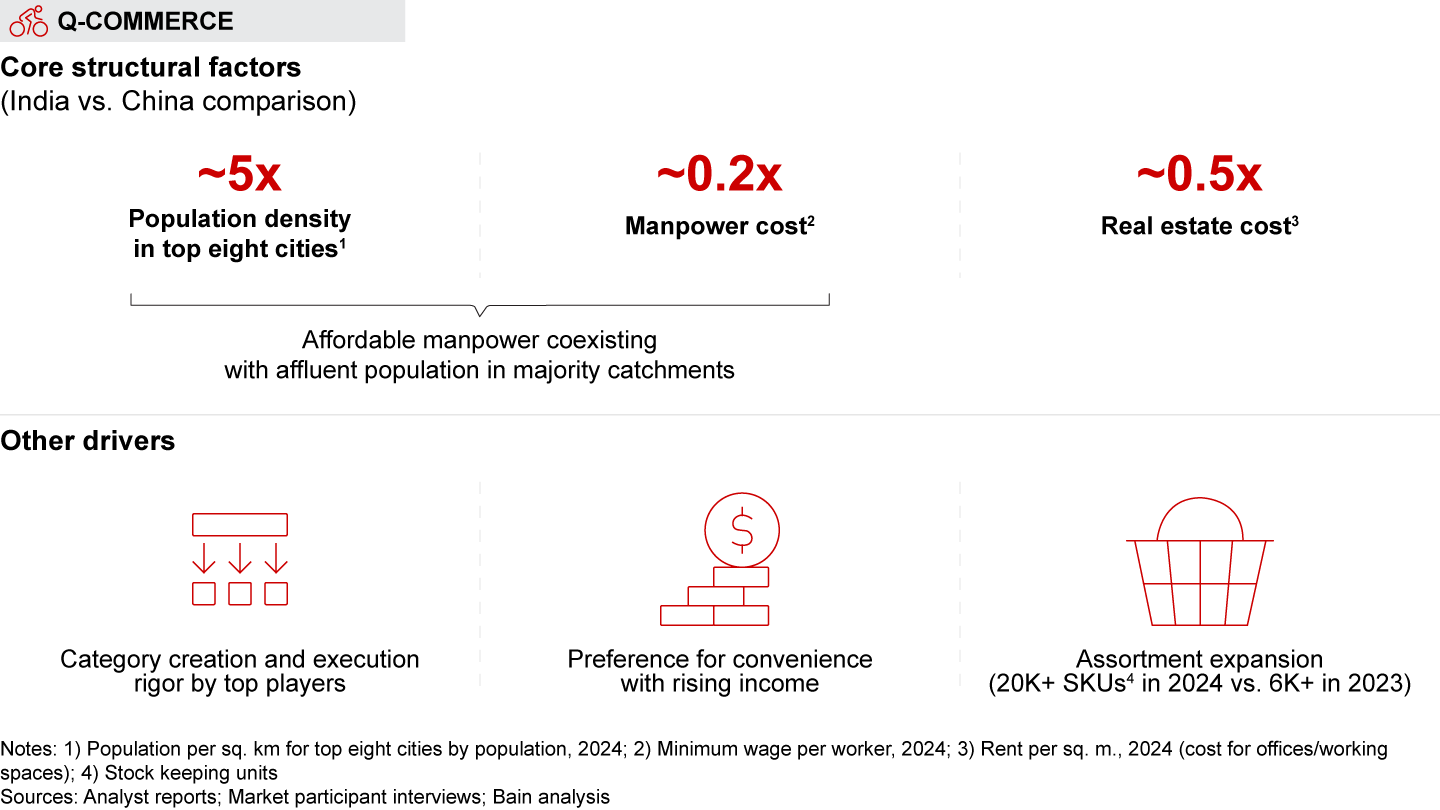
Quick commerce (Q-commerce; less than 30-minute delivery): Q-commerce is revolutionizing how consumers buy in India, with over two-thirds of all e-grocery orders and a tenth of overall e-retail dollars spent on these platforms. Indian q-commerce players have bucked global trends and scaled profitably. India’s unique structural advantages, including high population density and close access to a network of low-rent dark stores, have enabled this growth. Q-commerce has since attracted multiple players, which has made the consumer value proposition richer.
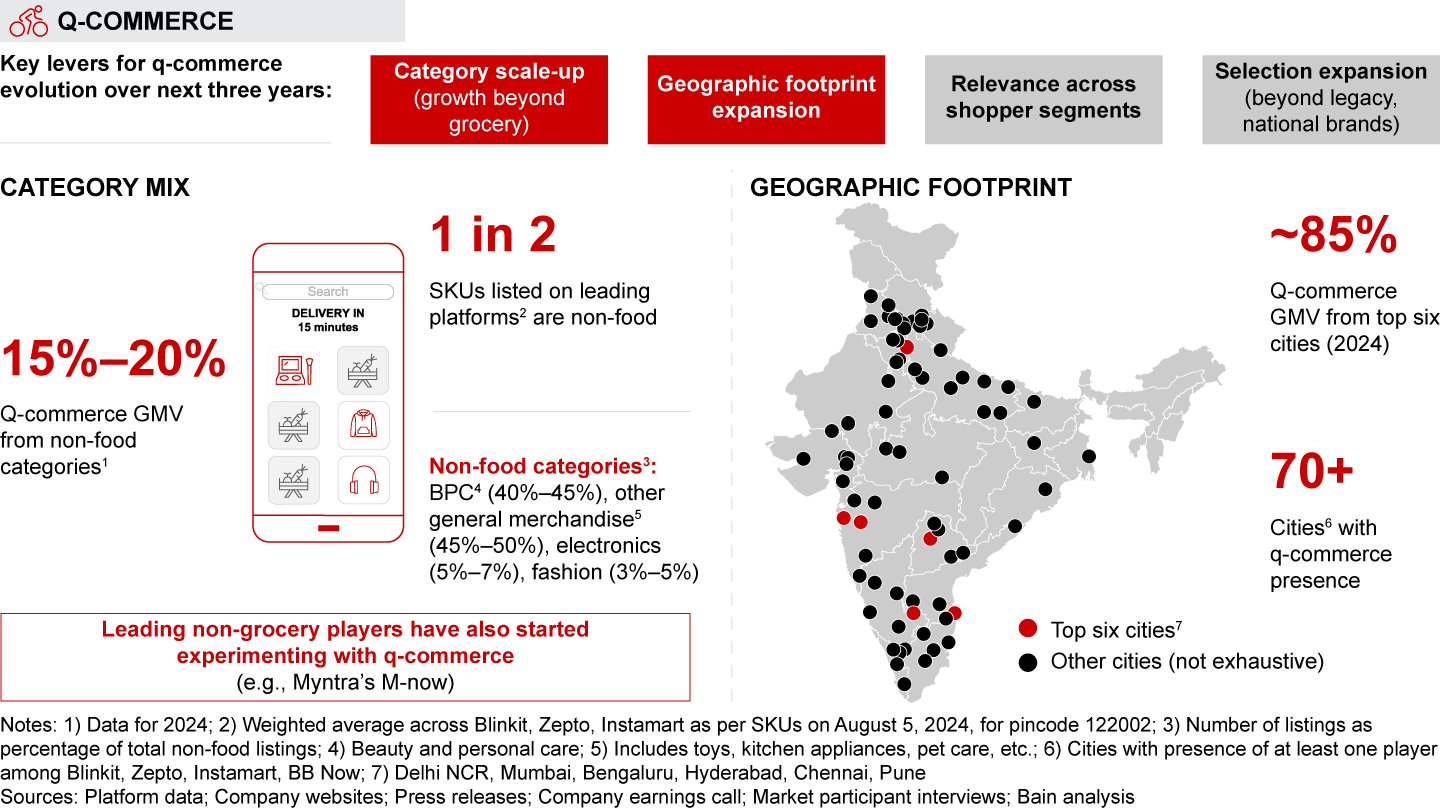
Q-commerce is projected to grow at over 40% annually through 2030, driven by expansion across categories, geographies, and customer segments. While q-commerce began with grocery, 15%–20% of its GMV now comes from categories such as general merchandise, mobile phones, electronics, and apparel. Expansion beyond major cities has also fueled growth, though the top six metros still account for the lion’s share of GMV.
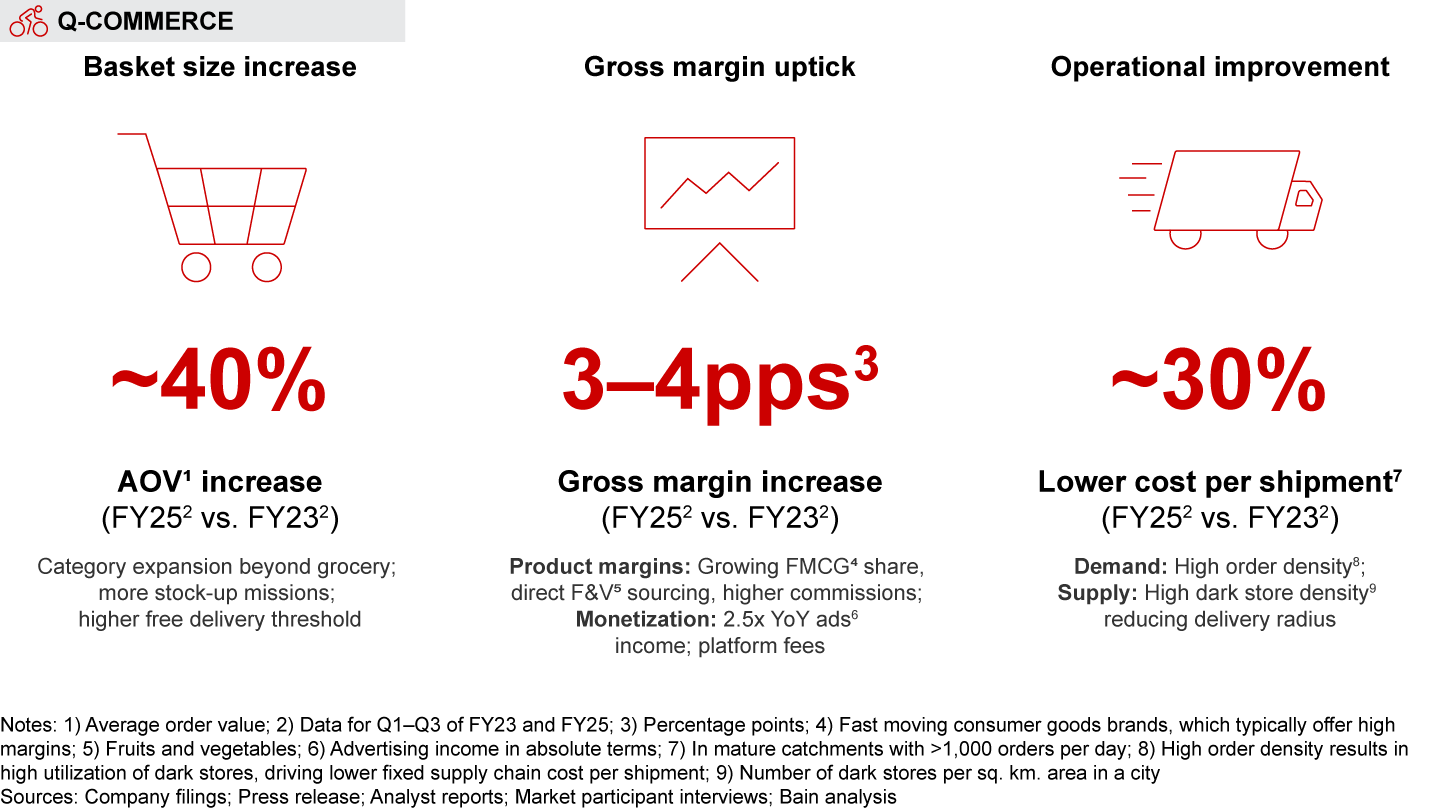
Q-commerce players have improved unit economics by increasing order values, lowering supply chain costs, and enhancing gross margins (via direct sourcing from producers and farmers, and deploying monetization levers such as advertising and platform fees). However, to sustain profitable growth, companies must adapt their business models for markets beyond major metros, manage rising competition, and optimize supply chains as the market evolves into a two-speed proposition—offering select products in under 15 minutes and a wider assortment within an hour.
