レポート

概要
- Bain’s new global survey of executives shows increased adoption of and satisfaction with two dozen customer experience tools. The gap in satisfaction widened between financial leaders and laggards.
- Covid-19 has changed consumer and workplace behavior in ways that are accelerating the use of many tools.
- It’s critical to select the appropriate tools for a particular use case, make a major effort and investment in a few tools, and integrate them into a well-oiled system. Returns are greater when tools are integrated within an IT system or with other tools.
- Rapidly shifting customer needs and priorities put a premium on Agile modes of in-market testing.
A retail health company advertising free consultations about a procedure wanted to raise the return on its campaign, as only 3% of leads eventually started the procedure. At the heart of the problem, the company had sorted potential customers into only two segments. By rigorously analyzing the journeys of each lead, the company created six segments and modeled the likelihood of customers in each segment showing up for their appointment. Using these segments and patient channel preferences, the company created more than three dozen automated marketing and scheduling journeys. As a result of these and other initiatives, completed consultations increased by more than 10% in the same clinics, flowing through to same-clinic revenue growth of more than 25%.

Customer Experience Tools and Trends
Our insights share how the right CX tools make customers’ lives richer and more fulfilling and strengthen a company’s economics by holding down costs and securing new revenue streams.
Advanced customer segmentation—the basis for a company to tailor its offerings and messages and serve each segment with a differentiated proposition—is just one of the 24 tools in four categories (sense, decide, act and manage) that can greatly enhance customers’ experience (see Figure 1). Such tools are proliferating, and companies globally have increased their adoption of them since Bain & Company’s first survey in 2018.
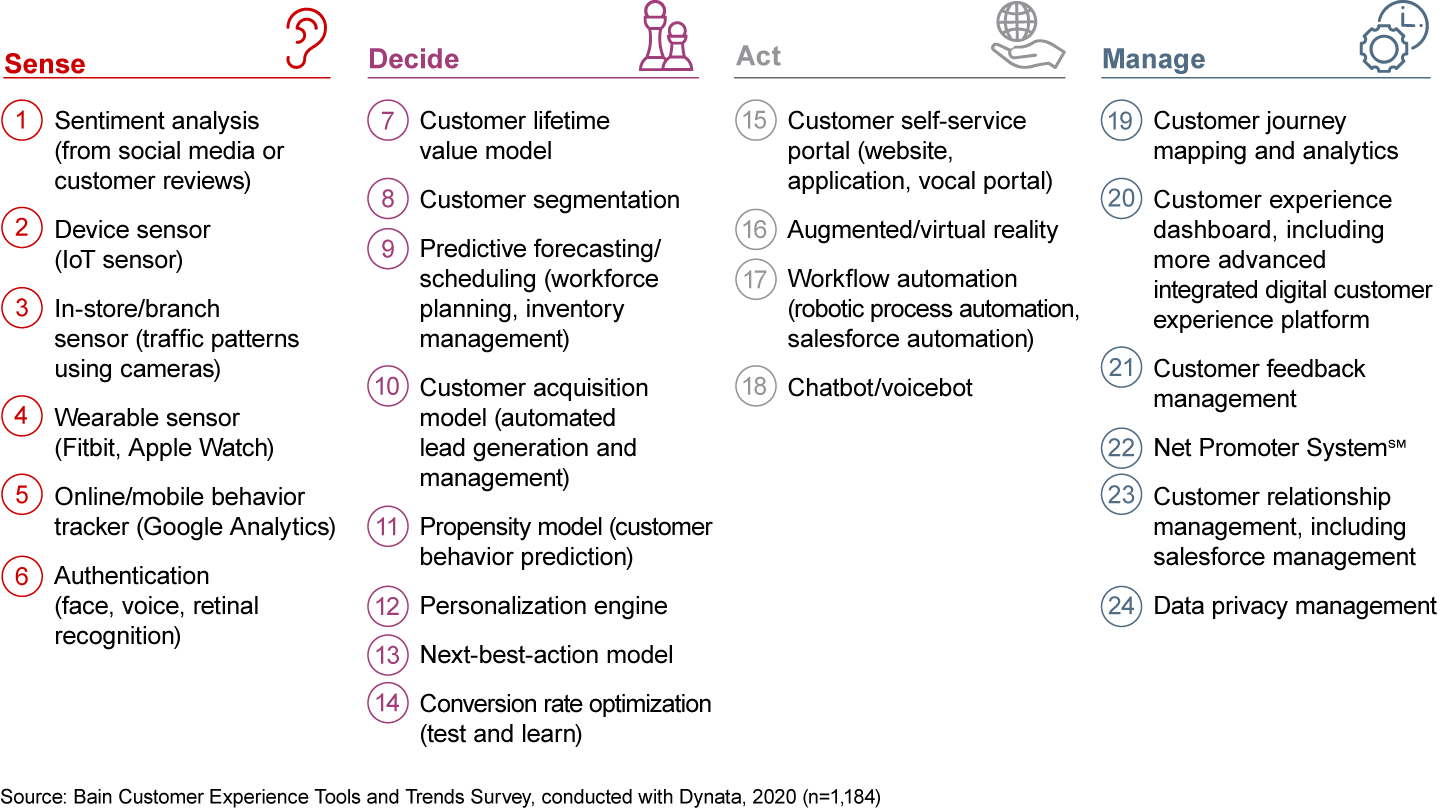

This year's survey, conducted with Dynata, of almost 1,200 executives in a range of industries found the average rate of adoption was 59% for the two dozen tools analyzed. The financial leaders (defined by revenue growth over the previous five years and satisfaction with financial results) used more tools than the financial laggards. Leaders also were more satisfied with the tools, on average, than the laggards (see Figure 2).
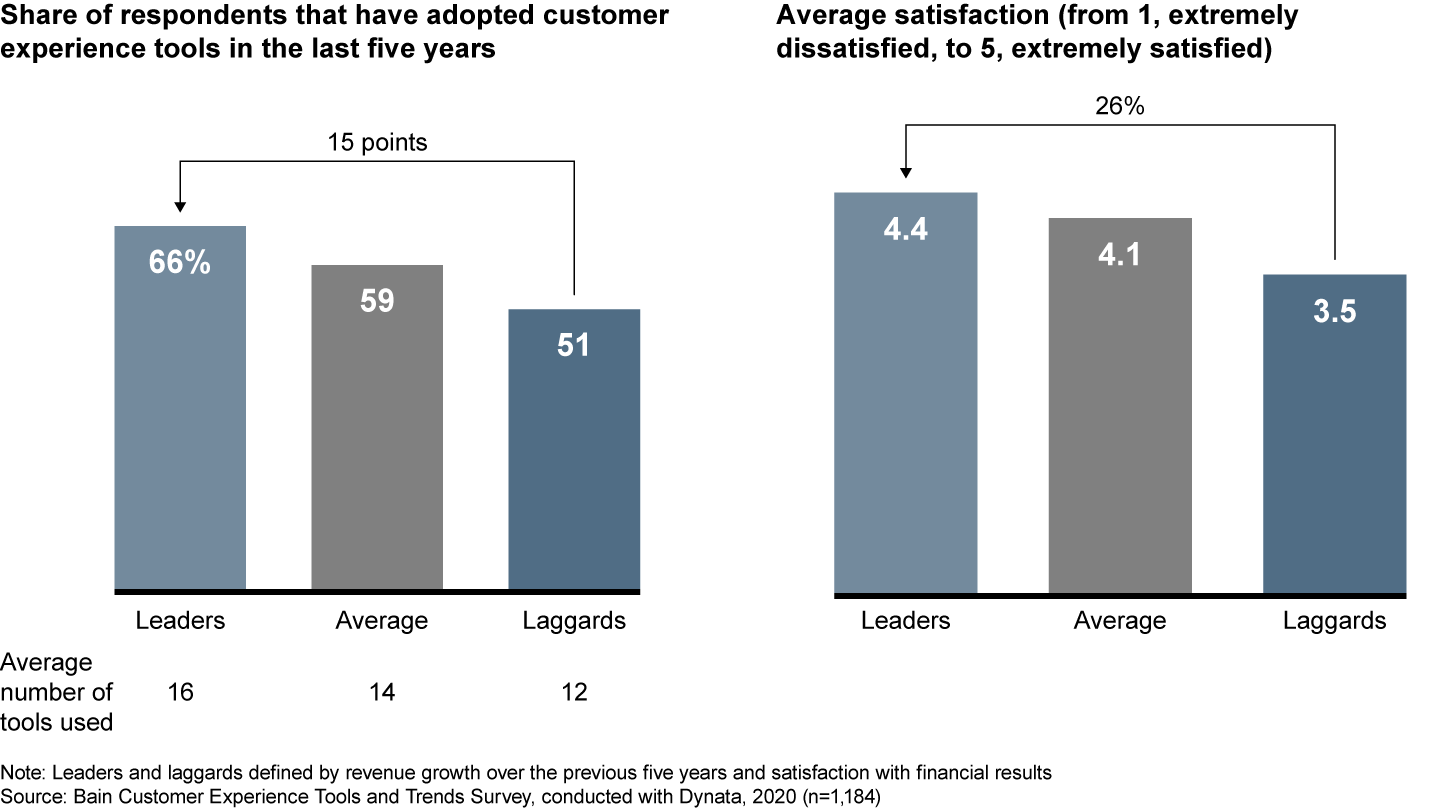

Analyzing the leader–laggard gap helps underscore the point of investing in the customer experience: to increase the total lifetime value of a company’s customer base. Companies do this by making the experience simpler and more convenient, thereby earning more business from existing customers, retaining them longer and attracting new customers.
