
In the aftermath of World War II, the US Air Force began studying why American fighter pilots often lost control of their planes. They initially suspected pilot error and poor training, but soon a different culprit emerged. The cockpits of US planes had been designed based on the average of 10 physical dimensions from a sample of 4,000 pilots, covering everything from torso length to chest circumference. The problem was that this “average” pilot simply didn’t exist. Instead, most men had one or more physical dimensions that differed significantly from the average. This meant their body fit awkwardly in the cockpit, making the plane difficult to control. The solution was to redesign the cockpit for the edge cases and introduce modifiable features, like adjustable seats.
Just like our physical dimensions, our personalities are also varied—and increasingly so. In less complex societies—such as the indigenous Tsimané tribe of Bolivia—researchers have found that personality traits tend to be fairly homogeneous and convergent. However, as anthropologist Joseph Henrich has shown, the emergence of the modern economy, with its specialized divisions of labor, has caused individuals to grow into increasingly distinctive social niches over time.
As personalities have fragmented, so have attitudes toward work. To explore these differences, we constructed a 10-dimension framework of attitudes, building off the existing literature in motivational theory and psychology. The 10 dimensions are:
- Work centricity: How much of my identity and sense of meaning comes from work?
- Financial orientation: How much does my level of income impact my happiness?
- Future orientation: Do I prioritize investing in a better future or do I focus on living for today?
- Status orientation: How concerned am I about being perceived by others as successful?
- Risk tolerance: Am I willing to take risks to improve my life if I might end up worse off?
- Variety: Do I prefer change or predictability?
- Autonomy: How much do I value being in control of my own work?
- Camaraderie: Do I see work as primarily an individual or a team effort?
- Mastery: How much satisfaction do I find in the process of perfecting my craft?
- Self-transcendence: How important is it to me to make a positive difference in society?
Far from a normal distribution, we found significant variation in scores on all 10 dimensions in all 10 countries covered in our research. In other words, thinking about what the average worker wants from a job no longer makes sense in the modern economy.

What Type of Worker Are You?
Six worker archetypes can help business leaders understand the messy world of individual personalities.
Despite the variation in attitudes from person to person, patterns do emerge (see Figure 2.1). We’ve identified six archetypes around which workers tend to converge (to find out which archetype best describes you, take our short quiz):
- Operators find meaning and self-worth primarily outside of their jobs. When it comes down to it, they see work as a means to an end. They’re not particularly motivated by status or autonomy, and generally don’t seek to stand out in their workplace. They tend to prefer stability and predictability. Thus, they have less interest in investing to change their future compared with other archetypes. At the same time, Operators are one of the more team-minded archetypes, and often see many of their colleagues as friends. At their best, they are the team players that form the backbone of the organization. At their worst, they are disengaged and lack proactivity.
- Givers find meaning in work that directly improves the lives of others. They are the archetype least motivated by money. They often gravitate toward caring professions such as medicine or teaching, but can also thrive in other lines of work where they can directly interact with and help others. Their empathetic nature typically translates into a strong team spirit and deep personal relationships at work. At the same time, their more cautious nature means they tend to be forward planners, who are relatively hesitant to jump on new opportunities as they arise. At their best, they are selfless, helping to build the trust every organization needs to function. At their worst, they may be impractical or naive.
- Artisans seek out work that fascinates or inspires them. They are motivated by the pursuit of mastery. They enjoy being valued for their expertise, although they are less concerned with status in the broader sense. Artisans typically desire a high degree of autonomy to practice their craft and place the least importance on camaraderie of all the archetypes. While many find a higher purpose in work, this is more about passion than altruism. At their best, they are able to solve even the most complex of challenges. At their worst, they can be aloof and lose sight of bigger objectives.
- Explorers value freedom and experiences. They tend to live in the present and seek out careers that provide a high degree of variety and excitement. Explorers place a higher-than-average importance on autonomy. They are also more willing than others to trade security for flexibility. They typically don’t rely on their job for a sense of identity, often exploring multiple occupations during their lifetime. Explorers tend to adopt a pragmatic approach to professional development, obtaining only the level of expertise needed. At their best, they will enthusiastically throw themselves at whatever task is required of them. At their worst, they are directionless and lack conviction.
