Engineering and R&D Report

概要
- Executives forecast a 10% compound annual growth rate for engineering and R&D spending through 2026, fueled by investments in digital engineering.
- Investing in engineering and R&D during a recession can help companies pull ahead in the innovation race.
- During past downturns, growth in engineering and R&D spending was more resilient than GDP growth.
This article is part of Bain's 2023 Engineering and R&D Report.
The innovation race has become more costly than ever. Investment in engineering and R&D (ER&D) as a percentage of revenue has increased significantly since 2016 (see Figure 1). And despite a looming recession, executives expect the growth in ER&D spending to continue rising, according to a recent Bain & Company survey of more than 500 senior executives (see Figure 2).
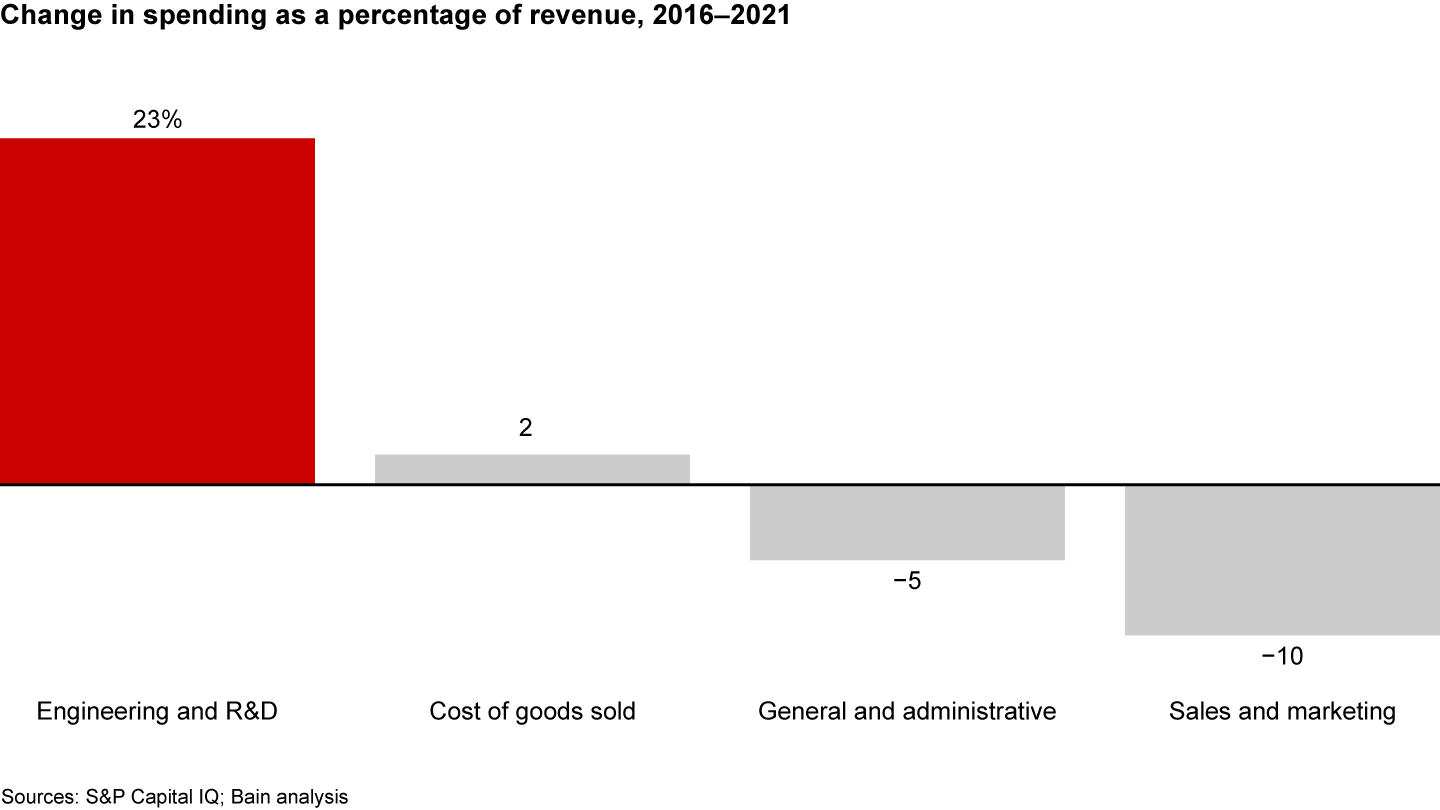

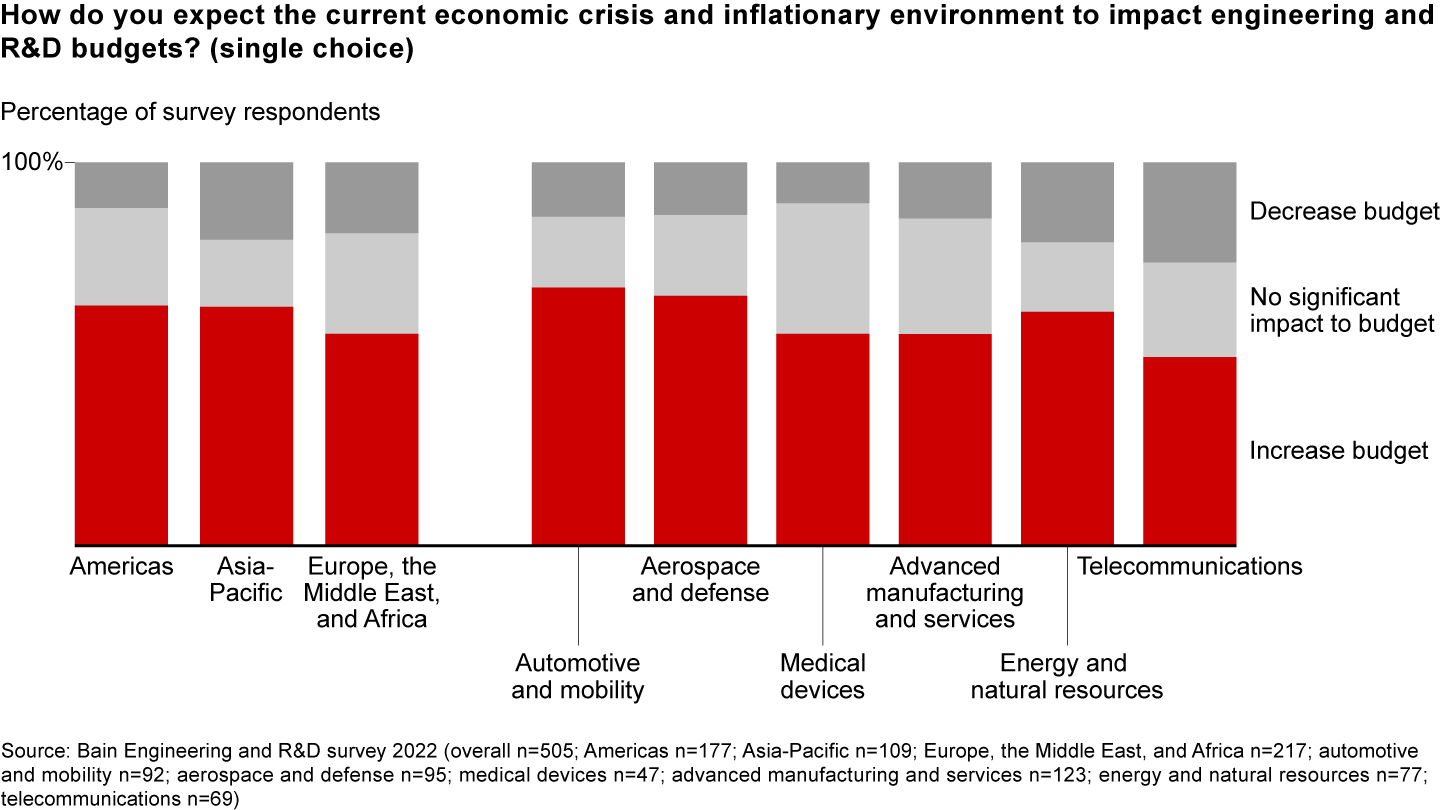

ER&D is a core function for many large companies. Historically, these firms have focused on making products better and cheaper. Today, a growing number see ER&D as a strategic capability that will determine their future success and shape new business models. Investments in ER&D not only improve products but also increasingly reinvent or disrupt parts of the business.