This brief explores the main themes that emerged from the analysis.
Covid-19 is accelerating the use of many tools
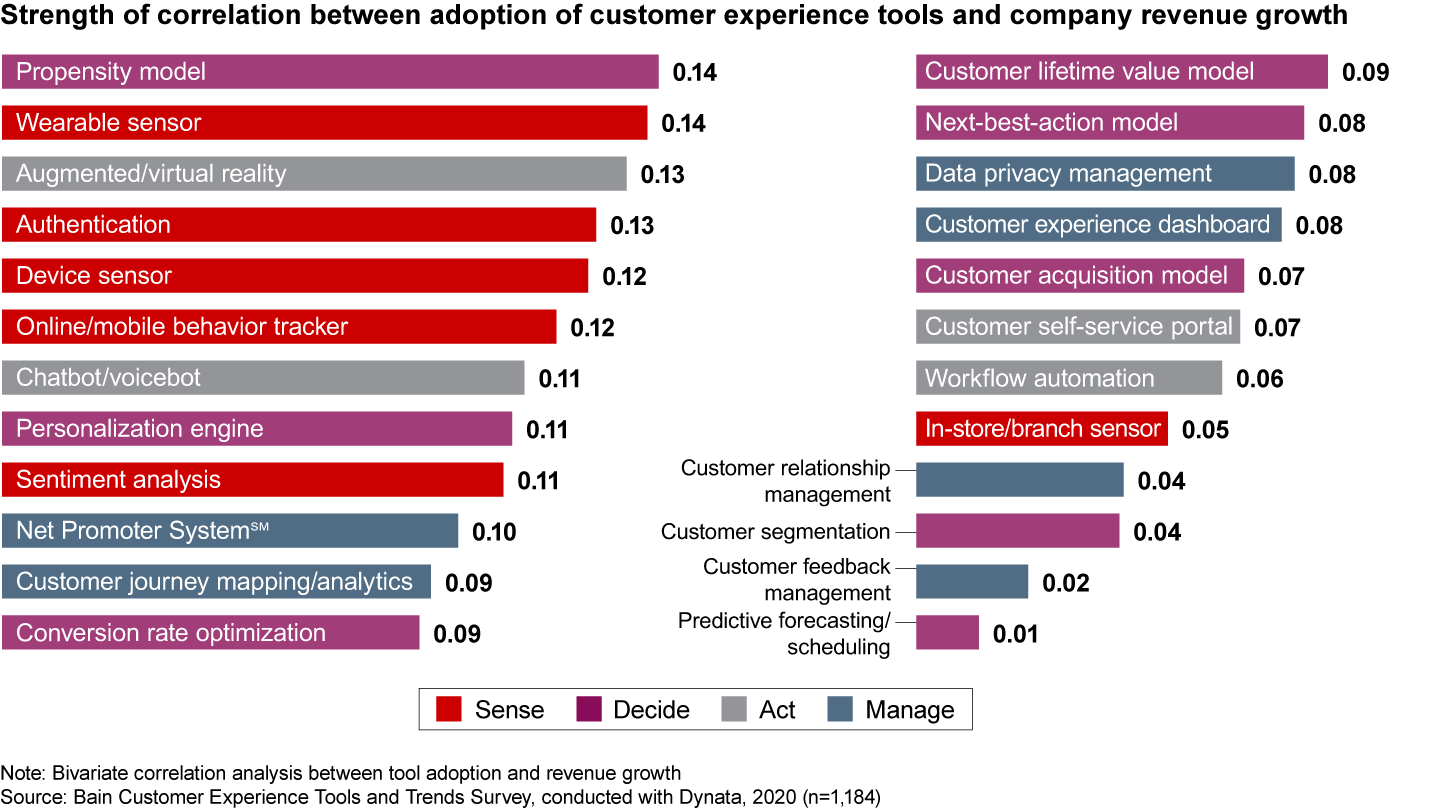
Now that the world has weathered months of Covid-19, it’s clear that consumers’ priorities have rapidly shifted, with most people putting more value on reducing their health and financial risks, relieving their anxiety, and maintaining a sense of community and belonging. To keep up with these evolving priorities at a decent level of specificity, companies are using sensing tools to listen to and track their customers. Indeed, tools in the “sense” category show the strongest correlation between adoption and financial performance (see Figure 3).

