論説

概要
- Utilities have underinvested in their transmission and distribution infrastructure for decades, but investment in the grid is on the rise.
- Strategic T&D investments improve reliability, which in turn reduces costs and improves the customer experience by reducing the frequency and duration of outages.
- Leading utilities use data and advanced analytics to make better decisions about where to invest in the grid.
The grid’s appetite for investment seems nearly infinite. Utilities could spend unlimited amounts upgrading their aging transmission and distribution (T&D) infrastructure to increase reliability and resiliency and to ensure the flexibility to integrate more renewable generation resources. However, since unlimited funds are rarely available, and utilities are under cost and earnings pressure, they have to decide which investments are most important. Executives must try to ensure that improvements in the grid will accomplish three important goals:
- increase reliability;
- improve the customer experience; and by doing so
- reduce operating and maintenance (O&M) costs.
Those questions have never been more pertinent or urgent, since investment in the grid is suddenly fashionable. For decades, large power generation projects attracted the lion’s share of investment, which resulted in limited funds for investment in the T&D grid. This has left the grid looking like a patchwork quilt of equipment varying in condition, reliability and cost to maintain. Now, with demand for electricity leveling off in developed markets, investments in traditional thermal power generation are less attractive. Interest has shifted to renewable generation and the grid.
Pratap Mukharji, a partner with Bain's Utilities & Renewables practice, describes how starting with the consumer and prioritizing failure points can help utilities successfully take steps toward modernization.
However, while T&D investment appeals to investors and senior executives, regulators can often remain wary, especially in some jurisdictions. This spending increases the rate base, but not all of it improves the value proposition for customers by delivering greater reliability, lowering costs or meeting other customer needs and expectations. Customer expectations continue to rise, and grid performance plays a significant role in customer experience and satisfaction levels. All customers have tipping points, some higher than others, when they experience too many “momentaries”—those annoying blinks in power supply that cause computers to crash and force one to reset all electronic clocks—or sustained outages. At these tipping points, their satisfaction falls off a cliff.
Leading utilities address this risk by using data and advanced analytics to make better decisions about T&D investment. These forward-looking companies take a more fine-tuned approach to understanding grid performance and customer preferences, which allows them to invest more precisely in the places with the most potential. This leads to a more effective deployment of capital and a much more data-driven and compelling story for regulators about the investment rationale and spending levels.
This brief looks at the correlations between reliability, customer experience and cost, and it describes how leading utilities tap the power of analytics to create value from those insights. We also highlight the most important capabilities that utilities need to execute these initiatives successfully and offer thoughts on how to get started.
Reliability, customer experience and cost
The rationale for investing more in the grid is real and tangible. Utilities have underinvested in their T&D infrastructure for decades, and these older and less maintained grids require more and costlier maintenance. Cost-to-serve performance correlates directly to the quality and reliability of circuits; less reliable circuits are more expensive to maintain (see Figure 1).