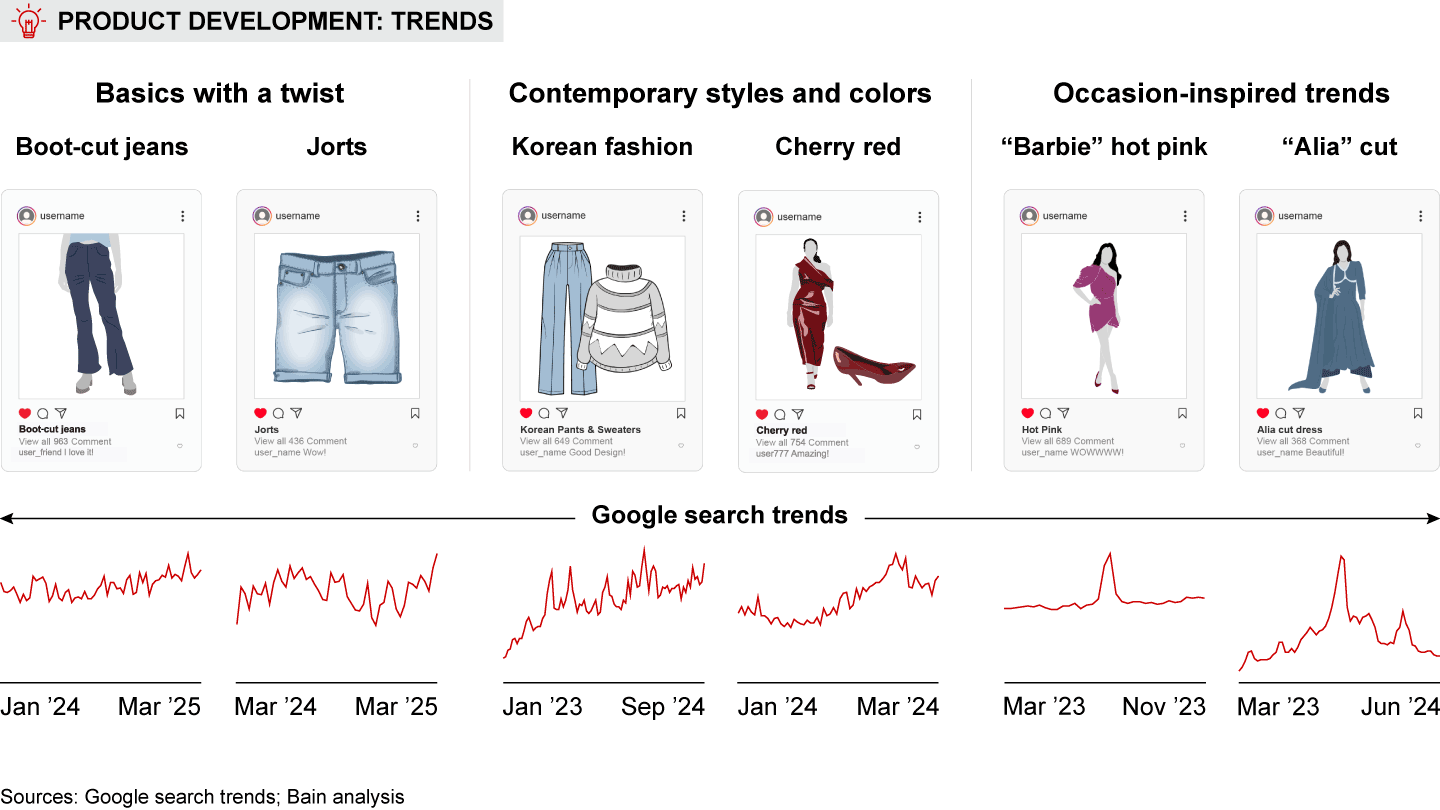
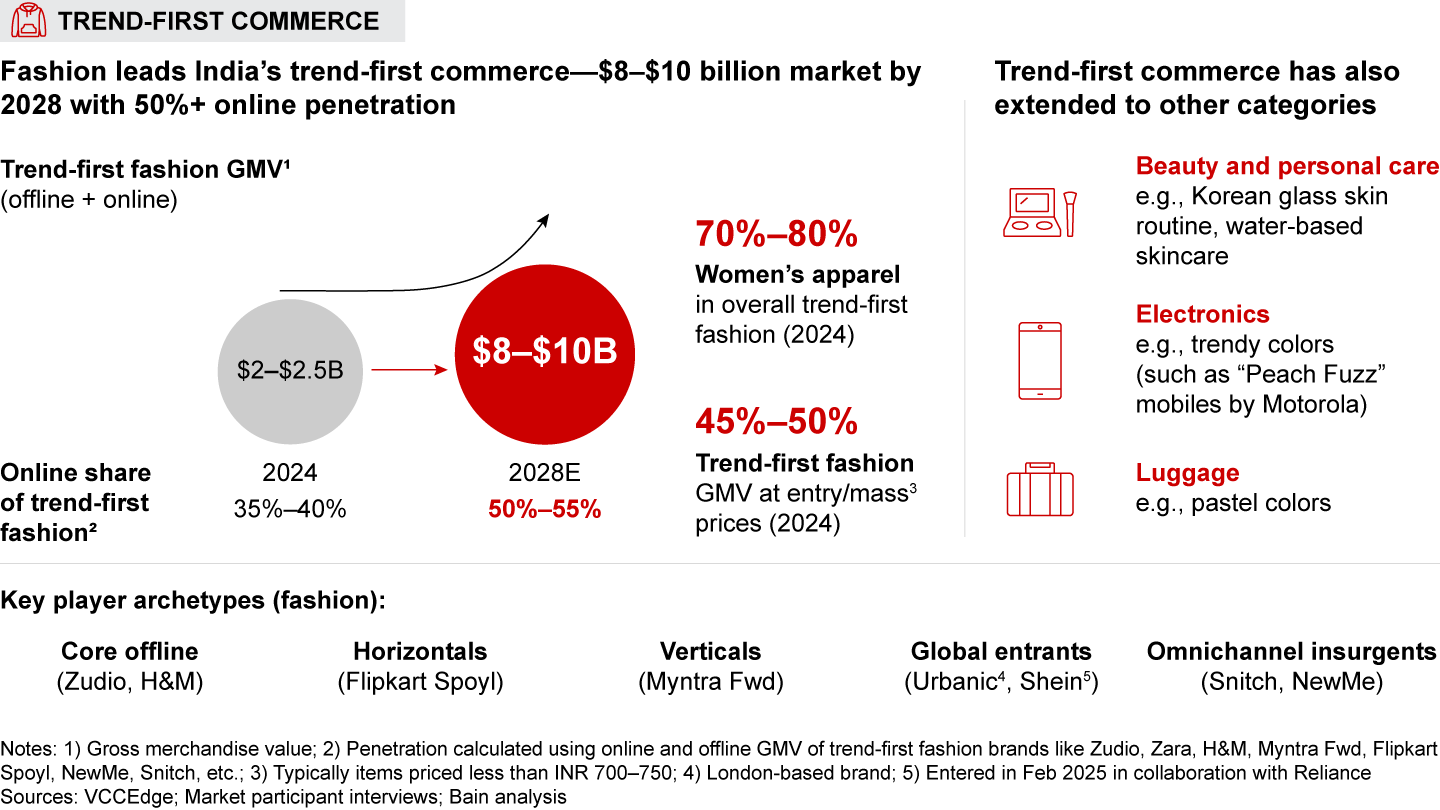
Trend-first commerce (frequent launches of trendy collections at affordable prices): This model is rapidly gaining momentum in India. Trend-first fashion alone is expected to grow fourfold, reaching approximately $8 to $10 billion by 2028, with more than half of this revenue from online sales. Interestingly, this model is also quickly expanding beyond fashion, with the role of trendy assortment expanding in categories such as beauty (e.g., Korean glass skin routine), electronics (e.g., vibrantly colored smartwatches), and luggage.
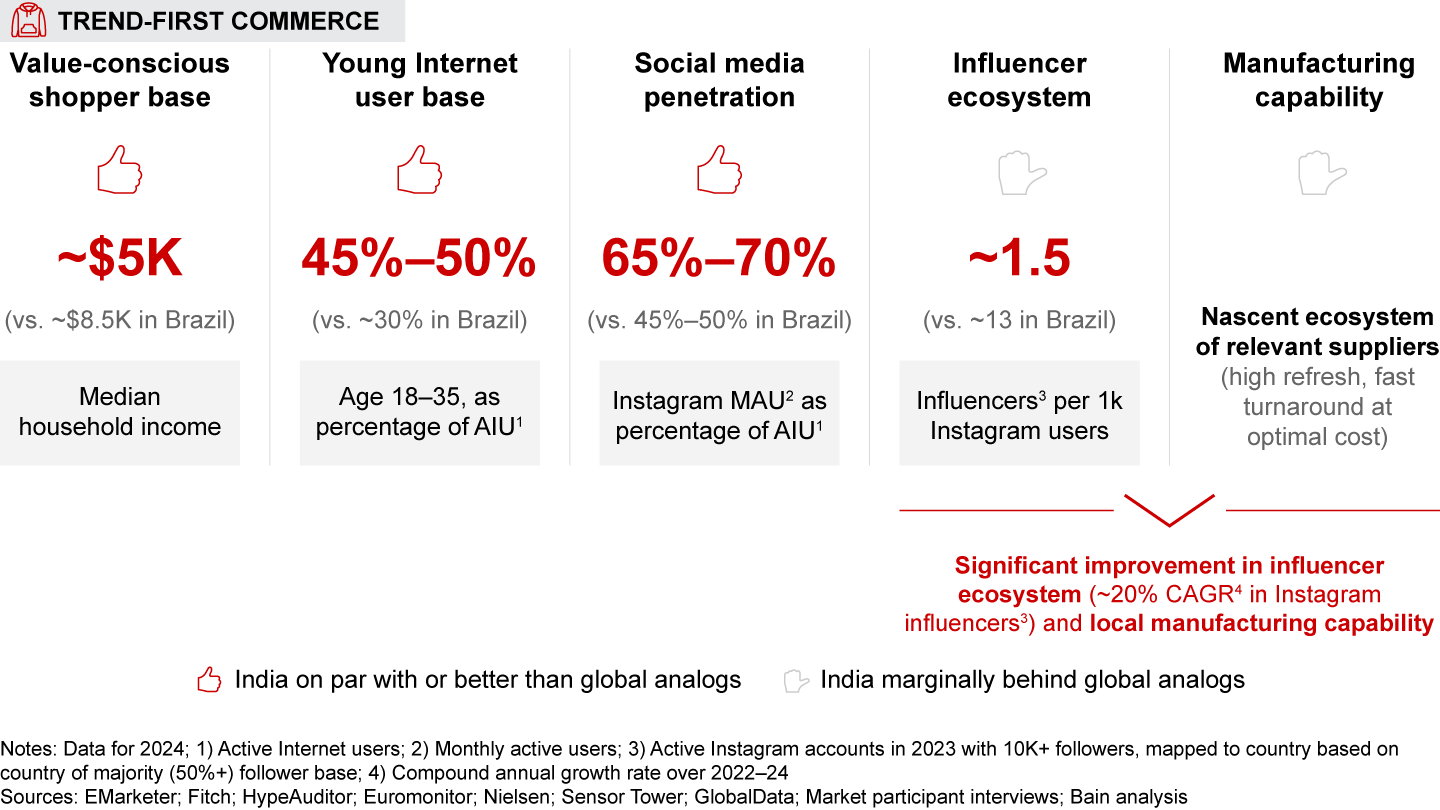
India’s unique demographics—with a large base of young, value-conscious consumers who are active on social media—position it perfectly for the trend-first commerce boom. The rapidly expanding influencer and supplier ecosystems will only further accelerate this growth.
