記事

A few years ago, Google hung a sign in its famously gourmet cafeteria explaining that people with bigger dishes are inclined to eat more. Small-plate use quickly jumped by one-half, to 32% of all plate traffic. The sign is a “nudge,” a simple, subtle cue that prompts people to make a better decision, to behave in a different way.
Grounded in insights from the field of behavioral economics, nudges have had broad impact in recent years. In one form or another, they’ve helped workers increase their rate of retirement savings in the US, tuberculosis patients stick to treatment plans in Moldova, police avoid phishing attacks in London, and teachers apply for hard-to-fill rural posts in Australia. The popularity of nudges as a tool for changing behavior dates in large part to the 2009 publication of Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth, and Happiness by Nobel Prize–winning economist Richard Thaler and Harvard Law School professor Cass Sunstein. Last year, the duo updated their bestseller, publishing Nudge: The Final Edition.
Well-designed nudges influence behavior and the choices people make in helpful ways, but they may not always be enough. “Nudge is part of the solution to almost any problem,” Thaler has said, “but is not the solution to any problem.”
For complex behavior or behavior occurring in a complex context, supplement nudges with other steps that activate and sustain behavior change. We know quite a lot about habits and behavior change today thanks to the work of academic scholars including Wendy Wood, BJ Fogg, and Katy Milkman, among others. Insights from cognitive behavioral science also underpin tools supporting personal habit changes like Noom for diet and Fitbit for exercise. Organizational change is complicated, depending on hundreds, or even thousands, of people shifting their behaviors in complex and varied contexts. The challenge is to design approaches that make it easy to do the “right” thing and hard to do the “wrong” thing, and are fulfilling when people succeed.
Traditional approaches to facilitating organizational change—like communication and training campaigns—are necessary, but often insufficient. Nudges help. So does something B.F. Skinner, a pioneer of behavior analysis, recognized the importance of long ago: reinforcement. We behave in a certain way because it works for us, because it’s easier, faster, safer, or appreciated. It is reinforced. If we want to change that behavior to something more aligned with our organization’s long-term goals, but perhaps harder, slower, or awkward, we must find ways to reinforce the new behavior.
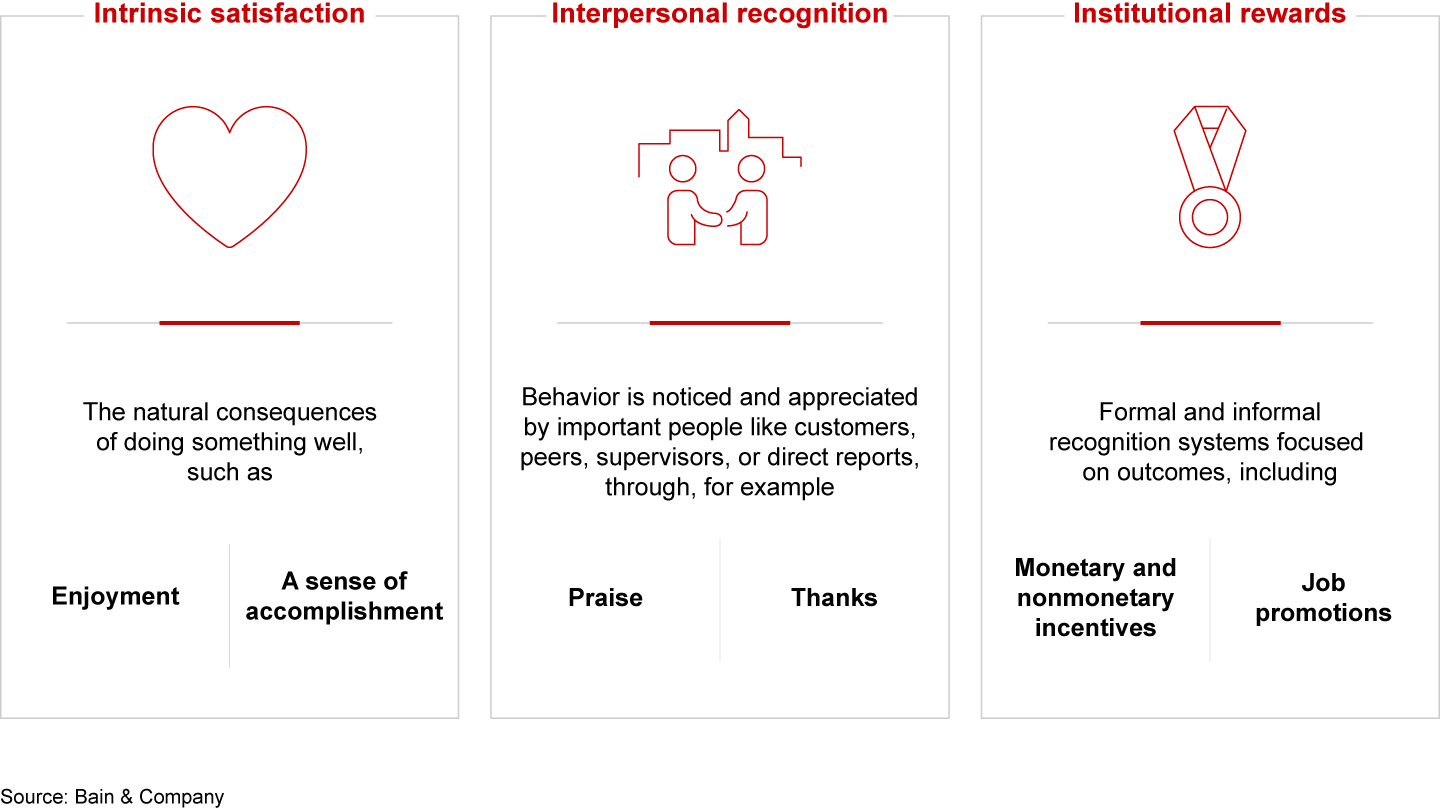
There are three categories of reinforcers: intrinsic satisfaction, interpersonal recognition, and institutional rewards (see Figure 1).
Intrinsic satisfaction is a natural consequence of behavior that a person finds important and leads to personal accomplishment. Whether it’s helping a customer solve a problem or making progress toward a goal one small step at a time, intrinsic satisfaction keeps us going. It can be eroded by sources of friction, including competing priorities, complex processes, ineffective tools, lack of appropriate autonomy, or the absence of a shared sense of purpose.