- Strivers have a strong desire to make something of themselves. They are motivated by professional success, and value status and compensation. They are forward planners who can be relatively risk averse, as they opt for well-trodden paths to success. Strivers are willing to tolerate less variety so long as it is in service of their longer-term goals. They tend to define success in relative terms, and thus can be more competitive and transactional in their relationships than most other archetypes. At their best, they are disciplined and transparent. At their worst, their competitiveness degrades trust and camaraderie within the organization.
- Pioneers are on a mission to change the world. They form strong views on the way things should be and seek out the control necessary to achieve that vision. They are the most risk-tolerant and future-oriented of all the archetypes. Pioneers identify profoundly with their work. Their vision matters more than anything, and they are willing to make great personal sacrifices accordingly. Their work relationships tend to be more transactional in nature. Their vision is often at least partly altruistic, but it is distinctly their own. At their best, they mobilize their infectious energy to bring about lasting change. At their worst, they are uncompromising and imperious.
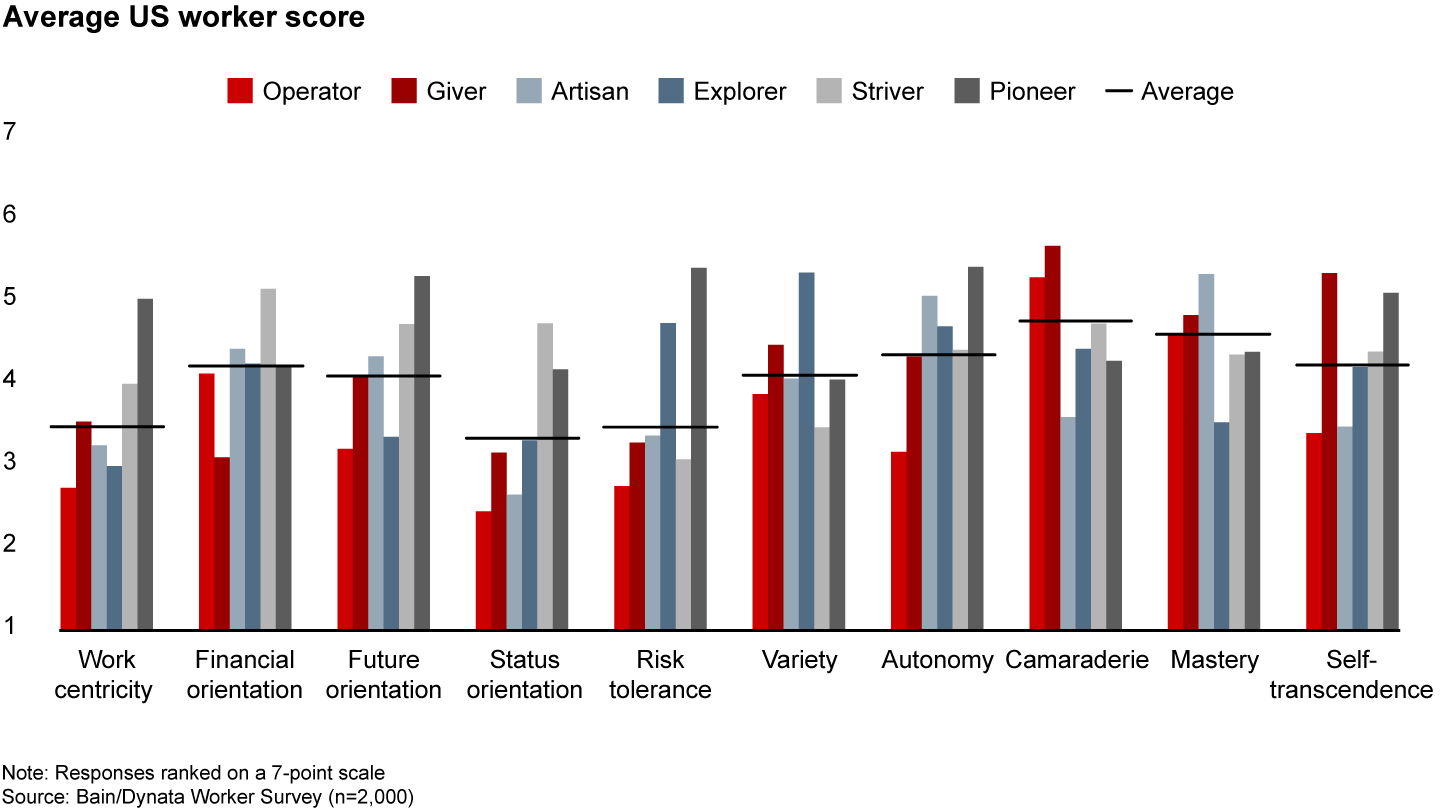

None of these archetypes is better or worse than the others. While a company full of Operators might lack the dynamism needed to compete in the modern economy, a company full of Strivers or Pioneers would undoubtedly collapse under the weight of conflicting egos. Instead, each archetype brings its own unique contribution to build a healthy, functioning firm.