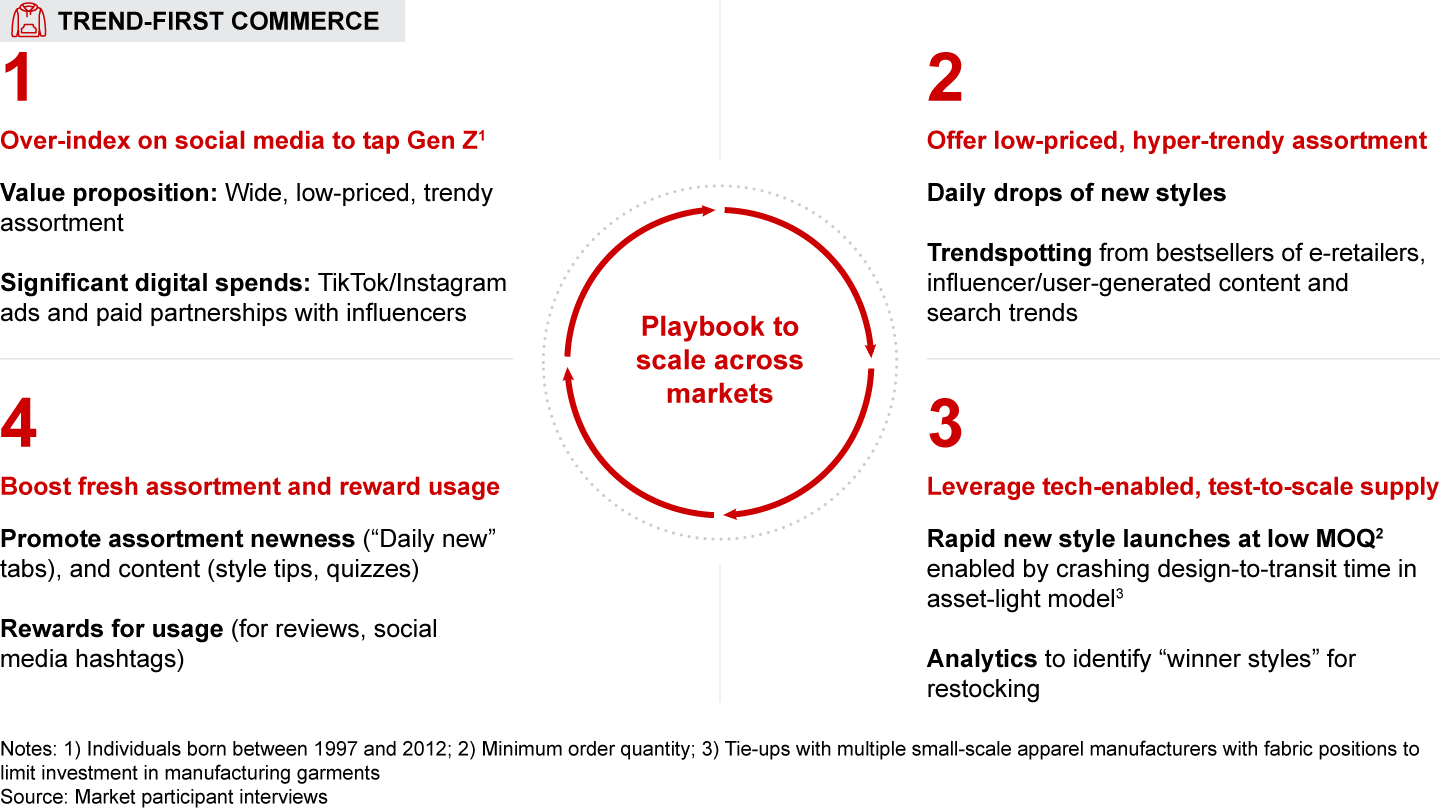
Globally, trend-first fashion has thrived by following a tech-driven, repeatable playbook involving four key components: (1) investing in social media to target Gen Z; (2) offering hyper-trendy, low-priced collections with daily launches driven by advanced trend-spotting algorithms; (3) utilizing a test-and-scale model to quickly introduce and restock popular styles; and (4) providing a bespoke user experience that emphasizes novelty and rewards user engagement.
In India, multiple players are looking to capture a slice of this market. Offline brands such as Zudio (by Trent), H&M, and Zara have successfully offered a compelling “trends-first” proposition to Indian consumers. Meanwhile, online platforms, such as Flipkart Spoyl, Myntra Fwd and Shein, along with emerging brands like Urbanic, Snitch, and NewMe, are also looking to win over Gen Z consumers and trend-savvy millennials.
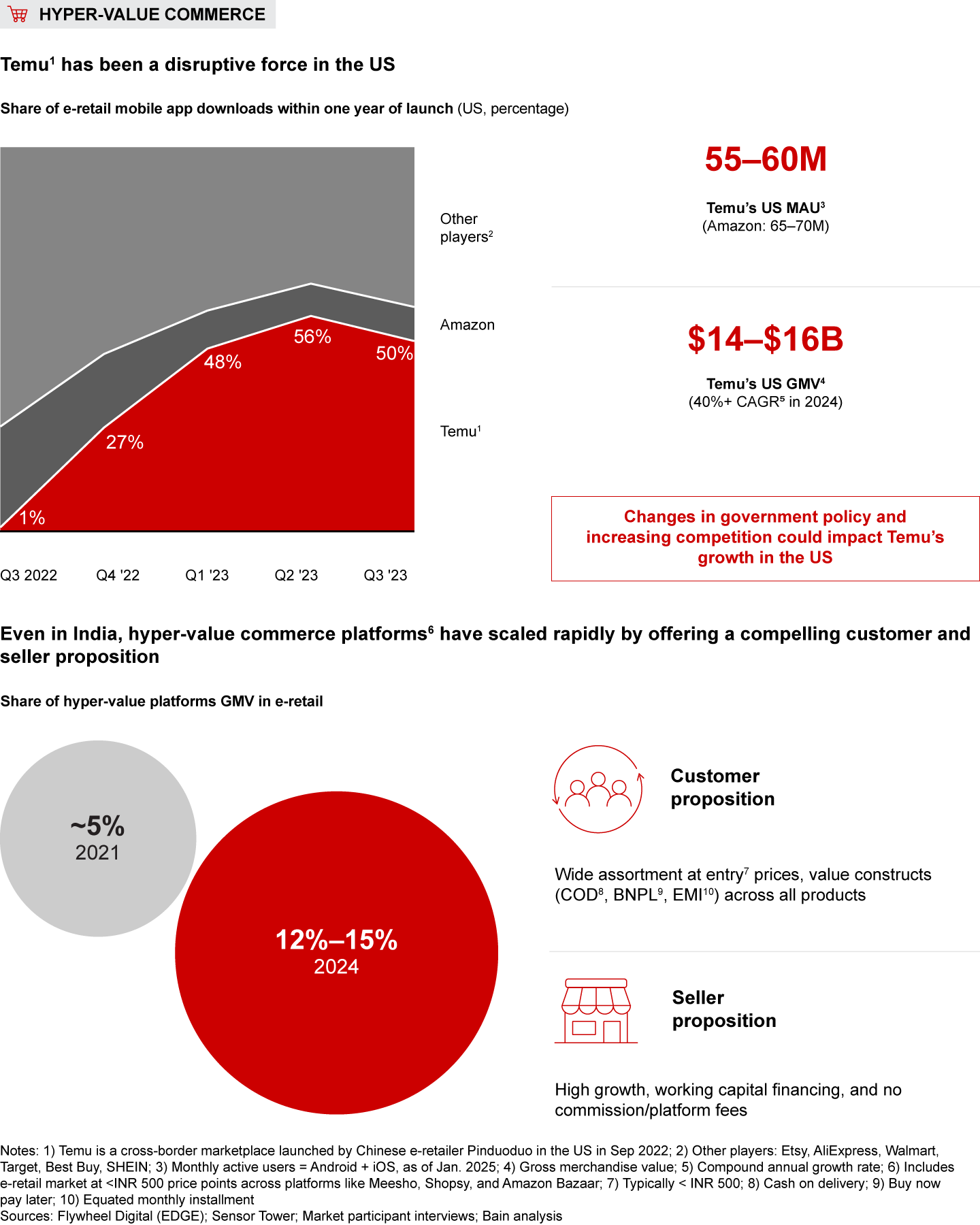
Hyper-value commerce (ultra-low price assortment): Hyper-value commerce has seen a global surge, exemplified by the success of Temu in the US, which accounted for roughly half of all American e-retail app downloads within a year of launch. Temu’s 55–60 million monthly active users were just shy of Amazon’s 65–70 million US users as of January 2025, with GMV having grown at over 40% annually to between $14–$16 billion by the end of 2024.
In India, hyper-value commerce’s contribution to e-retail has scaled from around 5% of e-retail GMV in 2021 to more than 12% in 2024. These platforms have gained strong traction among lower-middle-income consumers, particularly in Tier-2 or smaller cities, by focusing on an affordable product assortment. Additionally, these platforms have rapidly expanded their seller base by offering seller financing and zero-commission models.
