論説

概要
- Companies that lead in automation investment wind up reducing costs via their automated processes by more than twice the amount as laggards, Bain’s new survey finds.
- Beyond cost savings, automation frees up staff to do higher-value work, speeds up processes, and improves customer experiences.
- Proficient companies look for automation opportunities across the entire value chain.
- Generative artificial intelligence helps accelerate adoption of automation as employees find it easier and faster to automate tasks.
Automation is booming across virtually all industries, but the returns on automation investments are skewed toward the early and in-earnest adopters. Lockdowns following the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic prompted many companies to reevaluate how they operate and to accelerate their automation programs. The urgent need for business continuity and resilience motivated such investments, and companies had high expectations for success.
Two years later, what do we see? Well, according to Bain & Company’s new survey of 906 automation executives throughout North America and Europe, the firms that invested most heavily have met their lofty expectations, while laggards have fallen further behind. Experienced companies have been reinventing their businesses by using automation to support cost savings and growth.
In banking, HSBC brought in artificial intelligence (AI) and automation to help spot money laundering, fraud, and terrorist funding. Package delivery giant UPS uses AI for route optimization, saving millions of gallons of gasoline and reducing carbon emissions as a result. In consumer products, Procter & Gamble uses AI and automation to model inventory levels in most of its product changes, saving roughly $60 million per year.