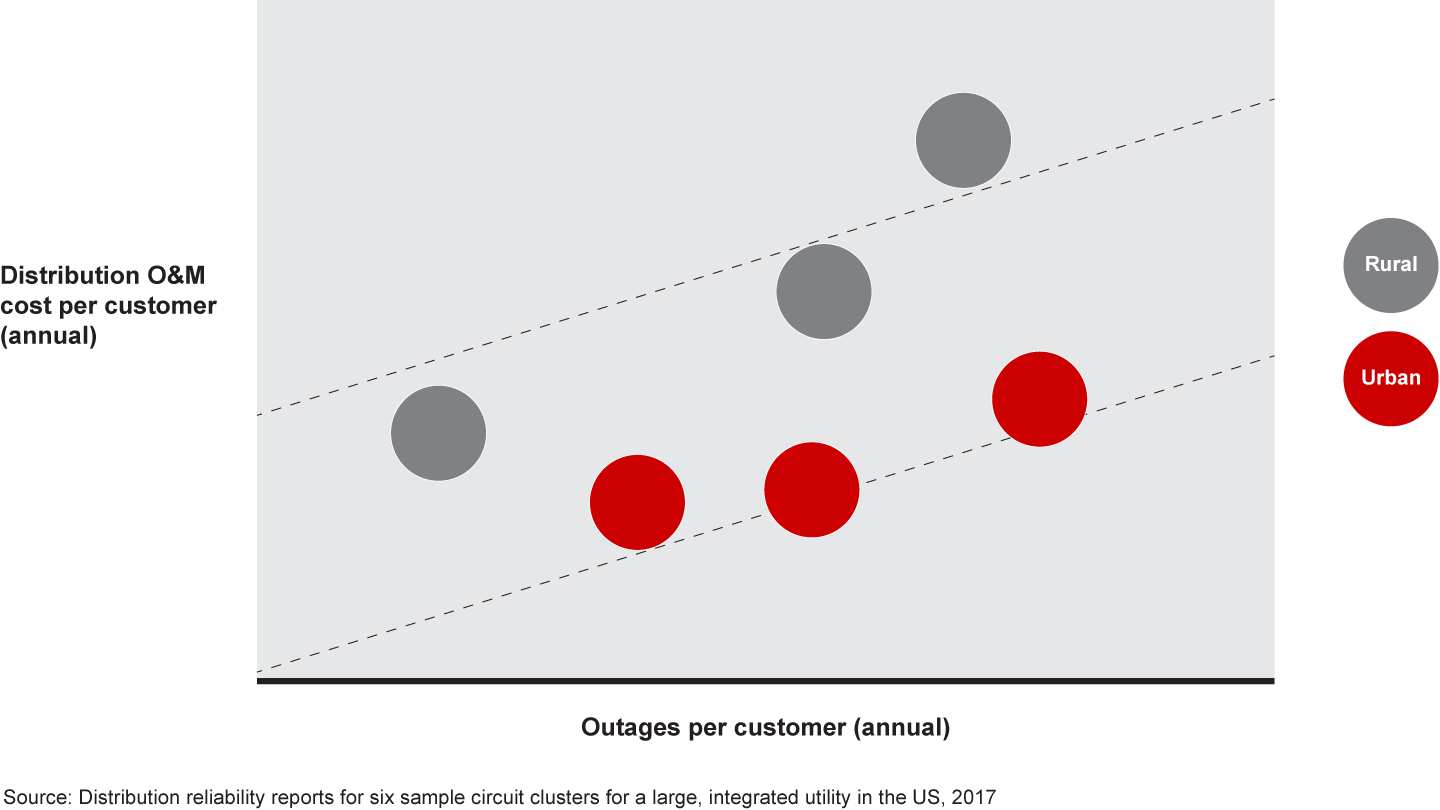

Lower reliability is expensive in other ways, too. Customer expectations are rising, and grid performance is a major factor in customer experience and satisfaction. Some customers have a higher tolerance for outages than others, but Net Promoter Score® analysis shows a clear trend: the more outages the higher the percentage of detractors (see Figure 2).