India’s e-retail market, akin to the broader retail landscape, is diverse, with purchase behavior varying dramatically by age, region, city tier, and e-retail maturity:
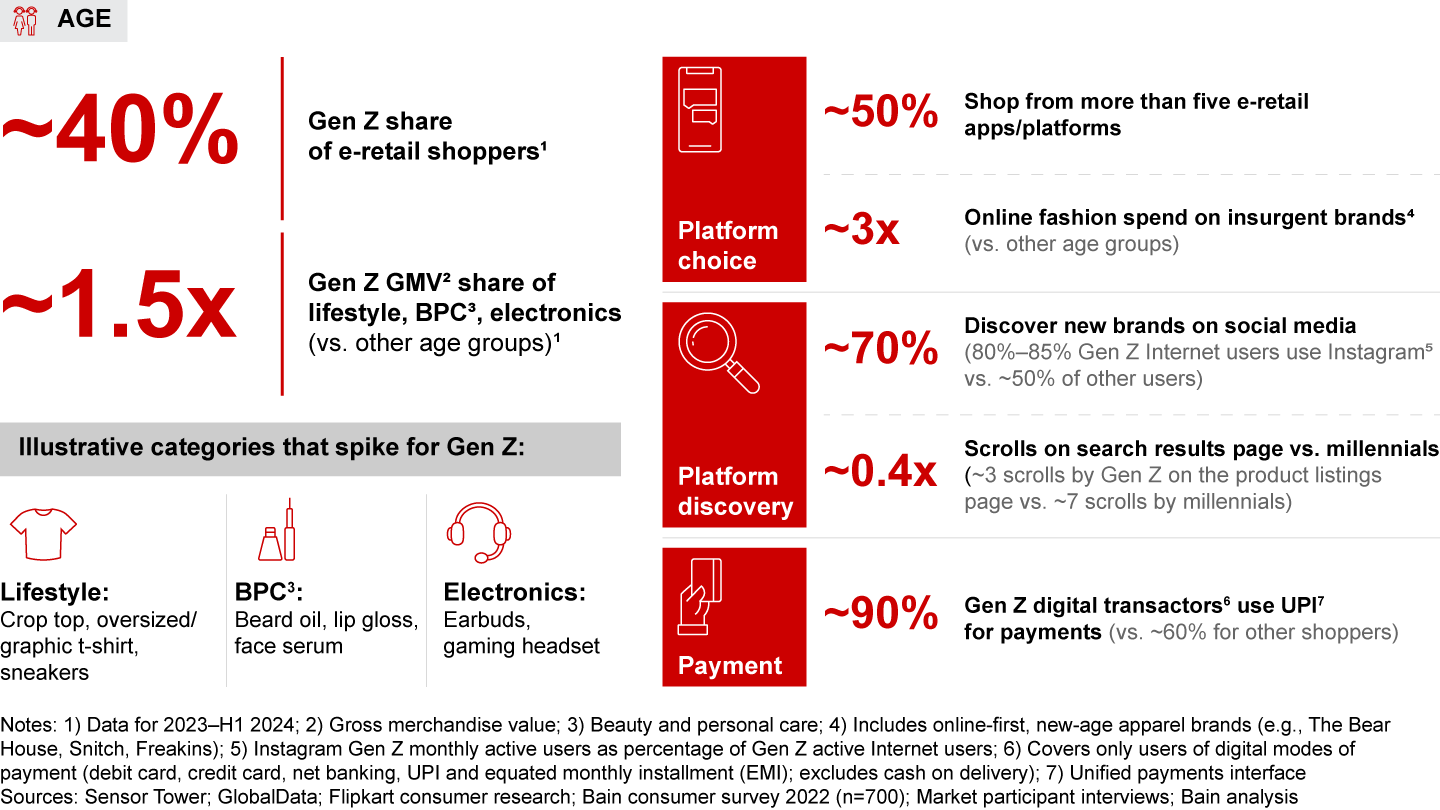
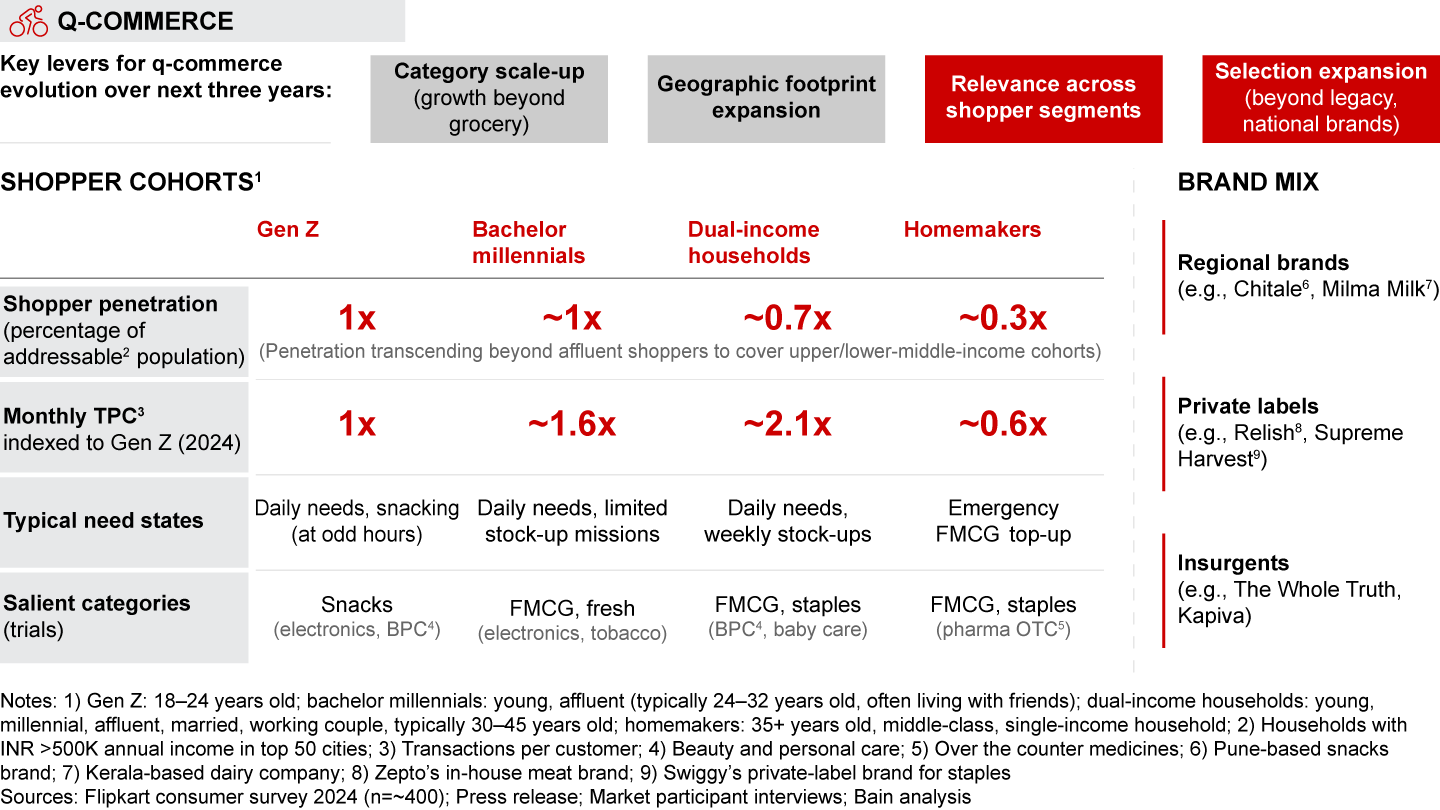
- Age: The gradual rise of Gen Z (born between 1997–2012), accounting for almost 40% of e-retail shoppers, has been the most salient shift in India’s shopper base. Gen Z shopper behavior stands out. Gen Z split their shopping basket, with half of them shopping from over five e-retail platforms annually; these shoppers are also more experimental, spending three times more on insurgent fashion brands vs. older cohorts. Heavily influenced by social media, 70% of Gen Z shoppers discover brands online and make quicker purchase decisions, browsing fewer search listings than millennials before buying. Over 90% of Gen Z digital transactors prefer Unified Payment Interface (UPI) for digital payments. A rise in Gen Z income and the addition of more Gen Z to the workforce will make it a crucial cohort for brands to solve for.
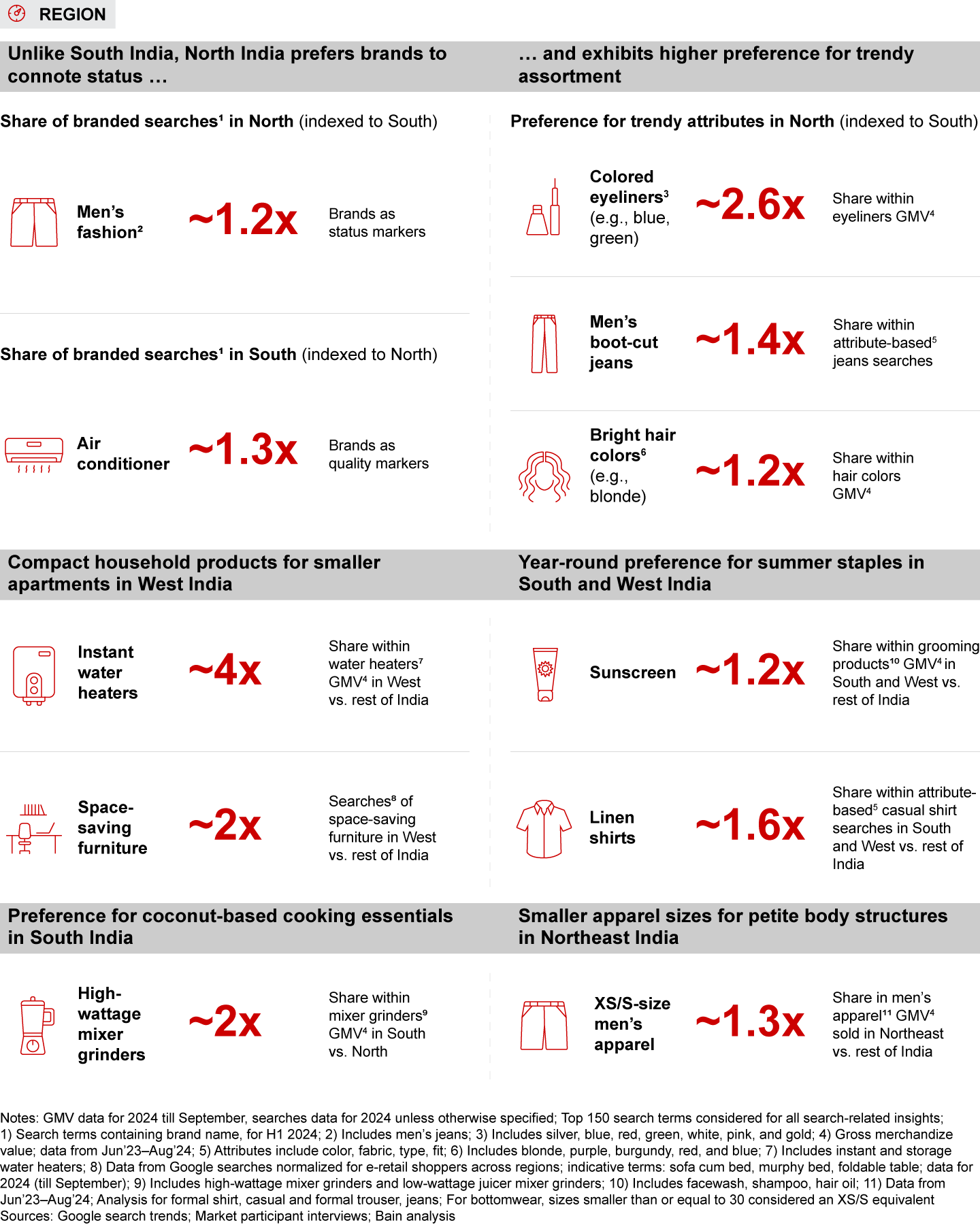
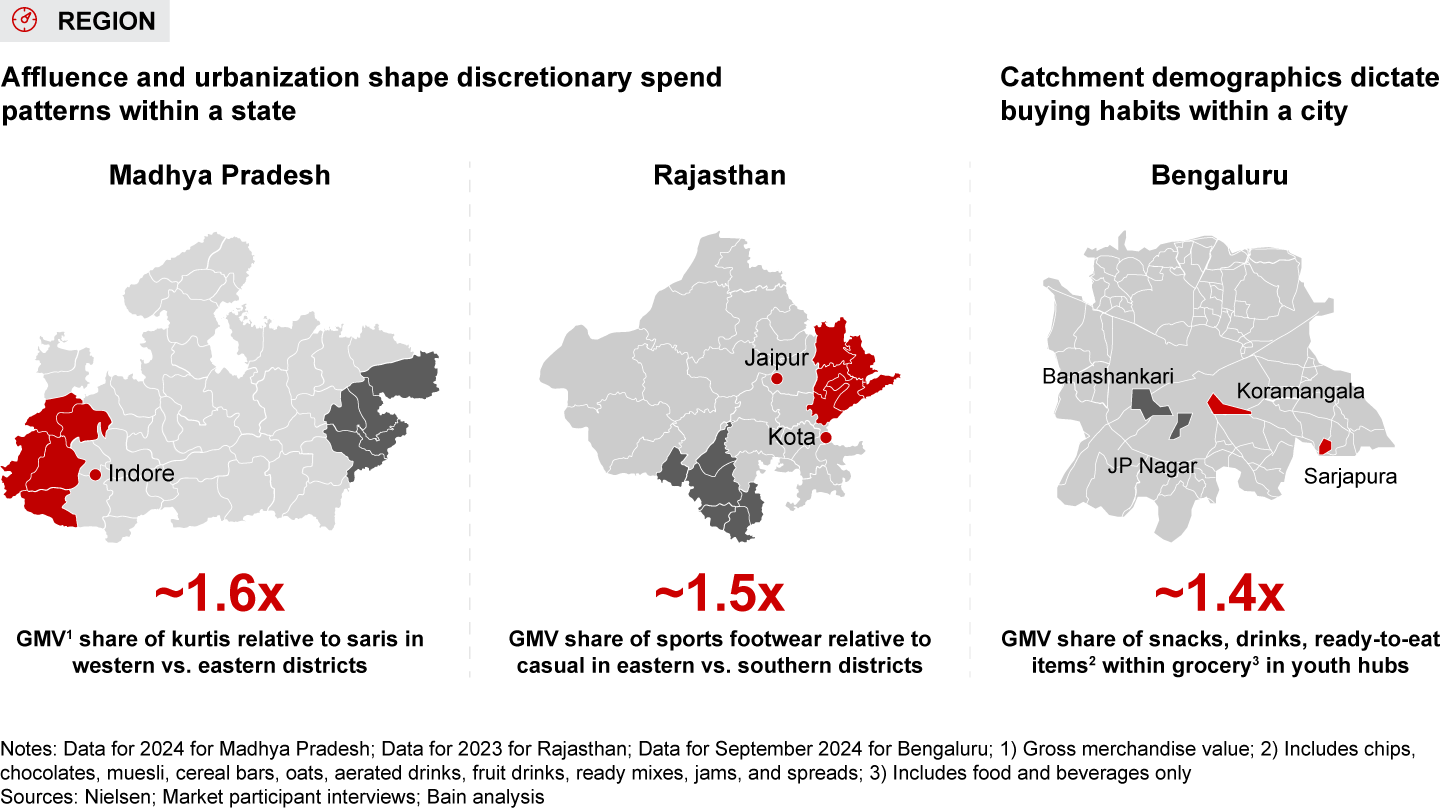
- Region: Socioeconomic and cultural factors influence consumer behavior across India’s diverse regions. In the North, brands are often associated with status, which is evident in the higher share of branded searches in men’s fashion. Conversely, in the South, shoppers view brands as markers of quality, manifesting in more