Now, recent advances in generative AI systems, such as OpenAI’s GPT-4, are poised to accelerate adoption of automation. In two separate Bain surveys, we found broad uptake of this technology. In a survey of about 500 cross-industry enterprise decision makers, we heard that around 40% are adopting or currently evaluating a variety of generative AI use cases—namely, embedding ChatUX into their offerings, software development and IT administration, contact centers, functional knowledge assistants, and marketing. And in a focused survey of 150 engineering leaders at software companies, we found that almost 60% of them are rolling out or have already rolled out coding assistants for software development.
Every penny counts
Cost saving figures prominently among the best companies in our new automation survey. Automation leaders—that is, companies investing at least 20% of their IT budget in automation—were able to reduce the cost of processes addressed by automation by 17%. Laggards—companies investing less than 5% of their IT budget in automation—achieved only a 7% reduction in costs (see Figure 1).
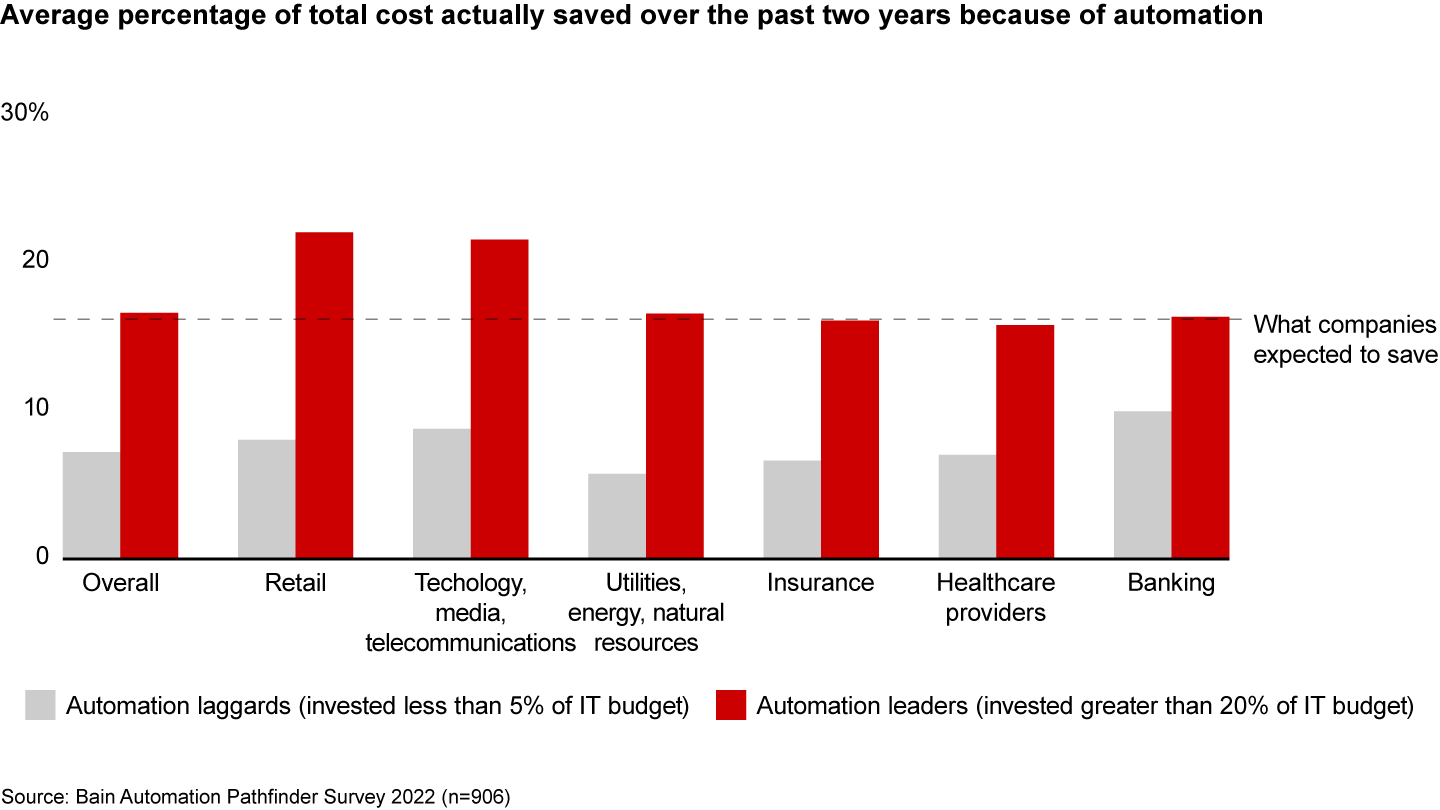

This gap persisted across industries. Retailers, for instance, saw heavy disruption during the pandemic as government restrictions and consumer caution curtailed store traffic and expanded digital channels. Retailers that invested heavily in automation were able to reduce costs by 22% through automation programs vs. 8% for laggards.
Retailer Sam’s Club used Brain Corp’s AI-infused robotics to roll out inventory scan towers that have been added to its existing fleet of autonomous scrubbers. The retail club deployed these tools chain-wide to eliminate low-value activities such as mopping floors and counting stock. This freed up associates to ensure that products are available on shelves, priced correctly, and findable, ultimately making it easier to engage with customers. All clubs can access critical inventory data in real time, which they can use to better inform decision making, operate more efficiently, and provide a better experience for customers.
What leaders do differently
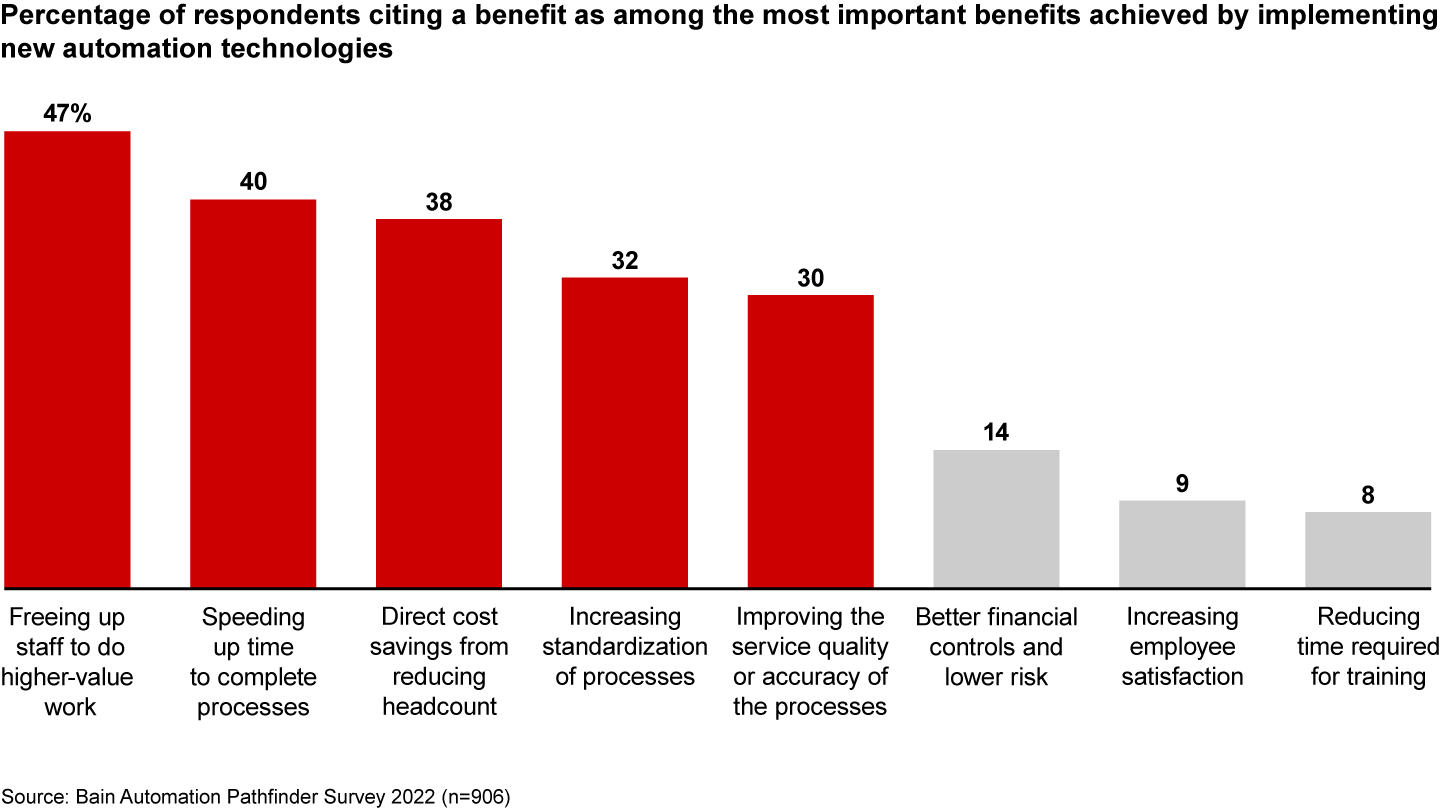
Beyond cost savings, automation affords other important benefits, respondents reported. Automation frees up staff to do higher-value work, speeds up processes, and improves customer experiences (see Figure 2). Telefonica, for instance, is experimenting with automated sales models, starting with airport customers.