The coronavirus set geographical and channel patterns in flux as well. For instance, urban centers have lost a huge volume of office workers and residents who may not return at previous levels, so foot traffic could remain low at retail stores in those neighborhoods. Meanwhile, online research and shopping for many products have soared.
This shift from physical to digital, along with uncertainties about when physical sales might bounce back, raises the importance for retailers obtaining traffic and behavioral data quickly through in-store sensors and online trackers. Retailers and other direct-to-consumer companies will also benefit from a range of tools that help improve the at-home experience.
A grocer in Europe, for instance, historically measured transactions, but not usage occasions. Now it’s working to determine what portion of shoppers will buy more pizza on the shelf to cook at home, or return to take-out pizza parlors. In the US, a large retailer set up a data decision-support hub to track trends at a state level, using internal and external data. That hub has already informed revisions of operational and functional plans for 2021.
At the same time, the organizational disruption caused by lockdowns favors digital tools such as workflow automation, chatbots or voicebots, and self-service portals. Insurance company Suncorp in Australia automated processes previously outsourced to India, after the outsourcers’ agents had to shelter at home while lacking sufficient digital connections and hardware.
By necessity, consumer resistance to bots and web chat has slightly eased during the pandemic, and conversational agents, which simulate voice or test conversations with customers, are on the rise. At Northwell Health in the US, a heavy influx of Covid-19 patients created a backlog of call-center queries. Northwell implemented a chatbot to diagnose patients and refer them to testing when necessary, and then to push out lab results. By reducing patients’ waiting and anxiety, bots thus enhanced the experience.
When accelerating digital tools—whether equipping service teams to work virtually, or investing in bots, or tailoring products to new customer segments—companies should keep several principles in mind:
- Make sure the new channel functions well before shutting off the old one.
- Lean heavily on in-market tests. An insurer wanting to launch usage-based auto policies will need to test intensively, among demographic groups and by location, rather than assume that the recent spike in demand will last.
- Emphasize flexibility over efficiency with IT systems. Transition from monolithic IT platforms to microservice, API-led (application programming interface) platforms, which can easily accommodate new tools bolted on.
Integrate tools into an overall management system
Leaders among the respondents typically invest in more tools than other companies and are more satisfied with them. Tools with the highest adoption rate help manage the experience holistically, including customer relationship management (CRM), customer feedback management and experience dashboard tools (see Figure 4).