branded searches in electronics. There are numerous examples of these regional distinctions. For instance, consumers in the North gravitate toward trendier styles, like boot-cut jeans and bold hair colors, whereas consumers in the Northeast demand smaller apparel sizes, reflecting petite body frames. Shopping behavior also varies within a few hundred kilometers within a region, or even within a few kilometers within a city, influenced by urbanization, affluence, and cultural factors. In Rajasthan’s eastern districts, close to student hubs such as Kota and Jaipur, sports footwear is more popular, whereas casual footwear prevails in southern districts. Similarly, in Bengaluru, younger residents in Koramangala favor party snacks and ready-to-eat products, while neighborhoods like JP Nagar and Banashankari show a different consumption profile.
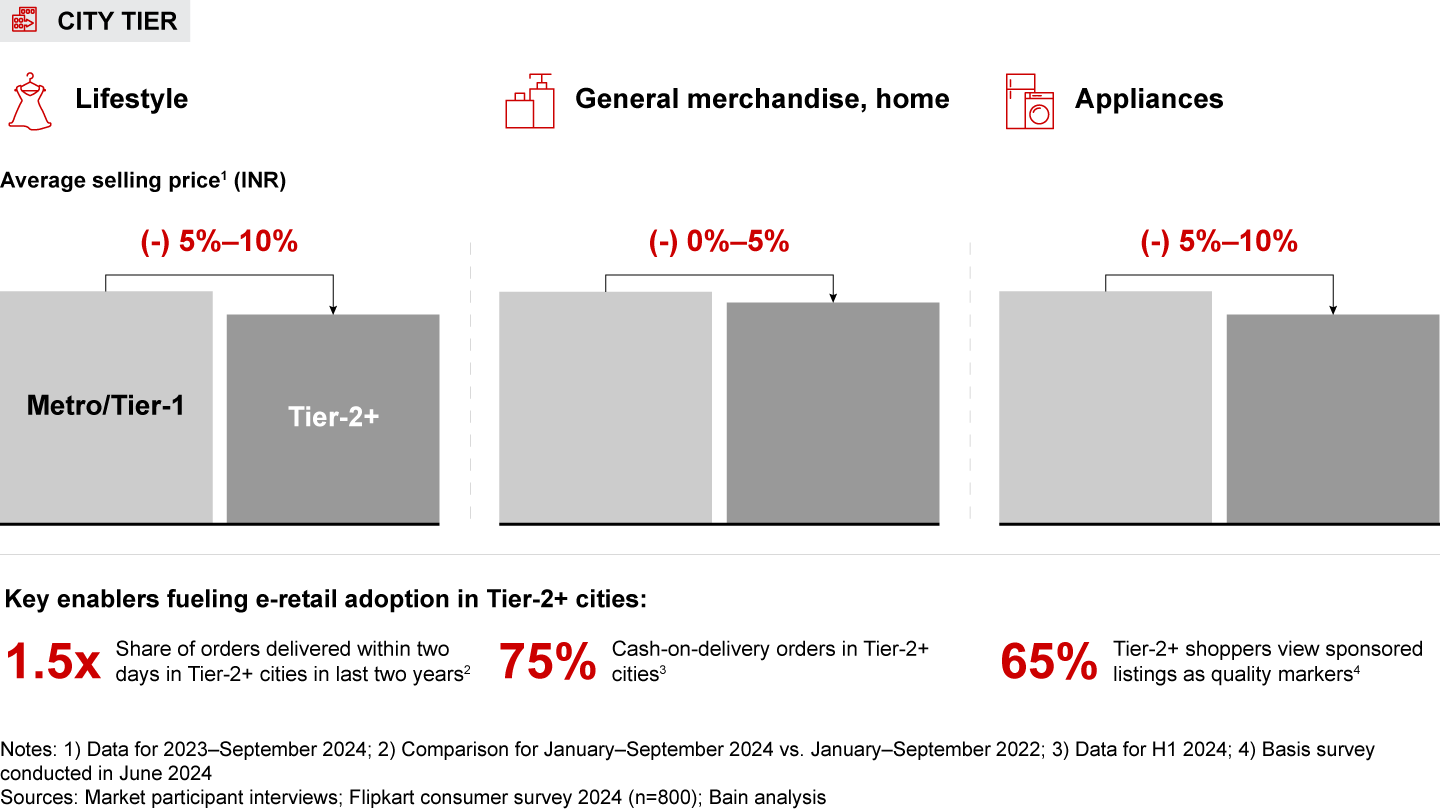
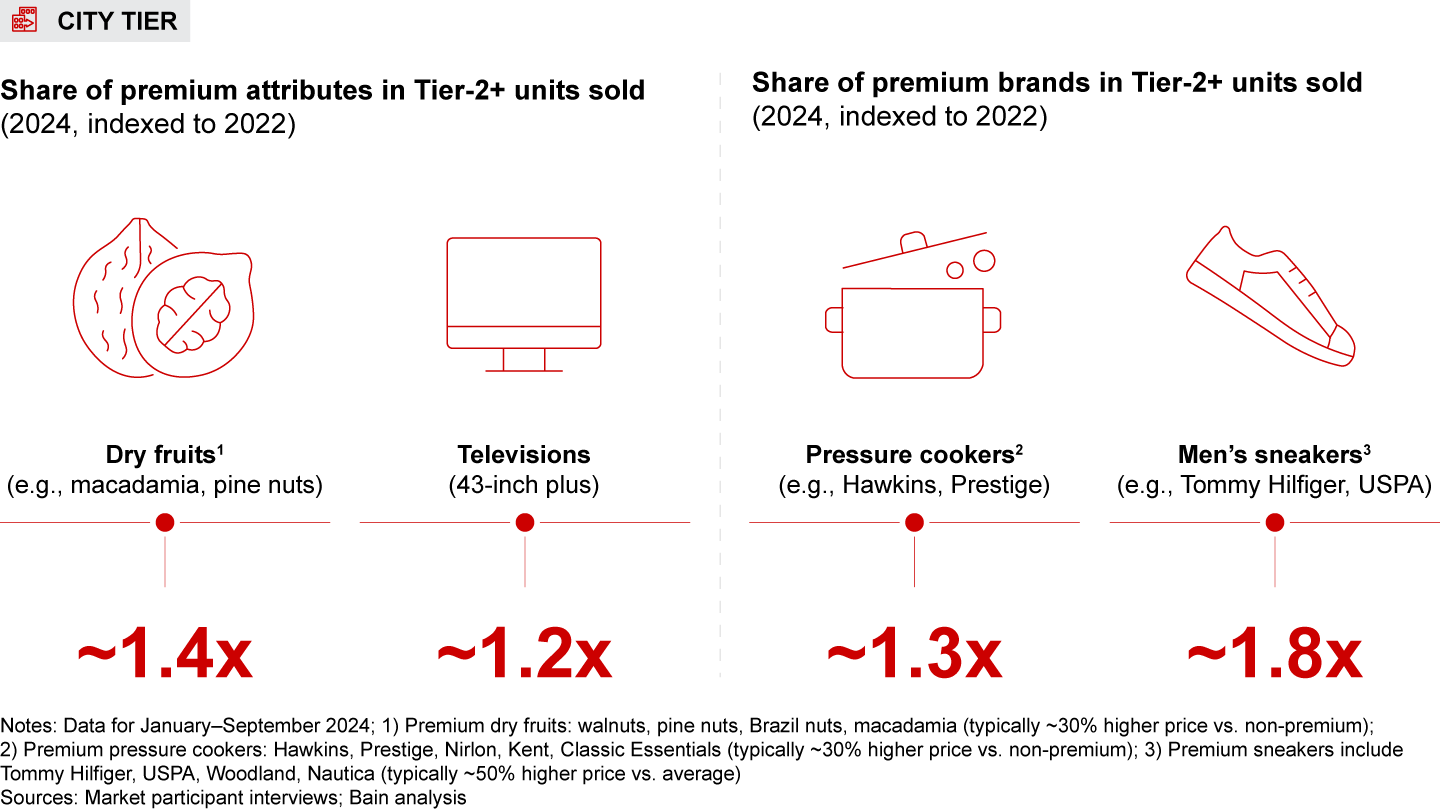
- City tier: Shoppers in Tier-2+ cities show comparable spending power to bigger cities, with average selling prices being in line or only marginally lower in categories such as electronics, appliances, and general merchandise. Shoppers from these cities are also increasingly embracing premium brands and attributes. Interestingly, shoppers in smaller cities often view sponsored listings as a marker for quality. Retailers must adapt their strategies to cater to the growing consumer base in these cities that values both affordability and quality.