It’s also important to recognize that while some workers present clear or even extreme manifestations of these archetypes, the line can be blurrier for others. Their distinctive set of attitudes may position them somewhere between two—or more—of these personas. Archetypes can also change over the course of a lifetime, as events and environments continue to shape workers throughout their careers. Business leaders should therefore view these archetypes as impressionistic rather than precise, a tool to help make sense of the messy world of individual personalities.

Six Worker Archetypes for the World Ahead
There’s no such thing as the “average” worker. Understanding six archetypes can help firms build an effective talent strategy.
We can see the attitudes of each archetype come through in workers’ rankings of different job attributes. Workers across all archetypes still rank compensation as their top attribute most frequently, showing that fair pay remains table stakes. But beyond pay, the story becomes more nuanced. Operators’ and Strivers’ lower risk tolerance means they place relatively high importance on job security. For Operators and Givers, a stronger desire for camaraderie translates into a higher ranking for good relationships with coworkers. Artisans place a relatively high importance on interesting work.
These archetypes help us better understand what it takes for different individuals to find a sense of purpose at work. For some archetypes, such as Pioneers and Givers, working in organizations with a clear social mission is often important. Strivers are more likely to find a sense of purpose in achievement, while Artisans may find it in mastery. For Explorers, it is likely to come from breadth of experience. Operators are more likely to find purpose outside of their work lives.
“These archetypes help us better understand what it takes for different individuals to find a sense of purpose at work.”
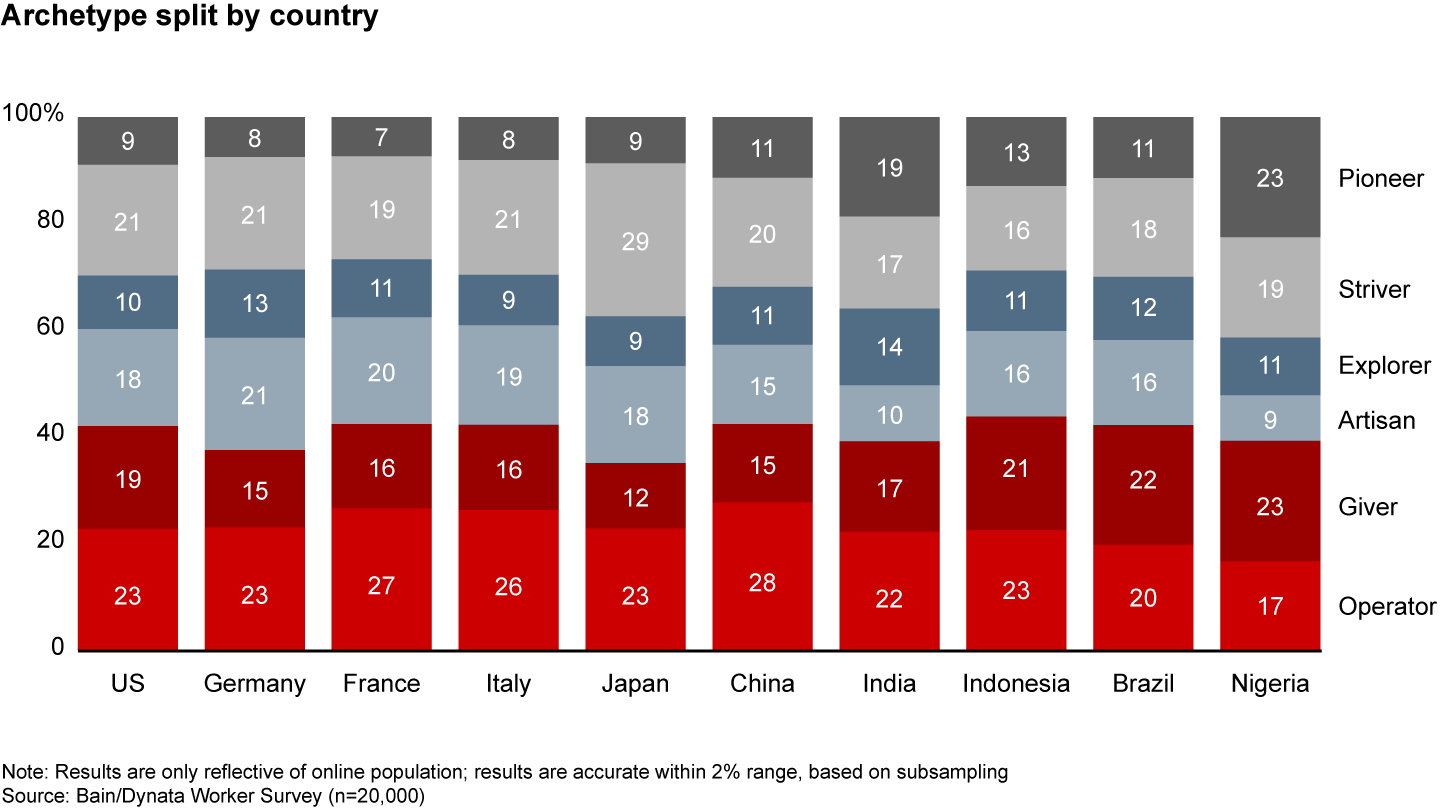
Looking globally, the six archetypes emerge across all 10 countries covered in our research. Different cultures exhibit different central tendencies across our 10 dimensions (see Figure 2.2). But the variation between countries is far less than the variation within them. That said, the patterns of scoring across countries differ enough to result in different mixes of archetypes around the world (see Figure 2.3).
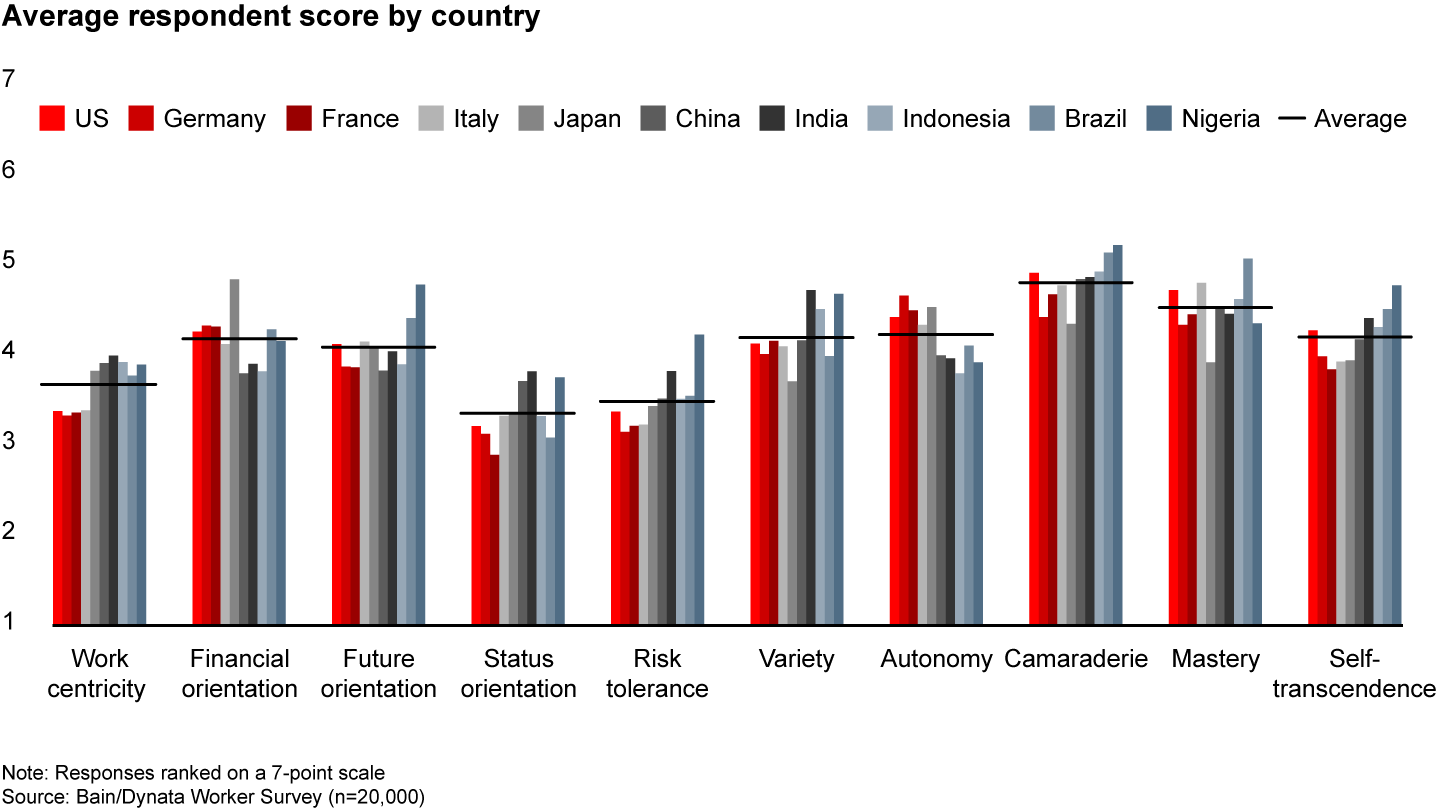