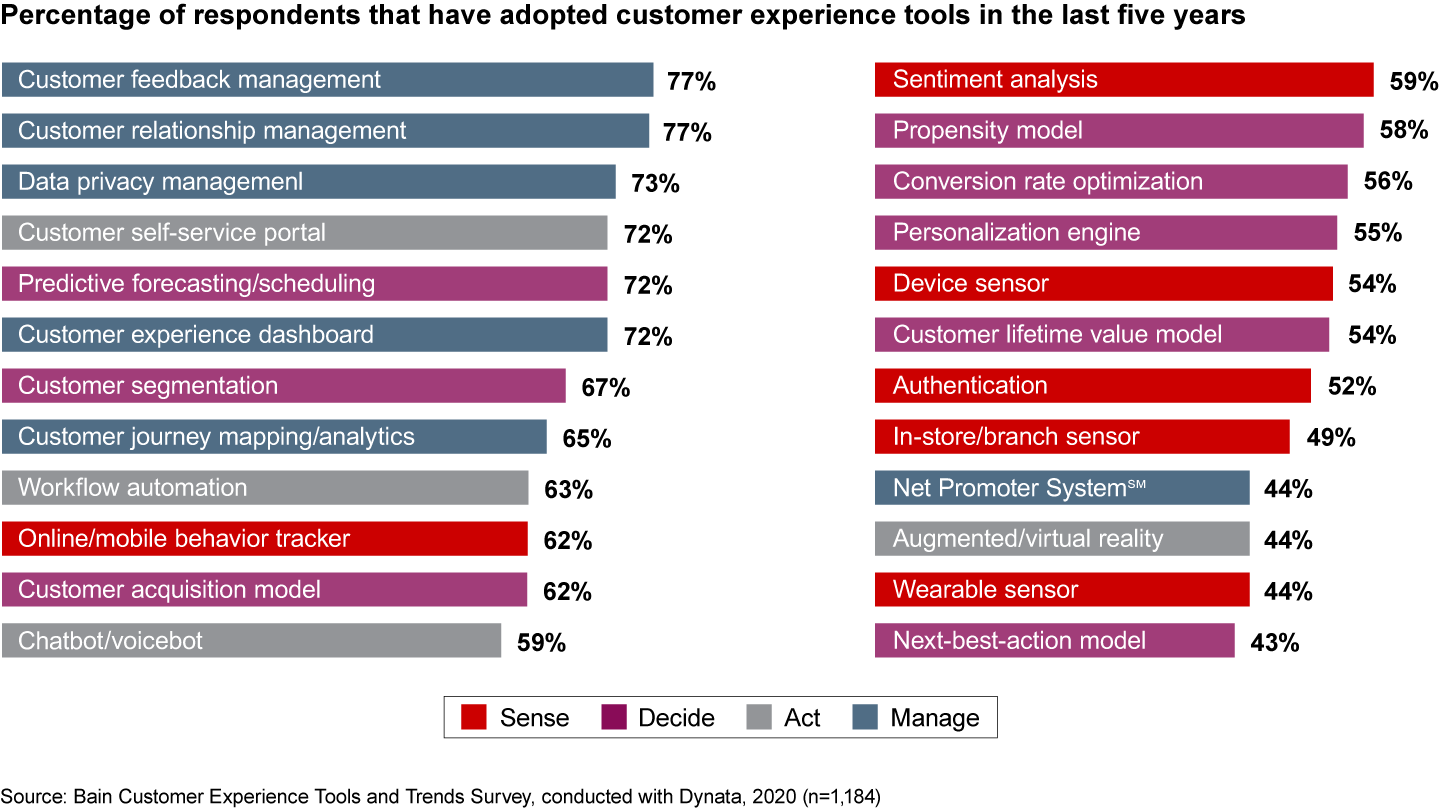

Some of these tools, especially CRM systems, have been around for decades, allowing companies to refine them and become familiar and productive with the user interface. The leaders, though, take CRM to a higher level through emerging customer data platforms:
- They use CRM to manage sales, marketing and service interactions.
- They use diversified sources of data and integrate external with internal data, as well as online and offline data.
- They use robotic process automation (RPA) to reduce manual, repetitive tasks.
- They’re testing how artificial intelligence can significantly improve the CRM’s prospecting.
Installing more tools alone doesn’t increase customer lifetime value or make customers’ lives easier. More important is selecting the appropriate tools for a particular use case, and integrating them into a well-oiled system. Bain’s survey finds greater returns to tools that are integrated within an IT system or with other tools. Tools connected to an enterprise resource planning system, for instance, have an 87% satisfaction rate among respondents, versus 73% satisfaction for tools that stand alone (see Figure 5). Moreover, companies must adapt operations to use their tools productively. If a tool doesn’t deliver the anticipated benefits, the fault may not lie with the tool itself, but rather with the processes surrounding the tool.