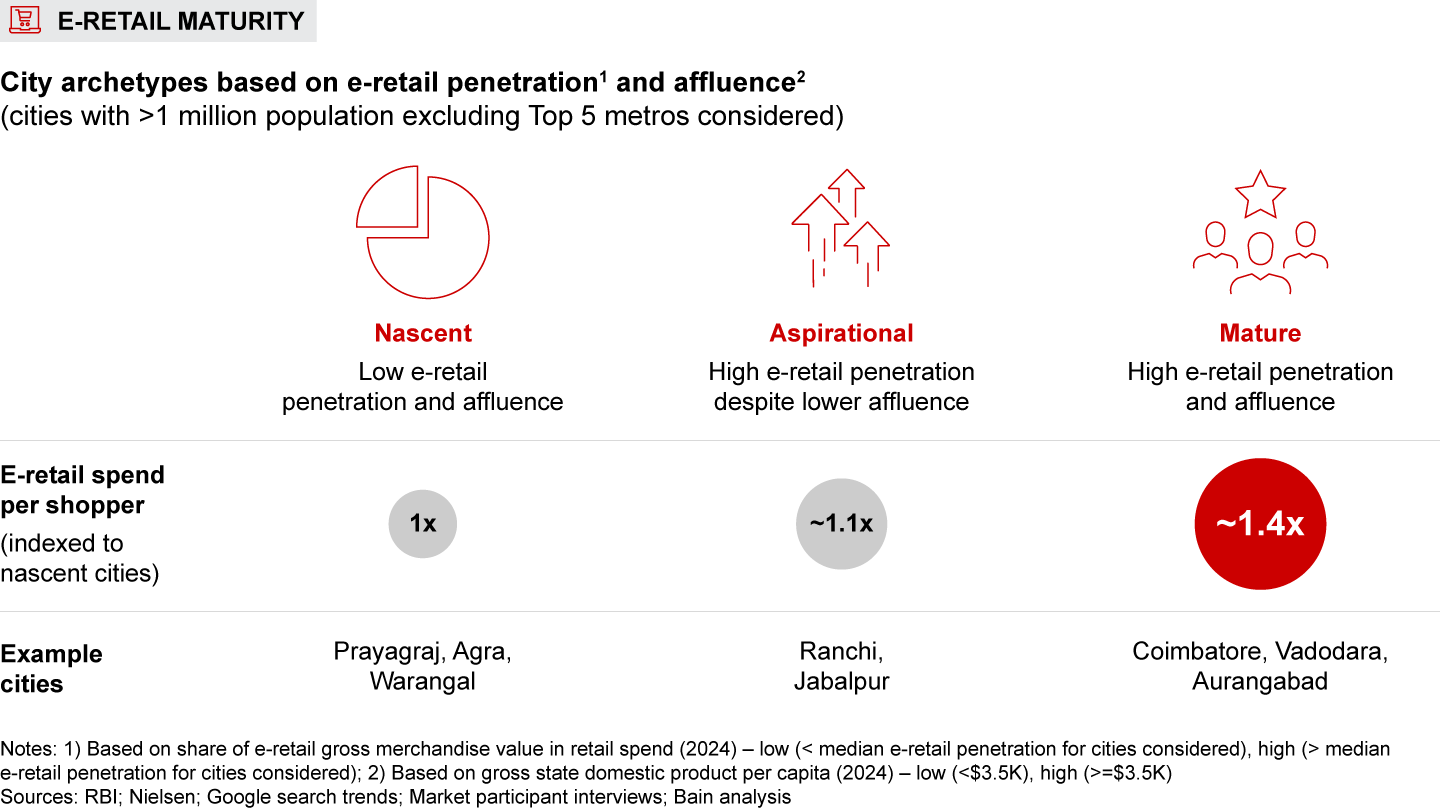
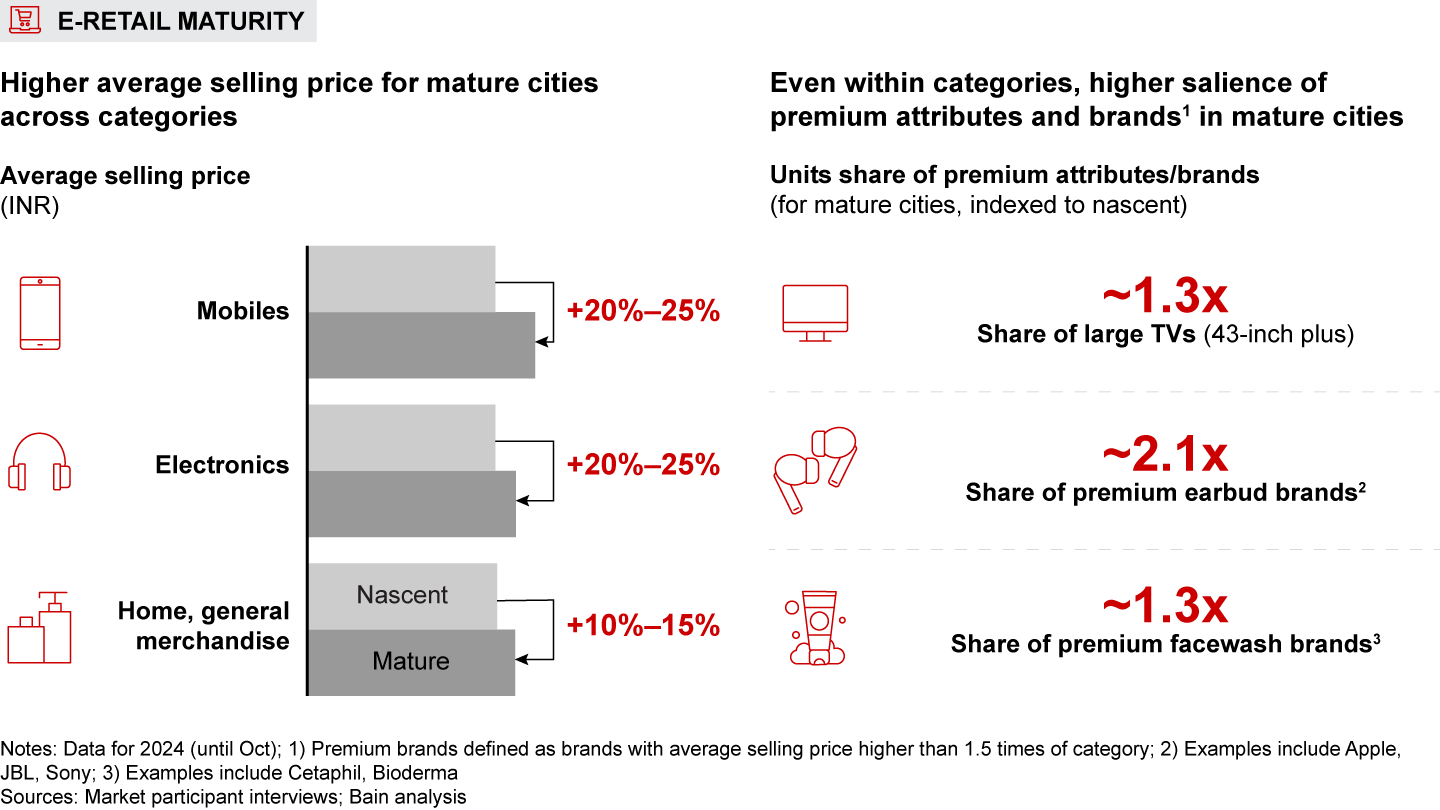
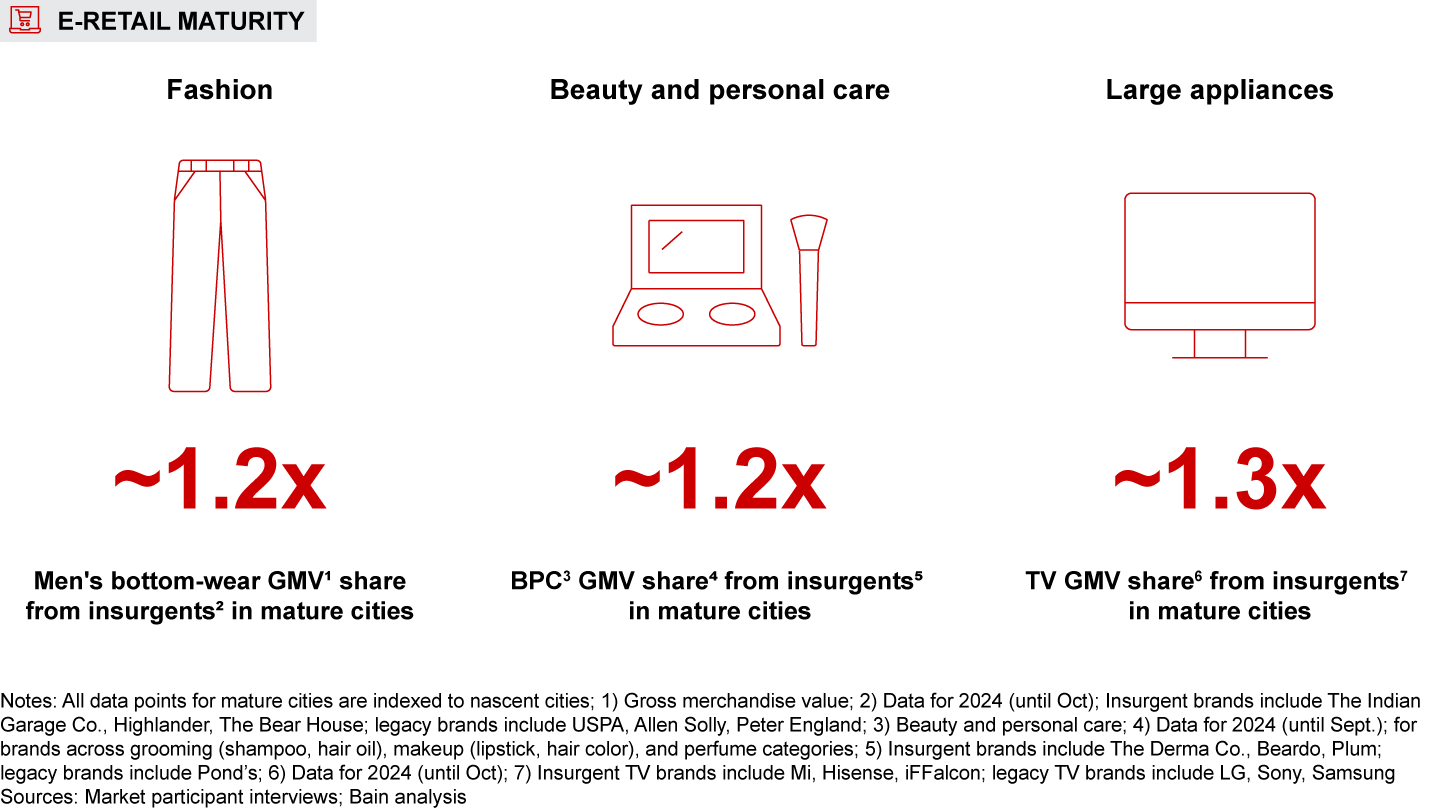
- E-retail maturity: Mature markets such as Coimbatore and Vadodara, marked by high e-retail penetration and affluence, see about 40% higher e-retail spend per shopper compared to nascent markets such as Prayagraj and Warangal. Consumers from these markets favor premium products, with 10%–25% higher average selling price across categories vs. nascent markets. These shoppers also display a stronger preference for insurgent brands.