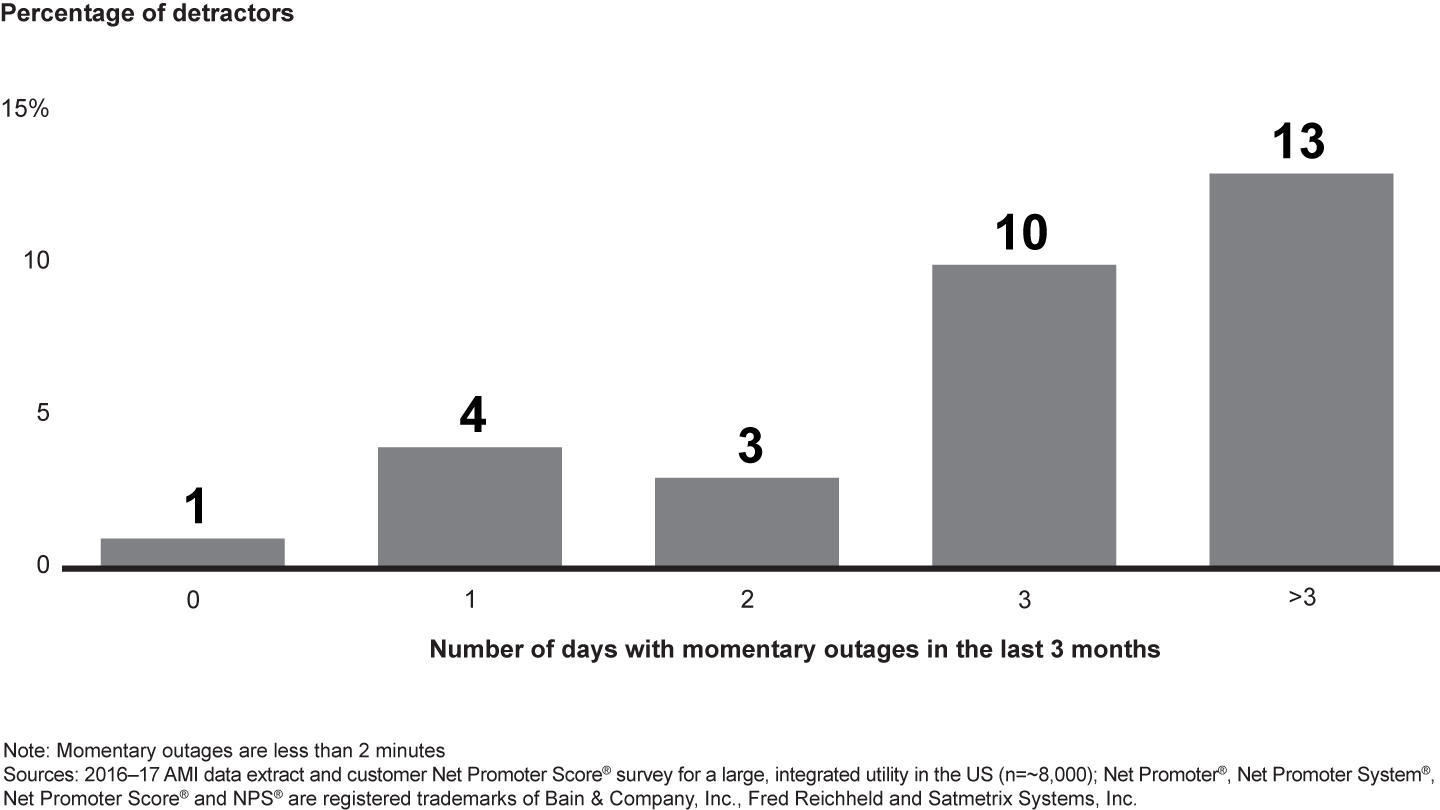

To maintain a good customer experience, some utilities overinvest in service recovery and other O&M functions, such as clearing trees near power lines. But there are smarter ways to pinpoint investment directly at the locations that will have the greatest impact on maintenance costs and customer experience.
Identifying the right investment opportunities
Bottom-up grid improvement, which builds a plan over time, can cost too much, adding more capital than a utility can effectively fund or deploy. Consequently, it is essential to determine an approach that links capital investment to improvements in reliability and cost reduction. Some utilities follow the “squeaky wheel” approach, responding to issues as they arise, or fixing the weakest circuits first. These investment patterns often add to depreciation levels, squeezing out other cost items and reducing the degrees of freedom for other important activities, like keeping lines clear of vegetation. In some cases, utilities have developed a plan for increasing reliability but are constrained by available funds, and are unable to address the prescribed needs of a sprawling geographic area. Many investments underdeliver on improvements in customer experience or reductions in cost due to their limited scale.