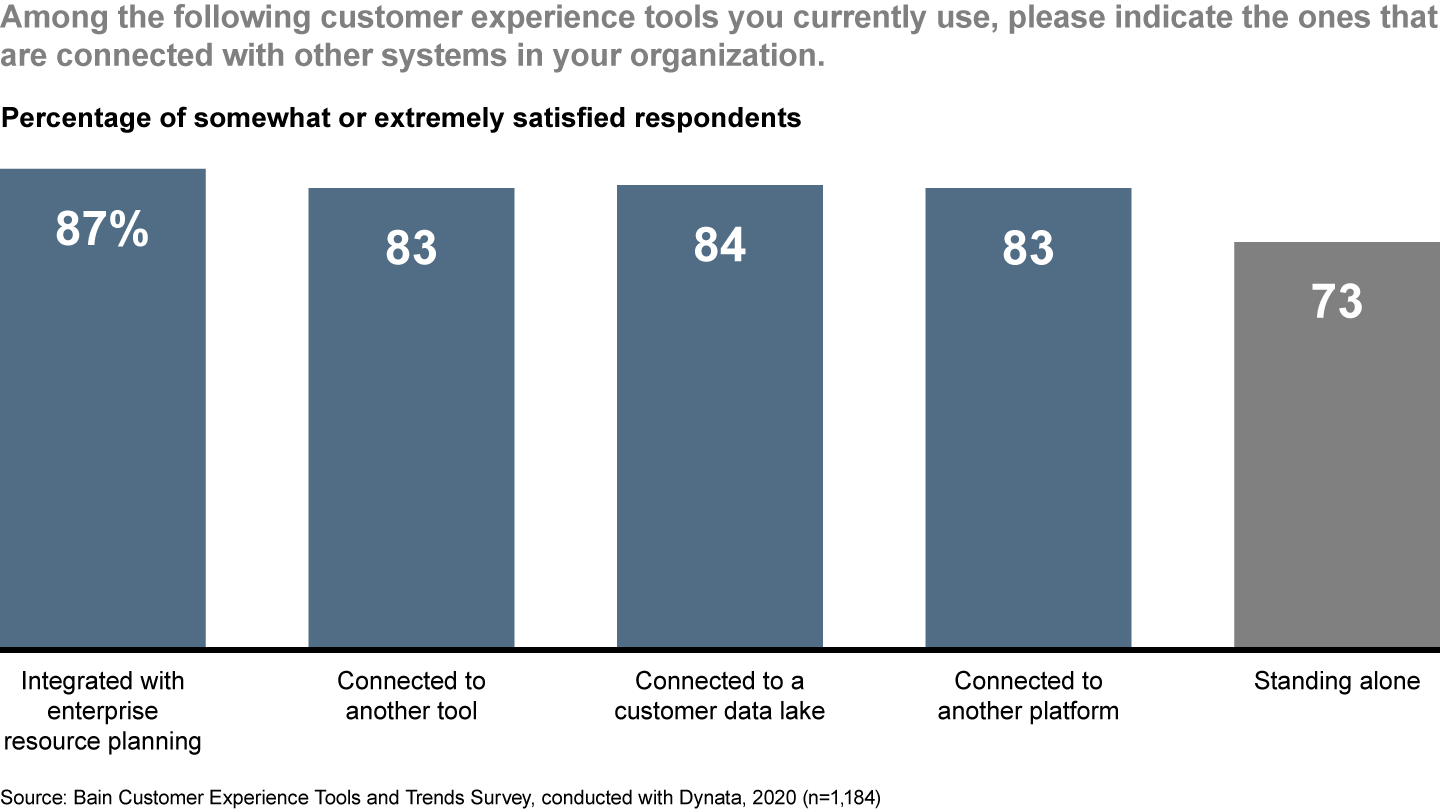

This makes intuitive sense, as any customer experience involves multiple corporate functions and channels. Tools used only by individual functions cannot connect the dots throughout the customer’s entire relationship with the company. By contrast, a manager using a dashboard that shows how leads move through the funnel and displays real-time loyalty and operational metrics will find it easier to make good decisions than if she had to find each of those data sets in separate places.
Use unique sources of data and algorithms
Relatively untapped sources of customer data, such as social media sentiment analysis to better predict demand for certain consumer goods, have grown more important for companies using device sensors and online behavior trackers. Advanced analytical tools in decision making, such as propensity models, also correlate closely with strong financial performance.
Insurgent digital firms often have advanced furthest in this regard. Root sets car insurance rates using telematics that monitor driving through a smartphone app measuring roughly 200 variables. Prospective customers apply through Root’s completely digital process. Likewise, subscription fashion firm Stitch Fix uses algorithms to understand what an individual would like for her monthly box delivery and how the clothing will fit. An employee adds value by reviewing the algorithm’s recommendations to check whether it’s a good look.