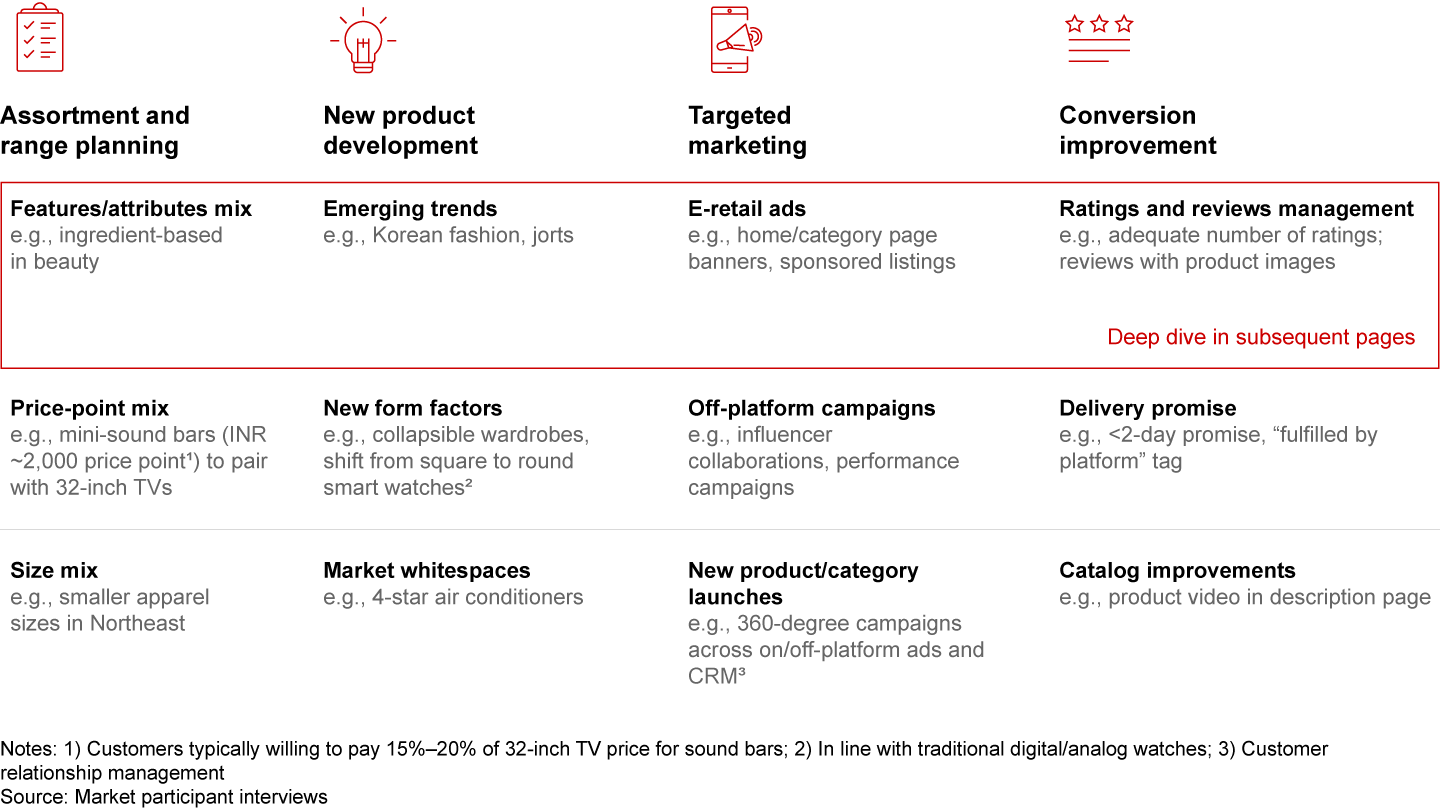
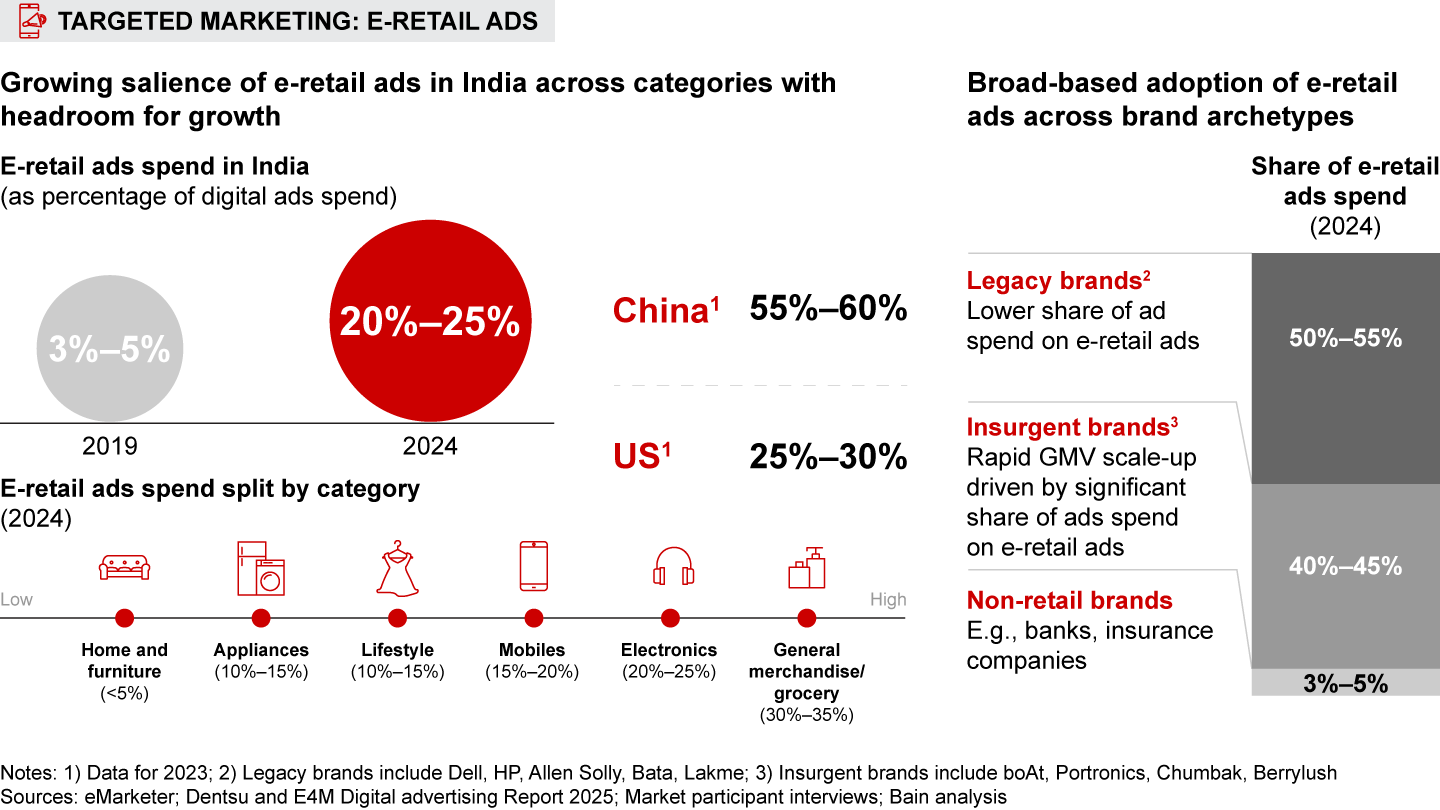
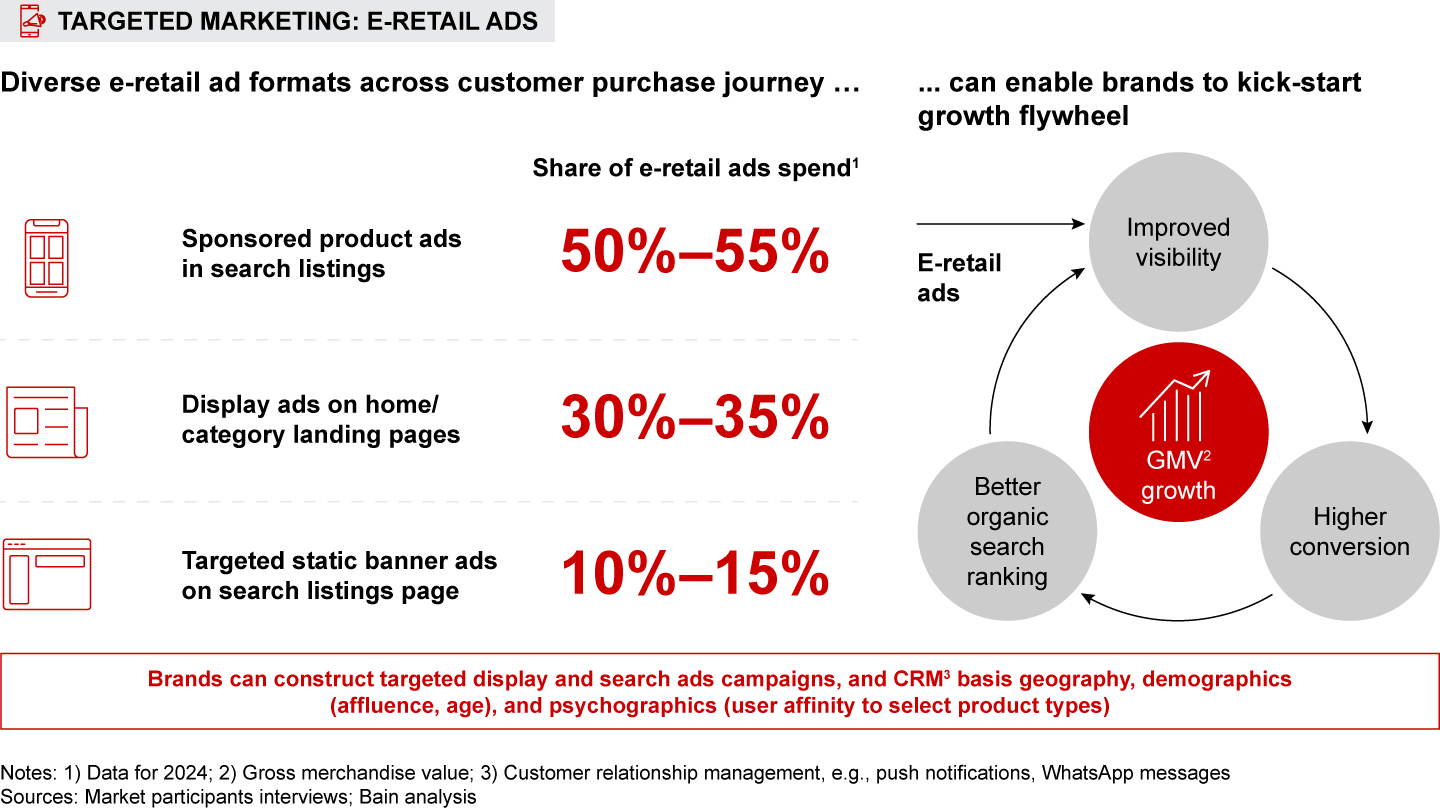
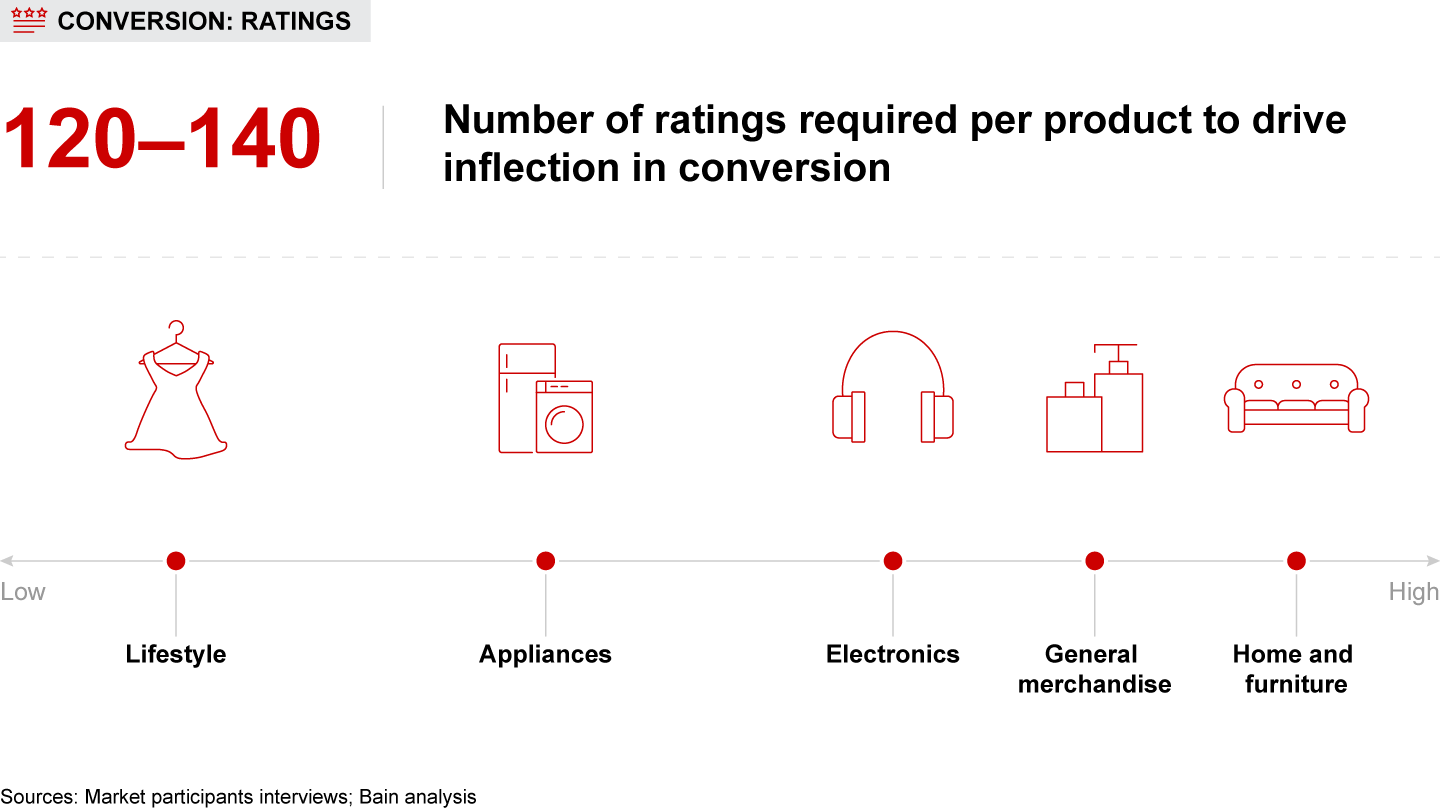
These differences in purchase behavior indicate massive opportunity for retailers. Brands and sellers can harness the diversity of consumer preferences across India by (1) tailoring their range and assortment to reflect regional variation in features and price points; (2) creating products that align with emerging trends (e.g., Korean-inspired fashion) and market whitespaces; (3) using targeted e-retail advertising (display and search) to enhance brand awareness and drive sales; and (4) improving conversion by focusing on ratings and reviews, offering faster delivery options, and enhancing catalogs.
E-retail market overview
- India’s e-retail market has scaled to an impressive ~$60 billion in 2024. Notably, with over 270 million Indians shopping online in 2024, India has pipped the US to become the second-largest e-retail market in terms of online shoppers.
- The e-retail market growth has slowed down to 10%–12% in 2024 vs. more than 20% seen historically, largely due to macroeconomic and consumption stress. Consumption growth has declined from approximately 11% pre-Covid (2017–19) to approximately 8% post-Covid (2022–24), a change caused by inflationary pressure and stagnating real wages.
- Despite near-term macroeconomic headwinds, the long-term prospects remain strong. The e-retail market is expected to scale to $170–$190 billion by 2030, growing at over 18% annually. Nearly 1 in 10 retail dollars is projected to be spent on e-retail by 2030, fueled by an uptick in discretionary spending as India’s GDP per capita crosses the crucial $3,500–$4,000 threshold, a key tipping point observed in e-retail spending globally.
- Categories with high purchase frequency, such as grocery, lifestyle, and general merchandise, are set to contribute around 70% of incremental growth, with penetration levels expected to climb two to four times from current levels.
- E-retail continues to democratize the shopping landscape in India. E-retail penetration has expanded from Tier-2 cities to Tier-3 and smaller cities. Almost 60% of new customers since 2020 hail from Tier-3 and smaller cities. The seller landscape is also evolving, with over 60% of new sellers onboarded since 2021 from Tier-2 and smaller cities.








Disruption in e-retail
Three disruptive business models—quick commerce, trend-first commerce, and hyper-value commerce—are changing the tapestry of India’s e-retail market:
- The dramatic rise of quick commerce (i.e., delivery in less than 30 minutes) has been one of the most defining hallmarks of India’s e-retail market over the last two years. In 2024, more than two-thirds of all e-grocery orders and one-tenth of e-retail spend happened on q-commerce platforms. Q-commerce is forecasted to grow by over 40% annually until 2030, fueled by expansion across categories, geographies, and customer segments. Players have also unlocked a profitable model to scale up through a blend of customer-facing and back-end initiatives. The space is also becoming more competitive, with new entrants such as Flipkart Minutes, Myntra’s M-now, BigBasket’s BB Now, and Amazon’s Tez joining the race.