While the six archetypes can also be found across all demographic segments within a country, factors such as age and socioeconomics play a role in the frequency of different archetypes (see Figure 2.4). In the US, older workers exhibit an increased emphasis on mastery and autonomy, making them more likely to be Artisans. They also place a greater importance on self-transcendence in their job, making them more likely to be Givers. On the flip side, a decreased emphasis on status means older workers are less likely to be Strivers, and a lower tolerance for risk means they are less likely to be Pioneers or Explorers.
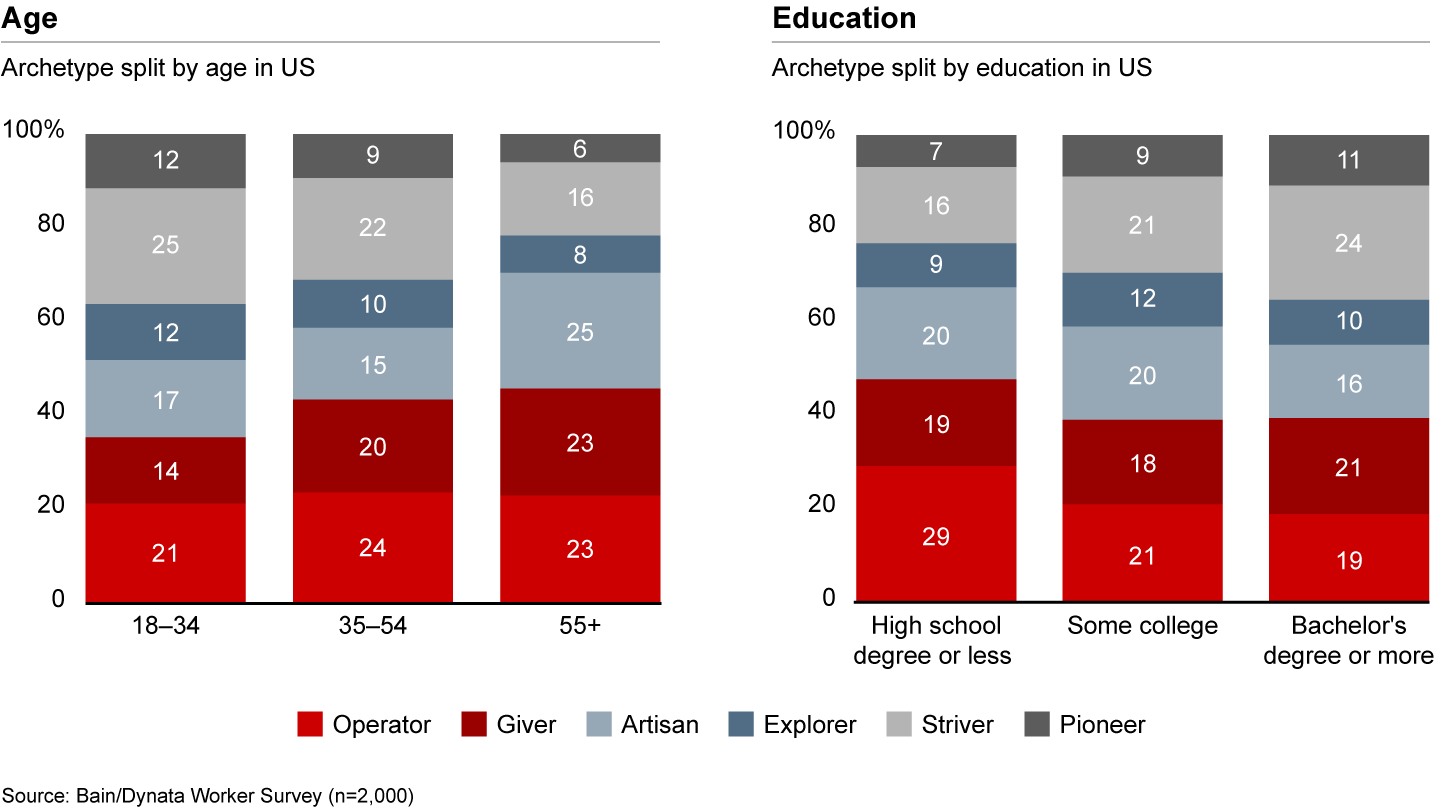

More educated—and therefore higher-earning—workers tend to score higher on autonomy, status orientation, future orientation, and self-transcendence. This translates into a higher share of Pioneers and Strivers, and a lower share of Operators.
These demographic factors contribute to the different archetype mixes across markets. For example, the younger populations of India and Nigeria likely skew these countries toward risk-tolerant archetypes, like Pioneers and Explorers.