Companies also use data and analytics to enrich service interactions. An artificial intelligence-enhanced routing system for a contact center can mine contextual data on a customer’s past interactions and profile to predict her needs, while voice analysis can guide the agent in real time.
Prescriptive analytics goes a step further, triggering outbound treatments such as targeted offers or messages, to enhance the customer relationship. These treatments are based not only on predicted behavior, but also on inferences about the most effective and economic content, timing and channel. For incumbent companies, prescriptive analytics may offer a critical defense against threats from digital natives, building on incumbents’ hidden asset: the data and history they amass about large numbers of customers.
Data produced in the Net Promoter System℠, including the metric of loyalty known as the Net Promoter Score℠, is another route used by leading companies to gain deeper insight into the experience. The leaders use competitive NPS® benchmarks and employee NPS significantly more than other companies. While bottom-up NPS is scarce, since fewer than 10% of customers may respond to an NPS survey, a company can use the data exhaust from positive and negative incidents to accurately predict a loyalty score for each customer and thereby anticipate and prevent churn, or predict which customers will be open to cross-selling.
To make sense of the many data sets now available, some companies have refined their management dashboards. One major telecommunications provider recently completed a customer experience command center with more than 150 data points, about half of them at the unique customer level, accessible through a multitiered dashboard. The data covers network performance (such as call setup success rates), channel performance (store foot traffic, call wait times), and customer journey performance (first 30 days experience, payment delays, churn). The company developed a predictive Net Promoter Score to estimate the loyalty of customers outside the survey, using data about these customers and their interactions. The command center ultimately aims to create a single source of insights about the experience and to spur customer-level, systematic improvements.
Make customer lifetime value a key metric
As more executives and investors realize that customers are the ultimate source of corporate value, companies have put more emphasis on identifying their most valuable customers and building those relationships. Given the importance of customer value, executives should track it as rigorously as they track other key assets, such as buildings, machinery and inventory. They also should disclose it consistently in their quarterly and annual earnings releases so that investors can make informed judgments about company performance and how it compares with that of industry peers.
Some public companies, such as Costco, AMC Entertainment Holdings, Humana and American Express, increasingly report various types of customer value metrics. Most telecommunications companies—including Verizon, AT&T and T-Mobile—do as well. The utility company E.ON reports year-over-year customer counts in its audited financials. We’ll truly enter the age of customer capitalism when financial accounting-standards bodies enact rules that require reliable, auditable disclosure of customer-relationship health.