Leading utilities recognize that traditional approaches are not as effective as they need to be, and so they have worked to understand customer requirements and their performance at a granular level, by geography and segment. They link that data to real experience, often by analyzing billions of power delivery records collected at the meters using advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), as well as substation and line performance data. They can then correlate the data with the actual assets deployed (including details on make, model, age and quality) and with real data on maintenance and operations.
Where utilities have done this and deployed capital efficiently (for example, in better circuit design, more undergrounding, more solid-state sensors and switchgear), reliability has increased dramatically, as the frequency and duration of outages has decreased (see Figure 3). For example, NextEra Energy invested capital in its grid with the specific intention of boosting reliability to improve customer service, raising its position as a leader in reliability, customer satisfaction and cost position.
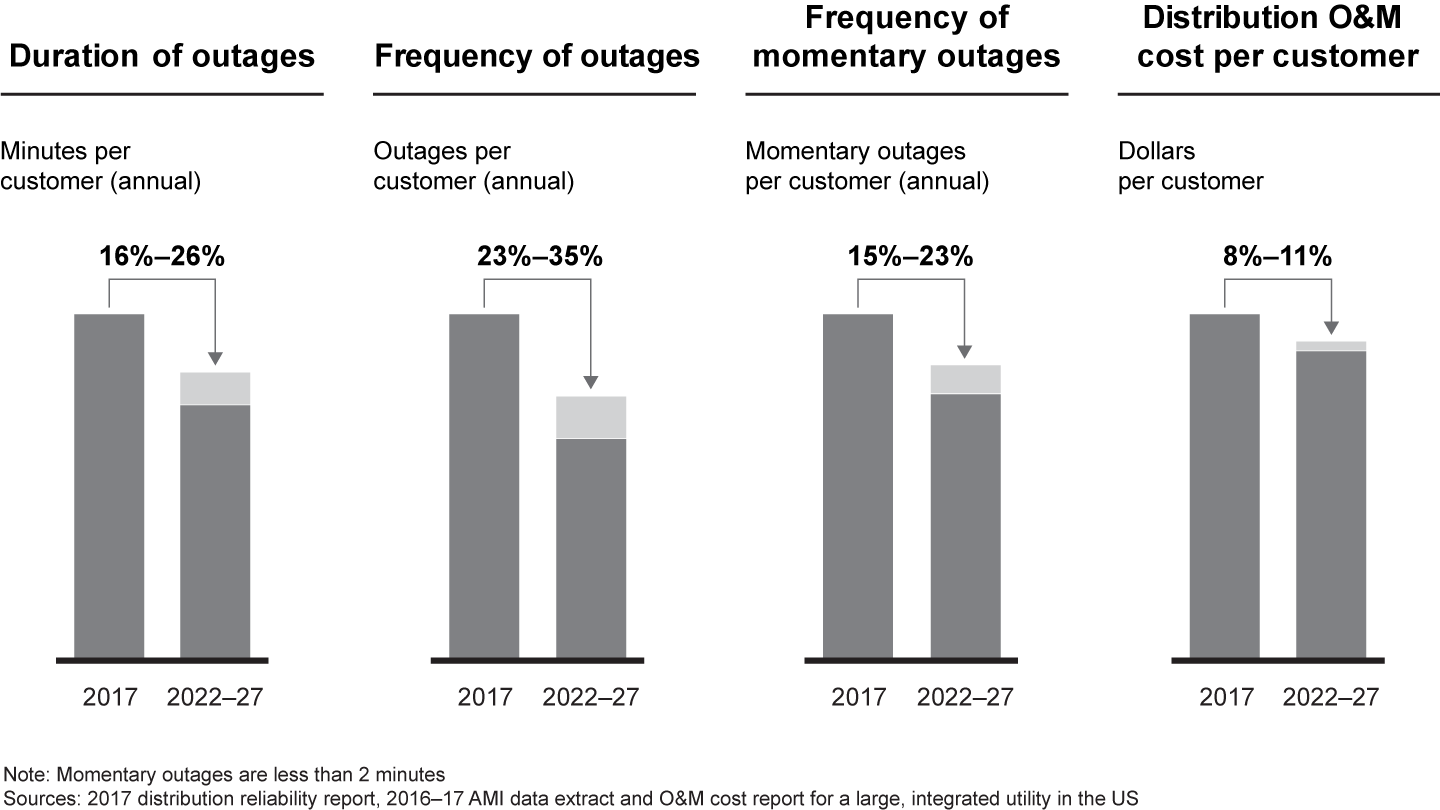

The results of programs like these can be dramatic—improved reliability, lower costs, a better customer experience and investment of new capital in a grid that desperately needs it.