Within some countries, we also see significant geographic differences. In China, workers in Tier 1 cities score much higher on risk tolerance than the population as a whole, leading to a greater share of Pioneers. In France, financial orientation is higher in Paris than the rest of the country, increasing the share of Strivers in the city.
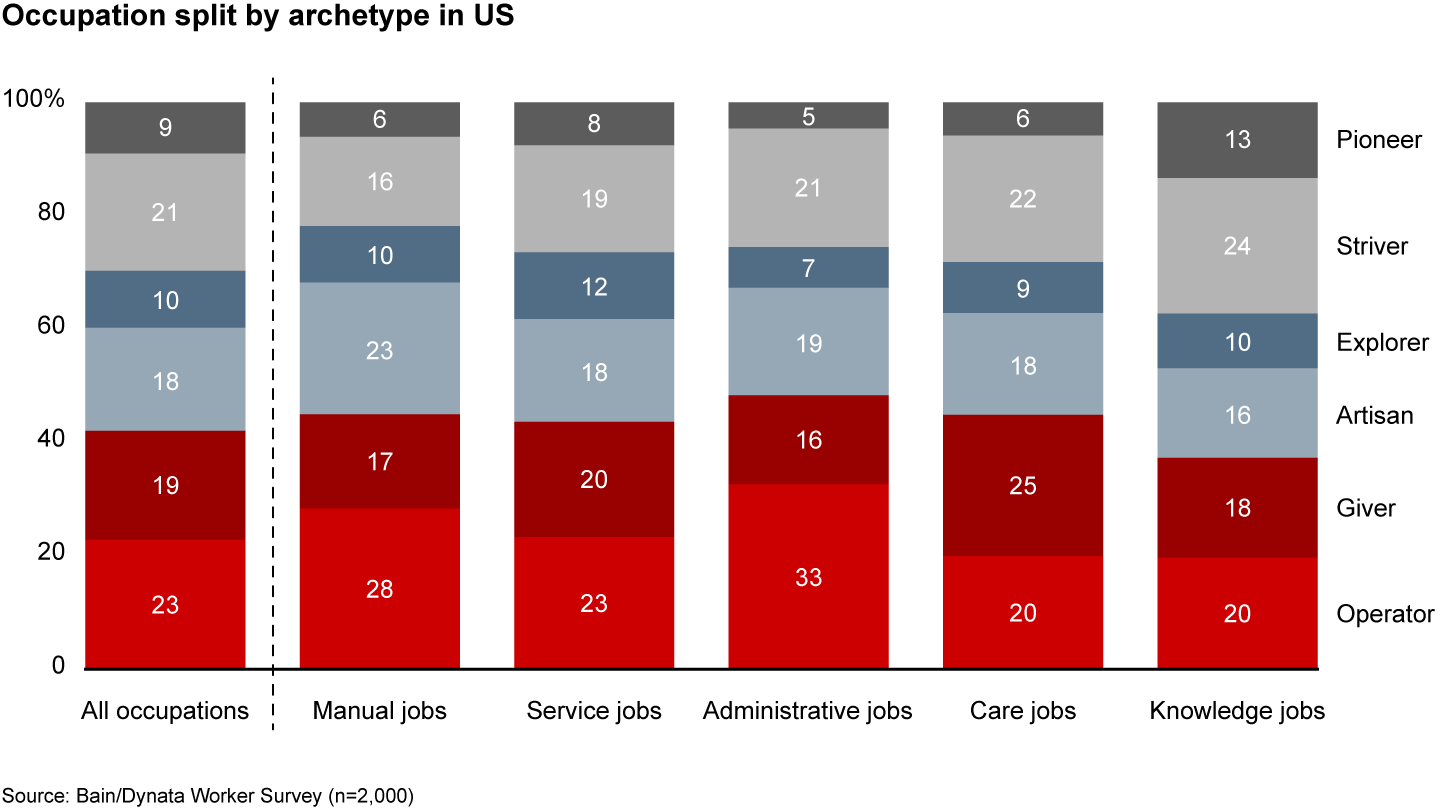
The archetype mix also differs across occupation types (see Figure 2.5). Manual workers, in occupations such as manufacturing, construction, maintenance, and logistics, are more likely to be Operators and Artisans. Administrative workers, in clerical and secretarial jobs, are the most likely to be Operators and least likely to be Pioneers. Care workers, in healthcare and education, are the most likely to be Givers. Explorers often gravitate toward occupations in service, such as hospitality, sales, and personal services. And Strivers and Pioneers are drawn to knowledge roles, in management, professional services, and technical occupations.

For the last group, it’s worth noting that business leaders’ attitudes toward work are far from representative of the population at large. For instance, 25% of US executives are Pioneers, compared with 9% of the nation’s working population. Business leaders need to recognize that their personal perspective of what a good job looks like won’t necessarily be shared by everyone in their organization, especially those on the front lines.
“Business leaders need to recognize that their personal perspective of what a good job looks like won't necessarily be shared by everyone in their organization.”
Looking at job satisfaction by archetype across occupations, we can see how different jobs tend to be better matches for some archetypes than others. Pioneers are 22% less satisfied in service jobs than they are in other jobs, on average, while Explorers are 12% less satisfied in administrative jobs than other jobs, on average.
The infrastructure for sorting workers into the right career paths has significantly improved in recent decades, from career counseling in schools to online job-searching platforms. However, the persistence of these types of mismatches suggests there is still substantial room for improvement in helping workers find jobs that will tap their full potential.

Rehumanizing the Way We Think about Work
Bain's Andrew Schwedel joined Christine Kashkari for a Barron's Roundtable virtual discussion on the future workplace.

About the Research
Data powered by Dynata, a leading global first-party data and insights platform.