No wonder, then, that automation leaders are doubling down. Some 29% of the leaders are investing significantly more than their already elevated 2020 investments. Meanwhile, only 14% of laggards are looking to invest significantly more, down from 27% in 2020.
Larger investments are just part of the story. Leading firms share several characteristics that help them raise the return on those investments.
They look for opportunities across the entire value chain. Although the early targets for automation often come in general and administrative as well as operations areas, broader benefits exist across a company’s value chain. Companies produce the largest labor time savings by looking beyond traditional back-office activities to front- and middle-office processes. A task-by-task approach typically is too fragmented to generate big results. That’s why leading companies redesign processes end to end, using a combination of different types of automation. They blend automation with other redesign techniques, such as changes in policies, roles and responsibilities, process steps and hand-offs, and behavior. Some reinvent the entire business.
As an example, Capital One has a diverse set of AI projects, such as improving the mobile app experience for consumers and building developer tools for the organization’s engineers. Capital One’s Auto Navigator, a machine learning–based application, prequalifies users for auto financing and can underwrite a loan in a fraction of a second. With the launch of the Capital One Navigator Platform, consumers can customize their down payment, trade-in, and term length to calculate a payment that works best. This allows dealers to work more efficiently and accurately by showing them what the customer can afford based on available inventory. Auto Navigator has helped Capital One increase loan originations, and it is one reason why Capital One Auto Finance ranks highest among the luxury auto lender brands in JD Power’s 2022 US Consumer Financing Satisfaction Study.