Elements of a successful modernization initiative
Utilities that do this well get three things right.
First is a clear commitment to customer experience. Customer satisfaction levels are ultimately the benchmark against which success is measured: Is the grid reliable enough to deliver the experience that customers demand? Traditional measures of reliability on the average duration and frequency of outages across the system—including the system average interruption duration index (SAIDI) and the system average interruption frequency index (SAIFI)—ignore what a customer experiences. Metrics like the momentary average interruption frequency index (MAIFI) and CEMI-5 (customers experiencing more than five interruptions of a minute or more in the past year) are more relevant since they more accurately reflect the customer experience—and are therefore useful in guiding investment decisions.
Investments in the grid can improve the customer experience in other ways, too, by improving transparency and providing customers with more data about their usage. Leading utilities have a clear-eyed view of these connections and plan their grid modernization programs around them.
Second, senior leadership must be able and willing to ruthlessly prioritize capital investments. Utilities have to keep in mind that these investments will need to be proven out to often-skeptical regulators. Successful initiatives require a clear understanding of the potential for improvement and the parameters of judicious investment. More than a few utilities have tried putting in place large improvement plans, only to be rebuffed by regulators who were unconvinced of the value that would accrue to customers from these investments.
Finally, leaders recognize that they need to bring the right capabilities to bear. This includes a sophisticated approach to advanced analytics, often supported by partners with strengths in data engineering, who can help utilities crunch the information and draw the right insights. Part of the puzzle is also to ensure an adequate supply of talent: This only works if there is enough qualified labor, both internal and contracted, to get the job done—and not only those who can operate heavy machinery and climb poles, but also those who can tap the power of automation and other new technologies.
For executives eager to get started, consider four principles of action essential to any grid modernization plan.
- Start with customer experience. Go beyond standard industry metrics (SAIFI, SAIDI) to understand customers’ experience with outages. Where is the tipping point at which they become detractors?
- Create similar clusters of circuits. Not all parts of the system are equal. Determine how to address each part, depending on its needs and the opportunities. Find ways to improve performance differences and correlate reliability with O&M performance.
- Analyze the power delivery system. Clearly identify the root causes of performance issues and areas of strength and weaknesses, including labor, assets and materials. Identify the cause of interruptions, from the high-voltage lines down to the customer feeder and back, to locate the pain points.
- Develop a prioritized investment and deployment plan. Establish internal mechanisms to execute the plan, including organization structure, governance, metrics, multiyear linked capex, O&M plans and the right sourcing relationships with critical suppliers.
As investor interest shifts from power generation to grid modernization, utilities have the opportunity to dramatically improve the reliability and resilience of their T&D infrastructure. With regulators keeping a close eye on investments that will increase the rate base, utility executives must be able to demonstrate the benefits of these initiatives, in terms of improved reliability, lower O&M costs and happier customers. A strategic investment plan that includes sharp analysis of customer sentiment as well as a clear understanding of the grid’s pain points is essential to a successful program.
Dedra Casey is a manager and Pratap Mukharji a partner in Bain’s Atlanta office. Martha Eggenberger is a principal in Toronto, and Jason Glickman is a partner in San Francisco. All four work with Bain’s Global Utilities practice, which Jason leads in the Americas.
Net Promoter®, Net Promoter System®, Net Promoter Score® and NPS® are registered trademarks of Bain & Company, Inc., Fred Reichheld and Satmetrix Systems, Inc.