ER&D costs are rising, in part because disrupting markets (or responding to disruption) is more difficult than improving an existing product—even with greater availability of data and computing power. A good example is Moore’s Law. The number of researchers required in 2017 to achieve the famous doubling every two years of the density of computer chips required 18 times greater the number of researchers that a company needed in 1971, according to a report by the National Bureau of Economic Research.
Overall, spending on ER&D is set to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10% between 2022 and 2026 (see Figure 3). As spending soars, leadership teams are redoubling their efforts to achieve a solid return. For the purposes of our analysis, we define ER&D as the wide array of activities aimed at developing new products and services and improving existing ones. These activities include early foundational research, the design testing and verification of products as well as developing infrastructure such as a manufacturing plant, and post-production support.
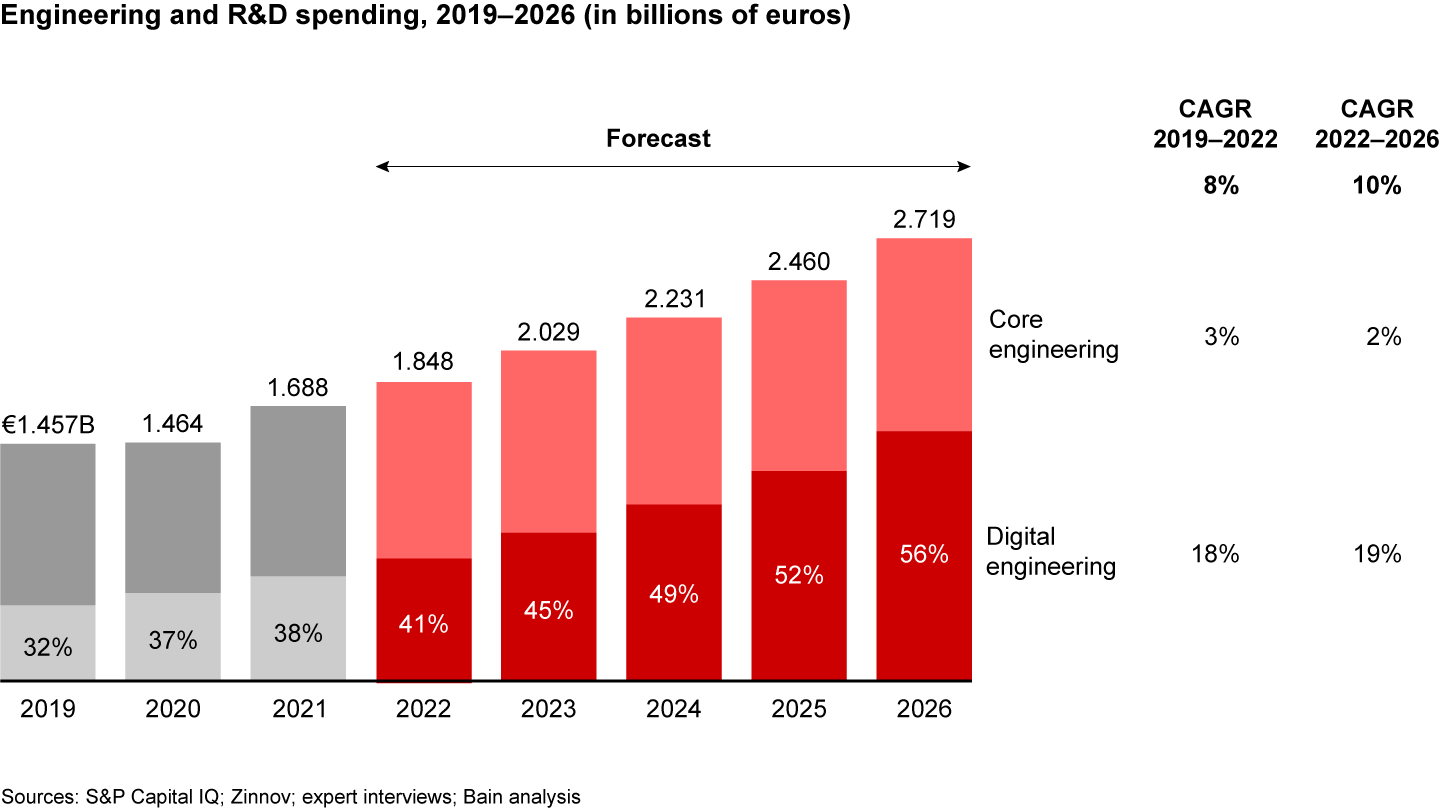

A key factor fueling higher ER&D spending is digital engineering, the discipline of developing new, connected, and digitally enabled products and services using technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and cloud computing. Examples of digitally engineered products include autonomous vehicles and production plants wired for Industry 4.0. Executives expect investments in digital engineering capabilities to rise even faster—with a CAGR of 19% between 2022 and 2026 nearly double the pace of overall ER&D spending.
In fact, investing in ER&D during a downturn can help companies pull ahead in the innovation race. During past recessions such as the 2008–2009 global financial crisis, ER&D spending was more resilient than GDP growth, according to Bain research. And between 2014 and 2021, global ER&D spending grew nearly four times faster than GDP. One explanation is that a large body of engineering and R&D work typically spans longer time horizons and thus tends to be less fungible than other types of spending. The most successful companies even use recession years to outinnovate competitors by acquiring companies at lower multiples, poaching critical talent, and investing in intellectual property and R&D; downturns that trigger large-scale layoffs in the technology sector also offer ER&D companies an opportunity to hire much-needed talent.