- Trend-first commerce (i.e., frequent launch of trendy assortment at affordable prices) has picked up the pace, particularly in fashion. Trend-first fashion is expected to quadruple to $8–$10 billion by 2028, with more than half the spends online. Globally, trend-first fashion players, such as Shein and Fashion Nova, have scaled through a tech-driven repeatable playbook involving leveraging social media to target Gen Z, offering hyper-trendy, affordable collections, deploying test-and-scale models to launch and replenish popular styles, and delivering an engaging user experience. India’s vast base of young, value-conscious, social-media-savvy shoppers will fuel this boom. However, the influencer ecosystem and local manufacturing capabilities will have to evolve further to enable the model to realize full potential.
- Hyper-value commerce (i.e., offering a wide range of ultra-low price point assortments) has witnessed a surge globally, as evidenced by the success of Temu in the US. Within a year of launch, the app amassed nearly half of e-retail app downloads and currently boasts 55–60 million monthly active users, closely trailing Amazon’s 65–70 million in the US, as of January 2025. In India, hyper-value commerce platforms’ share of e-retail GMV has surged over the last three years to reach 12%–15%. Players have gained traction with lower-middle-income consumers, especially in Tier-2 and smaller cities, due to affordable product offerings. These platforms have also rapidly onboarded sellers by offering attractive growth with a zero-commission model and seller financing.












Winning in “many Indias”
India’s e-retail landscape is heterogeneous, reflecting “many Indias.” Variations in purchase behavior exist across age, region, city tier, and e-retail maturity:
- The scale-up of e-retail spend by Gen Z (born between 1997 and 2012) has been particularly notable. Representing 40% of India’s e-retail shoppers, Gen Z boasts 1.5 times the e-retail spend share on categories such as lifestyle, beauty, and electronics compared to other age groups. Gen Z has a distinct shopping behavior—they are more experimental, rely heavily on social media for brand discovery, make faster purchase decisions, and show a marked preference for UPI for digital payments.
- E-retail spending patterns vary widely across regions, shaped by deep-rooted socioeconomic and cultural differences. For instance, North India leans toward trendier fashion while the Northeast sees higher demand for smaller apparel sizes due to generally petite body frames. These nuances can be observed within a few hundred kilometers in a region or even within a few kilometers in a city, influenced by varying catchment-level demographics and affluence.
- E-retail spending of shoppers in Tier-2 and smaller cities is broadly at par with that of Metro/Tier-1 cities, with similar or only slightly lower average selling prices across categories. These shoppers are also showing a growing interest in premium brands and features. This growth is driven by faster delivery options, cash-on-delivery availability, and e-retail ads serving as indicators of quality.
- E-retail purchase behavior also varies based on e-retail maturity. In mature cities characterized by high e-retail penetration and affluence, the e-retail spend per shopper is around 40% more than in nascent cities. Shoppers in these cities show a strong preference for premium brands and attributes, with average selling prices elevated by 10%–25% across categories. They also demonstrate greater adoption of insurgent brands across categories.
Brands and sellers can capitalize on the nuances of “many Indias” by (a) adapting their product range and assortment, (b) developing new products aligned with evolving trends and market whitespaces, (c) leveraging targeted e-retail advertising (display and search) to improve brand awareness and kick-start a growth flywheel, and (d) enhancing conversion by building a critical mass of ratings, offering faster delivery options, and optimizing product catalogs.