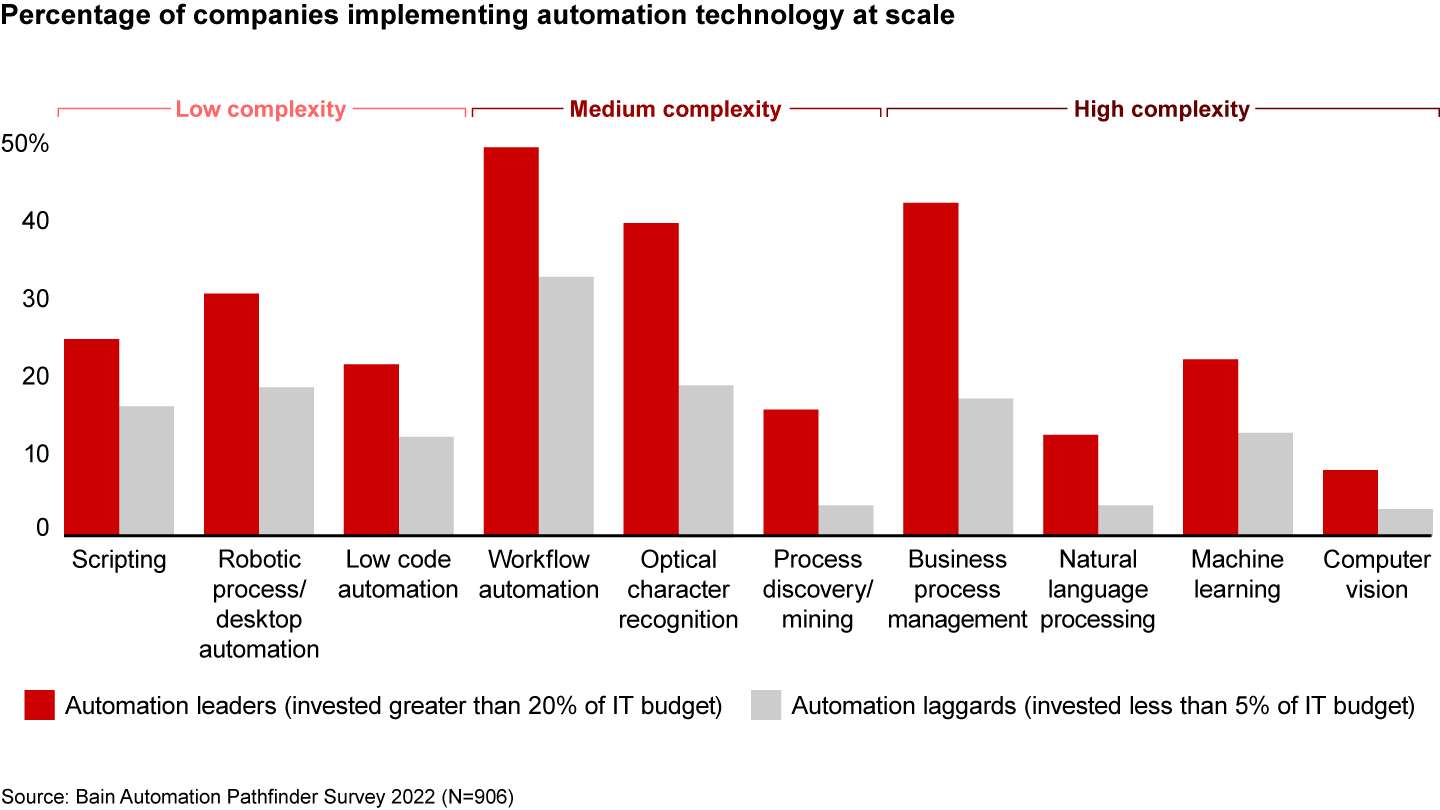
They have more mature implementations across the board. Because many of the leading firms have deployed automation longer than others, they’ve had the chance to apply these tools to more processes and at a broader scale. Applications include robotic process automation, workflow automation, and natural language processing (see Figure 3). Complex, primarily AI-driven forms of automation, such as natural language processing and machine learning, still have relatively low penetration, but we expect them to accelerate during the next wave in automation.