Interpersonal recognition works because it’s rooted in the human need to connect with the important people in our life. Sincere appreciation from a peer, customer, manager, or direct report is valuable, and one way to make sure people hear it is to embed rapid feedback loops into daily routines, the way the Net Promoter System℠, for example, connects employees with customer feedback.
Formal institutional rewards, including monetary and nonmonetary incentives or consequences for adhering to professional standards, are important but generally not sufficient to change behavior on their own. These mechanisms are limited by their focus on outcomes rather than behavior and because they occur relatively infrequently. A pay review, for example, is likely to occur at the end of the fiscal year, making it harder to link to specific behavior as it occurs.

By aligning reinforcers from all three categories, organizations give themselves the best chance of successfully supporting important new behaviors. An organization adopting an Agile operating model, for example, taps into all three. Intrinsic satisfaction is boosted because Agile links an individual’s work to important, larger organizational goals while breaking that work into smaller, achievable steps. Agile rituals tap into interpersonal reinforcement. The retro (from “retrospective”), for example, is an Agile practice of openly sharing feedback at the end of a sprint about what worked and what could have been done better. And in time, many Agile organizations end up rethinking their institutional rewards too, redesigning how they measure and compensate individual contributions in a way that keeps institutional friction from interfering with an Agile approach to work.
Several years ago, a global consumer products company’s leaders discovered from a staff survey that their teams didn’t find them inspirational. This came as a surprise, and the leaders took the feedback seriously. Together they agreed on a half-dozen specific behaviors they’d cultivate in the hopes of empowering their teams and improving engagement. They then designed upward feedback loops to help assess progress, interpersonal reinforcers in which direct reports could comment anonymously on managers’ leadership behaviors. Quarterly surveys asked how trusting, respectful, and inspiring leaders were, and how frequently employees saw their leaders exhibit those behaviors. Acting on that feedback paid off: Employee engagement scores improved in the parts of the business where leaders made the most progress. These loops were one aspect of an overall behavior change approach that also included a number of nudges, capability building, and better communication.
A steady stream of insights from the growing field of behavioral science is helping organizations learn new and useful approaches to behavior change challenges all the time. By learning from scholars, including those mentioned earlier, and by combining strategies, including nudges and reinforcers, organizations can effect robust behavior change, benefiting employees, customers, and the business overall.
Net Promoter®, NPS®, NPS Prism®, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks, and Net Promoter Score℠, NPSx℠, and Net Promoter System℠ are service marks of Bain & Company, Inc., NICE Systems, Inc., and Fred Reichheld.