Our research shows that five major challenges for ER&D-focused companies are fueling the innovation race—namely, shortening time to market; making new technologies more affordable; embedding digital capabilities into hardware-centric engineering teams; exploring new frontiers of value creation; and reengineering for environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) strategies.
1. Shortening time to market
Engineering companies face growing pressure to bring new products to market faster and to incorporate cutting-edge technologies into the R&D process to generate a stronger return on investment (ROI). For example, powerful chipsets and microprocessors are enabling products and solutions based on AI. That shift supports differentiation, increases revenue and profits, and speeds time to market. But it also requires new capabilities.
The lengthy and complex process of drug discovery illustrates the challenge. A new Massachusetts Institute of Technology deep learning model designed to identify drug candidate molecules performs that task 1,200 times faster than existing computational models. Advances in AI for drug discovery are likely to accelerate in the coming years, and pharmaceutical companies without in-house AI or deep learning capabilities will have to acquire that capability. Many are likely to partner with or acquire promising biotech start-ups rather than build their own technology from scratch.
2. Making new technologies more affordable
When companies shift to new technologies such as cloud-based software or electric cars, the immediate result is often higher costs since products need to be redesigned from scratch. Mass-market electric cars are still more expensive than their combustion-engine equivalents, for example. But the firms that lead in bringing down the cost of new technologies gain a significant competitive edge. Automakers such as Hyundai and Tata Motors are investing heavily to build more affordable models. Hyundai is planning to build a small electric car that would cost less than $20,000, and Tata recently launched preorders for an electric car that will cost $10,000.