Given its broad range of potential uses, generative AI, in particular, should accelerate adoption of these more complex technologies (see Figure 4).
And generative AI enables automation in three ways.
First, it augments or replaces digital tools through copilots or assistants that improve the quality of existing applications. HubSpot, a software provider for sales and marketing organizations, launched ChatSpot.ai so that users can ask questions and provide detailed instructions for a task through natural language in a chat interface. This allows organizations to send emails or review leads faster and more effectively.
Generative AI can also augment or replace other forms of AI. Consider Arria’s natural language generation, which turns data into textual commentary on financial reporting. Arria layers on generative AI to summarize, enhance, and translate commentary. In early trials, Arria reports that users achieve an 85% boost in productivity by adding generative AI to their current tools.
Beyond these extensions, generative AI will enable new uses for automation. An example is creating the first draft of a legal contract. Ironclad, a contract life cycle management software provider, recently released an AI Assist feature that supports legal contract review. AI Assist generates tracked changes for contracts that can be accepted or rejected with a single click.
They have an effective operating model. From senior executive sponsorship to incentives, the leading companies have adjusted their operating model to accommodate automation.
In the area of governance, for instance, the leaders tend to take a centralized approach. A dedicated center streamlines decision making, minimizes repeated mistakes, and legitimizes automation efforts. Companies with a dedicated automation center of excellence have realized savings of 14%, our survey found, vs. just 10% for those without a center. Yet more than 40% of respondents don’t have such a center, relying instead on a federated model in which each office or region has its own small group.
The gap in automation performance will likely widen further
Propelling the leaders is the dynamic that as companies gain automation experience, they can successfully implement more complex technologies. Our survey found that 82% of companies that have successfully deployed high-complexity automation technologies at scale have been deploying automation for more than three years. Firms that already deploy more complex technologies have realized an average of 18% in cost savings, more than twice that of firms limited to low-complexity automation. These leaders will likely gain a favorable position from which to capitalize on the expected wave of generative AI adoption.
As companies expand and refine their uses of automation tools, they advance to an autonomous system, reducing the need for human intervention to constantly review and sign off at stages of the automated process. These systems will also increase speed and transparency in many customer experiences.