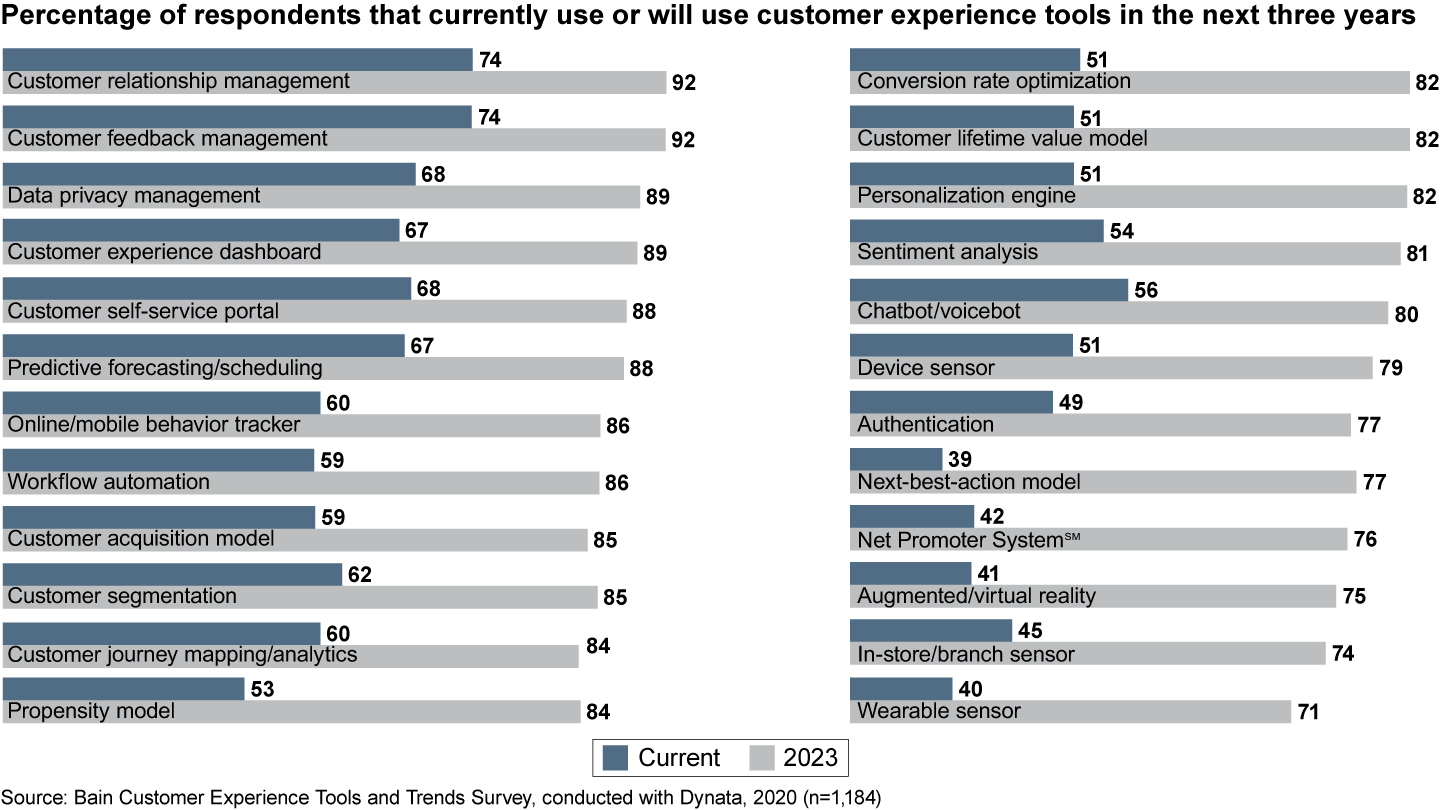
Customer experience tools support that goal. For the near future, survey respondents expect adoption to rise for all two dozen tools, with the biggest lift for some of today’s nascent tools (see Figure 6). With customer behavior changing so fast, companies need better online trackers, better acquisition models and better recommendation engines. As customer data becomes more valuable, while consumers want to protect their personal data, privacy-management tools gain importance.

Tool kit principles for shifting sands
Innovation and experimentation with the customer experience has flourished over the past few years, with the relevant tools getting more powerful. However, a sizable gap remains between leading and lagging firms, and of course, digital insurgents continue to challenge any incumbent’s hold on its customer base. Covid-19 poses the additional challenge of how providers can allay customers’ concerns about safety, household finances and isolation. In this complicated environment, the leading firms keep the following tool kit principles in mind.
- Test, test and test again. Customers’ needs and priorities are shifting more rapidly than in the past. That calls for rapid, Agile modes of in-market testing. The right tools must be in place, of course, but companies also need an operating rhythm that ensures fast feedback, allows teams to make fast course adjustments, and promotes behavior that improves both treatment of customers and business outcomes.
- Identify the use case. It may sound obvious, but the point of a tool is to solve a problem. Each tool must serve specific use cases as well as the overall experience strategy.
- Balance tool usage across each category in order to maximize value for customers.
- Reap all of the practical business benefits that tools can produce. Every step to improve the experience through digital self-service, for example, should simultaneously reduce costs.
Customers are enduring trying times. The tools discussed here can make their lives, and those of employees, richer and more fulfilling. They can also strengthen a company’s economics by holding down costs and securing new revenue streams. With careful linkage to use cases, the right set of tools embedded in a test-and-learn culture can substantially improve the experience and improve customer lifetime value.
The authors would like to thank Martha Moreau, Basma Abdel Motaal, Ksenia Peresvetova, Mira Kalscheuer, Shreya Gandhi, Camille Lefebvre and Arnaud Bousquie for their contribution to the report.
Net Promoter®, NPS®, NPS Prism®, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks, and Net Promoter Score℠, NPSx℠, and Net Promoter System℠ are service marks of Bain & Company, Inc., NICE Systems, Inc., and Fred Reichheld.

About the Research
Data powered by Dynata, a leading global first-party data and insights platform.

