3. Embedding digital capabilities into hardware-centric engineering teams
Digital technologies underpin new business models. They also help organizations move from a cyclical, multiyear R&D process to a continuous one. One leading German engineering company has increased its digital training budget by 10 times over the past three years, a move that more than doubled the number of workers with next-generation digital skills.
4. Exploring new frontiers of value creation
For many industries, searching for new ways of creating value means redefining business models to focus on outcomes instead of products. Siemens Building Technologies, for instance, is shifting from selling building products to providing a building performance management system that combines its traditional products with cloud-based solutions and edge computing, which is a form of computing done on-site or near the source of data, thereby eliminating the need for remote processing.
5. Reengineering for ESG strategies
As governments and industries set targets to achieve net zero emissions, industrial companies are rethinking their use of resources in an effort to move toward sustainable inputs and circular supply chains. One leading European metals processing company is increasingly deploying digital twins and thermodynamic modeling across its operations to better calibrate equipment and significantly reduce energy consumption.
Addressing the five challenges above amid engineering talent shortages and high attrition is even harder. Our research shows more than 70% of engineering and R&D companies report talent shortages, and many are losing engineers to tech competitors such as Alphabet and Meta.
Best practices for maximizing ROI
As the cost of innovation rises, leadership teams are rethinking ER&D strategies and redoubling their efforts to make them as efficient as possible. Successful companies ensure the highest ROI by following a few best practices:
- Redefine core vs. noncore capabilities. Leaders regularly assess which engineering capabilities are core, or key, to differentiating the business and winning new customers. Some capabilities are becoming critical differentiators, such as Industry 4.0 technologies for machinery and equipment companies. For instance, a leading industrial equipment maker specializing in pumps, compressors, and turbines recently reevaluated its product portfolio and engineering activities as part of its ESG strategy, choosing to prioritize the development of components, which can dramatically reduce energy consumption in its compressors and vacuum pumps.
- Centralize and democratize access to strategic technologies. Ensure technological capabilities are available to the entire organization and not siloed inside one division. One global medical technology company that previously had robotics and digital capabilities embedded in specific divisions has now created digital- and robotic-enabled healthcare platforms that combine the best capabilities in one place, accessible to all divisions. That allows the company to leverage those technologies for surgical equipment, orthopedics, and neurotechnology.
- Organize for speed. Deploy continuous development models. A leading European automaker is adopting a more Agile process to shorten its development cycles and innovate faster. In a first step, the automaker will shift to continuous software development for each car model. Over time, it will do the same for other parts of the development process. To prepare for that change, it is retraining thousands of engineers. The full migration represents a paradigm shift: Instead of completing a product cycle and starting a new one, original equipment manufacturers will continuously improve each car model and use software updates to keep digital features current. For automakers, the shift to continuous development means greater flexibility and faster time to market.
- Become a talent magnet. Rising attrition levels have made attracting and keeping engineering talent a top priority for many traditional ER&D companies. One solution is to develop what some companies call a technology hub in cities teeming with tech expertise. A second approach is to acquire software companies as cultural umbrellas that draw tech talent. Some companies embrace a bigger shift, transforming the culture of their engineering and R&D departments to appeal to young engineers. To do that, they flatten hierarchies, offer permanent learning opportunities, focus teams on the most exciting problems, and allow remote work.
- Play offense on innovation. Collaborate with external partners, including start-ups and other innovation sources, to accelerate the pace. Acquire new capabilities and technologies through M&A. Verizon, for instance, has created a new business incubator to develop its product ecosystem, including 5G, and explore adjacent technologies such as location technology and sensor intelligence. Verizon’s investments in these new business areas aim to further help the company innovate and outpace the competition.
Engineering-heavy companies face a once-in-a-generation strategic shift. Digital technologies offer the opportunity to reshape traditional ER&D businesses, but deploying them brings new challenges. Winners in the coming decade will be those that use those technologies to accelerate time to market, lower the cost of new products, and take a novel approach to value creation.