At a crossroads, the best next steps
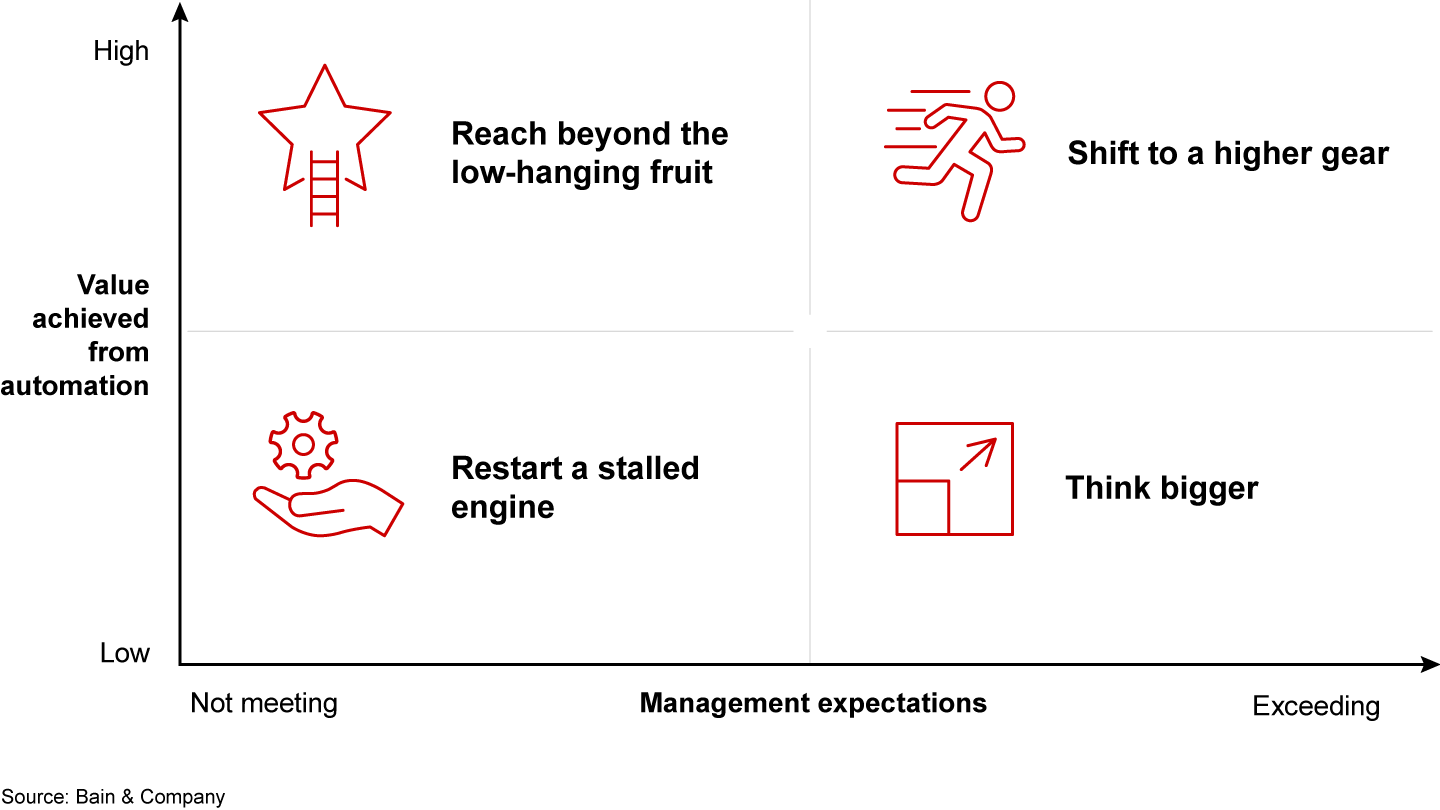
Companies that lag the leaders in their industries may still have a chance to catch up. But it’s critical for managers to understand where their organization stands on automation—and if the program has hit a wall, what they can do; or if a company already leads its competitors, how it can advance even further. Organizations typically find themselves in one of four positions from which they’ll need to take the following actions (see Figure 5).
Restart a stalled engine. Companies in this position have invested in a handful of automation tools, mostly focused on individual tasks of relatively small value, so they have not fully achieved the expected financial benefits. The remedy here starts with sponsorship from a major business or functional executive who can elevate automation as a higher business priority. Other useful actions include revising governance, the technology stack, and the funding model that identifies and realizes automation opportunities.
Reach beyond low-hanging fruit. These firms have implemented automation for simpler processes. They may have implemented automations that please business functions, yet senior executives remain impatient with the pace of expansion to new business areas. To expand automation, companies may want to elevate its importance in their business strategies, starting with sizing and detailing what full value might look like. Seeking opportunities beyond cost savings, such as automating processes to improve the quality of customer service or to support the launch of a new product, will widen the organization’s focus.
Think bigger. This group has applied automation to an entire customer journey, but usually just one or two. Now, they can expand automation solutions to other customer journeys by establishing cross-functional teams to scout for new opportunities. And they should consider other approaches to cost savings and productivity gains, such as business process redesign.
Shift to a higher gear. Although these leaders have implemented automation to high-value uses, they still have a long list of smaller opportunities such as back-office processes. In addition, they can reinvent the customer experience through, for instance, easier, more convenient digital channels. They can nurture employee-created automation and use more complex complementary technologies such as generative AI. The most advanced companies can use automation to disrupt markets and create a competitive advantage by, say, devising a more profitable product or service offering to enter a new market.

* * *
Although the gap has widened, it’s not too late for laggards if they step up investment now with a centralized team that selects the highest-value processes. Even newcomers to automation can use recent technological changes, such as generative AI, to their advantage. With the right investment strategy and execution, companies can leapfrog their rivals and automate their way to more efficient and faster operations.